UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
______________________________
FORM
(Mark One)
For the fiscal year ended
or
For the transition period from ________________ to __________________.
Commission file number:
____________________
DIAMEDICA THERAPEUTICS INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
____________________
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | Not Applicable (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| | | The |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☐ | Accelerated filer ☐ | | Smaller reporting company |
| Emerging growth company |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s voting common shares held by non-affiliates, computed by reference to the closing sales price at which the voting common shares were last sold as of June 30, 2021 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter), as reported by The Nasdaq Capital Market on that date, was $
As of March 8, 2022, there were
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K incorporates by reference information (to the extent specific sections are referred to herein) from the registrant’s Proxy Statement for its 2022 Annual General Meeting of Shareholders to be held May 18, 2022.
[page intentionally left blank]
DIAMEDICA THERAPEUTICS INC.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2021
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Page | ||
| CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS |
1 |
|
| INDUSTRY AND MARKET DATA |
2 |
|
| PART I |
3 |
|
| Item 1. |
Business |
3 |
| Item 1A. |
Risk Factors |
33 |
| Item 1B. |
Unresolved Staff Comments |
65 |
| Item 2. |
Properties |
65 |
| Item 3. |
Legal Proceedings |
65 |
| Item 4. |
Mine Safety Disclosures |
66 |
| PART II |
67 |
|
| Item 5. |
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
67 |
| Item 6. |
[Reserved] |
77 |
| Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
78 |
| Item 7A. |
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
87 |
| Item 8. |
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
88 |
| Item 9. |
Changes In and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
109 |
| Item 9A. |
Controls and Procedures |
109 |
| Item 9B. |
Other Information |
109 |
| Item 9C. |
Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
110 |
| PART III |
|
111 |
| Item 10. |
Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
111 |
| Item 11. |
Executive Compensation |
111 |
| Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
111 |
| Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
113 |
| Item 14. |
Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
113 |
| PART IV |
114 |
|
| Item 15. |
Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
114 |
| Item 16. |
Form 10-K Summary |
117 |
| SIGNATURES |
118 |
|
_____________
This annual report on Form 10-K contains certain forward-looking statements that are within the meaning of Section 27A of the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and are subject to the safe harbor created by those sections. For more information, see “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
As used in this report, references to “DiaMedica,” the “Company,” “we,” “our” or “us,” unless the context otherwise requires, refer to DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. and its subsidiaries, all of which are consolidated in DiaMedica’s consolidated financial statements. References in this report to “common shares” mean our voting common shares, no par value per share.
We own various unregistered trademarks and service marks, including our corporate logo. Solely for convenience, the trademarks and trade names in this report are referred to without the ® and ™ symbols, but such references should not be construed as any indicator that the owner of such trademarks and trade names will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, their rights thereto. We do not intend the use or display of other companies’ trademarks and trade names to imply a relationship with, or endorsement or sponsorship of us by, any other companies.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Statements in this annual report on Form 10-K that are not descriptions of historical facts are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 that are based on management’s current expectations and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could negatively affect our business, operating results, financial condition and share price. We have attempted to identify forward-looking statements by terminology including “anticipates,” “believes,” “can,” “continue,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “potential,” “predicts,” “should,” “will,” “would,” the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, and the use of future dates.
The forward-looking statements in this report are subject to risks and uncertainties and include, among other things:
| ● |
our plans to develop, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize our DM199 product candidate for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) and our expectations regarding the benefits of our DM199 product candidate; |
|
| ● |
our ability to conduct successful clinical testing of our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD and certain anticipated or target dates, site activations and enrollment numbers with respect to our clinical studies, especially in the light of the novel strain of coronavirus, or COVID-19 pandemic on site activations and enrollment, hospital and medical facility staffing shortages, and worldwide global supply chain shortages; |
|
| ● |
the adaptive design of our ReMEDy2 trial, which is intended to enroll approximately 350 patients at 75 sites in the United States, and the possibility that these numbers and other aspects of the study could change depending upon certain factors, including additional input from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the blinded interim analysis; |
|
| ● | our expectations regarding the final results of our REDUX trial and timing of the release thereof; | |
| ● |
the perceived benefits of our DM199 product candidate over existing treatment options for AIS and CKD; |
|
| ● |
the potential size of the markets for our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD and our ability to serve those markets, and the rate and degree of market acceptance of our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD both in the United States and internationally; |
|
| ● |
our ability to partner with and generate revenue from biopharmaceutical or pharmaceutical partners to develop, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD; |
|
| ● |
the success, cost and timing of planned clinical studies, as well as our reliance on collaboration with third parties to conduct our clinical studies; |
|
| ● |
our expectations regarding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our business, including in particular our progress with site activation and patient enrollment in our clinical studies and our ability to hire additional personnel; |
|
| ● |
our commercialization, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and strategy; |
|
| ● |
expectations regarding federal, state, and foreign regulatory requirements and developments, such as potential FDA regulation of our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD; |
|
| ● |
our estimates regarding expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and needs for additional financing; |
|
| ● |
our expectations regarding our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our DM199 product candidate; |
|
| ● |
expectations regarding competition and our ability to obtain data exclusivity for our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD; |
|
| ● |
our ability to obtain funding for our operations, including funding necessary to complete planned clinical trials and obtain regulatory approvals for our DM199 product candidate for AIS and CKD; and |
|
| ● |
our anticipated use of the net proceeds from our underwritten public offerings and recent private placement. |
These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including those described under “Part I. Item 1A. Risk Factors in this report. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly-changing environment. New risks emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the forward-looking events and circumstances discussed in this report may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as predictions of future events. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, levels of activity, performance or events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur. Except as required by law, including the securities laws of the United States, we do not intend to update any forward-looking statements to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in our expectations.
INDUSTRY AND MARKET DATA
In addition to the industry, market and competitive position data referenced in this report from our own internal estimates and research, some market data and other statistical information included in this report are based in part upon information obtained from third-party industry publications, research, surveys and studies, none of which we commissioned. Third-party industry publications, research, surveys and studies generally indicate that their information has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, although they do not guarantee the accuracy or completeness of such information.
We are responsible for all of the disclosure in this report, and while we believe that each of the publications, research, surveys and studies included in this report are prepared by reputable sources, we have not independently verified market and industry data from third-party sources. In addition, while we believe our internal company research and estimates are reliable, such research and estimates have not been verified by independent sources. Assumptions and estimates of our and our industry’s future performance are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described in “Part I. Item 1A. Risk Factors.” These and other factors could cause our future performance to differ materially from our assumptions and estimates. See “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
PART I
Item 1. Business
Overview
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company committed to improving the lives of people suffering from serious diseases. DiaMedica’s lead candidate DM199 is the first pharmaceutically active recombinant (synthetic) form of the human tissue kallikrein-1 (KLK1) protein to be studied in patients, an established therapeutic modality for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke and chronic kidney disease. We have also identified a potential novel new treatment for inflammatory diseases, DM300, currently in the pre-clinical stage of development. Our goal is to use our patented and in-licensed technologies to establish our Company as a leader in the development and commercialization of therapeutic treatments from novel recombinant proteins. Our current focus is on the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). We plan to advance DM199, our lead drug candidate, through required clinical trials to create shareholder value by establishing its clinical and commercial potential as a therapy for AIS and CKD.
AIS and CKD patients suffer from impaired blood flow in the brain and kidneys, respectively. These patients also tend to exhibit lower than normal levels of endogenous (produced by the body) KLK1, which is a protein produced primarily in the kidneys, pancreas and salivary glands. We believe treatment with DM199 could replenish levels of KLK1, thereby allowing the natural function of kallikrein-kinin system (KKS) to release bradykinin (BK) in the body where and when needed, generating beneficial nitric oxide and prostacyclin, setting in motion metabolic pathways that can improve blood flow (through vasoregulation), dampen inflammation and protect tissues and end-organs from ischemic damage, supporting structural integrity and normal functioning.
In September 2021, we announced the initiation of the first site for our pivotal ReMEDy2 trial, a Phase 2/3 clinical trial of DM199 for the treatment of AIS and the first patient was enrolled in November 2021. The ReMEDy2 trial is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 2/3 adaptive trial intended to enroll approximately 350 patients at 75 sites in the United States. Patients enrolled in the trial will be treated with either DM199 or placebo within 24 hours of the onset of AIS symptoms. The trial excludes patients treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) or any other thrombolytic and those with large vessel occlusions. The study population is representative of the approximately 80% of AIS patients who do not have treatment options today, primarily due to the short treatment window - tPA must be administered within 4.5 hours from symptom onset.
The ReMEDy2 trial has two separate, independent primary endpoints and is powered for success with either endpoint: 1) physical recovery from stroke as measured by the well-established modified Rankin Scale (mRS) at day 90, and 2) the rate of ischemic stroke recurrence through day 90. Recurrent strokes represent 25% of all ischemic strokes, often occurring in the first few weeks after an initial stroke and are typically more disabling, costly, and fatal than initial strokes. Secondary endpoints for the trial will evaluate, among other things, participant deaths, mRS shift (which shows the treatment effect on participants across the full spectrum of stroke severity) and additional standard stroke scores (NIHSS and Barthel Index).
Also in September 2021, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) granted Fast Track Designation to DM199 for the treatment of AIS where tPA and/or mechanical thrombectomy are not indicated or medically appropriate. Fast Track is a process intended to facilitate the development and expedite the review of investigational drugs for the treatment of serious or life-threatening conditions where there is an unmet medical need.
With respect to our Phase 2 REDUX trial of DM199 in CKD, interim data was presented at the American Society of Nephrology’s (ASN) annual Kidney Week meeting in November 2021. In the IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) cohort, in addition to continuing to show statistically significant reductions (over 30% decrease) in albuminuria in participants with moderate to severe baseline albuminuria, the trial also demonstrated early signals of potential disease modification with the APRIL and IgA1 biomarkers decreasing 35% and 22% overall, respectively. In the African American cohort, participants were hypertensive with CKD and non-diabetic. Patients in this cohort with moderate to severe baseline albuminuria saw an over 50% reduction in albuminuria, improvement in blood pressure and stable eGFR. We have now completed enrollment in REDUX and are evaluating next steps for our CKD program.
We believe DM199 has the potential to treat a variety of diseases where restoring healthy function requires sufficient activity of KLK1 and its system, KKS.
Today, forms of KLK1 derived from human urine and the pancreas of a pig (porcine pancreas) are approved and sold in Japan, China and Korea to treat AIS, CKD, retinopathy, hypertension and related vascular diseases. We believe millions of patients have been treated with these KLK1 therapies and the data from more than 200 published papers and studies support its clinical benefit. However, there are numerous regulatory, commercial and clinical drawbacks associated with KLK1 derived from human urine and porcine pancreas which can be overcome by developing a synthetic version of KLK1 such as DM199. We believe higher regulatory standards and antibody reactions are the primary reasons why KLK1 derived from human urine and porcine pancreas are not currently available and used in the United States or Europe. We are not aware of any recombinant version of KLK1 with regulatory approval for human use in any country, nor are we aware of any recombinant version in development other than our drug candidate, DM199.
Kallikrein-Kinin System
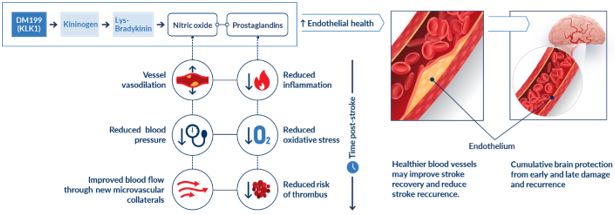
KLK1 is a serine protease, or protein, produced primarily in the kidneys, pancreas and salivary glands. KLK1 plays a critical role in the regulation of local blood flow and vasodilation (the widening of blood vessels, which decreases vascular resistance) in the body, as well as an important role in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress (an imbalance between potentially damaging reactive oxygen species, or free radicals, and antioxidants in the body).
KLK1 is involved in multiple biochemical processes. The most well-characterized activity of KLK1 is enzymatic cleavage of low molecular weight kininogen (LMWK) to produce Lys-bradykinin (BK)-like peptides, collectively known as kinins, which activate BK receptors (primarily BK2R with some BK1R). Activation of BK receptors by kinins sets in motion metabolic pathways which locally produce nitric oxide, prostaglandins and other anti-inflammatory mediators that can improve blood flow (through vasodilation), dampen inflammation, and protect tissues and end-organs from ischemic damage. Scientific literature, including publications in Circulation Research, Immunopharmacology and Kidney International, suggests that lower endogenous KLK1 levels in patients are associated with diseases related to vascular disorders, such as kidney diseases, stroke and hypertension. DM199, as a protein replacement therapy, may replenish KLK1 levels to properly activate the KKS locally producing nitric oxide, prostaglandins and other anti-inflammatory mediators to promote endothelial health and protect the brain and kidney from damage. By providing additional supply of the KLK1 protein, DM199 treatment could potentially improve blood flow to and reduce inflammation in damaged end-organs, such as the brain and the kidneys, supporting their structural integrity and normal functioning.
DM199 (KLK1) and Our Therapeutic Hypothesis

We have conducted numerous internal and third-party analyses to demonstrate that DM199 is structurally and functionally equivalent to KLK1 derived from human urine. Specifically, the amino acid structure of DM199 is identical to the human urine form, and the enzymatic and pharmacokinetic profiles are substantially similar to both human urine and porcine derived KLK1. The physiological effects of DM199 on blood pressure, from our completed studies, is similar to that of human urine and porcine-derived forms of KLK1. We believe that the results of this work suggest that the therapeutic action of DM199 will be the same or, potentially, better than that of the forms of KLK1 marketed in Asia.
We believe DM199 may provide new treatment options with significant benefits over the current standards of care by offering a therapeutic treatment option to a greater number of patients with the potential for fewer side effects.
Summary of Clinical Results
To date, clinical trials have been and/or are being conducted in the United States, Europe and Australia. We believe the clinical data generated to date by DM199 supports the continued development of DM199 as a treatment for AIS and CKD.
| ● |
Our Phase 2 ReMEDy1 trial of DM199 in the treatment of AIS (n=91) met our primary safety and tolerability end points and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in the number of participants with recurrent ischemic stroke in the active treatment group: 0 (0%) patient treated with DM199 vs. 6 (13%) on placebo (p=0.012), with 4 of the 6 resulting in participant death. |
| ● |
Additionally, in our Phase 2 ReMEDy1 trial, in a subset of participants (n=46) which represents the group of participants most closely aligned with the target treatment population for DM199 in our ReMEDy2 trial, a positive therapeutic effect on participant physical recoveries was demonstrated. In participants treated with DM199 (n=25) vs. supportive care and/or tPA (n=21), the results showed that 36% of participants receiving DM199 progressed to a full or nearly full recovery at 90 days (NIHSS: 0-1), compared to 14% of participants in the placebo group. This represents a 22% absolute increase in the proportion of participants achieving a full or nearly full recovery. Additionally, subject deaths decreased from 24% in the placebo group to 12% in the active therapy group, a 50% relative reduction. |
| ● |
Interim data from our Phase 2 REDUX trial of DM199 in CKD was presented at the American Society of Nephrology’s (ASN) annual Kidney Week meeting in November 2021. In the IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) cohort, in addition to showing statistically significant reductions (over 30% decrease) in albuminuria in participants with moderate to severe baseline albuminuria, the trial also demonstrated early signals of potential disease modification with the APRIL and IgA1 biomarkers decreasing 35% and 22% overall, respectively. The African American cohort demonstrated an over 50% reduction in albuminuria in patients with moderate to severe baseline albuminuria and significant reductions in blood pressure levels, both systolic and diastolic. |
| ● |
DM199 was generally safe and well tolerated across all cohorts of the REDUX trial. Adverse Events (AEs) were generally mild to moderate in severity, with the most common being local injection site irritation that resolved. Enrollment was closed at the end of 2021 and we do not believe that the final results will differ significantly from the data presented at ASN. |
In all studies, DM199 was shown to be generally safe and well tolerated. The primary adverse events noted in our studies include local injection site irritation, constipation, nausea and headache, all of which resolved without medical intervention.
We are developing DM199 to treat AIS and CKD in the following clinical trials:
| Indication |
Delivery |
Stage |
Status |
Endpoints |
| Neurological Diseases |
||||
| Acute Ischemic Stroke |
Intravenous IV/SC |
Phase 2/3 |
Enrolling |
Independent primary endpoints at day 90: ● Modified Rankin Scale score of 0-1 ● Stroke recurrence Secondary endpoints at day 90: ● NIHSS and Barthel index ● Deaths ● Modified Rankin Scale scores of 0-6 (shift analysis) |
| Kidney Diseases |
||||
| IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) |
SC |
Phase 2 |
Enrollment complete |
Primary endpoint at day 95: ● Safety & tolerability ● Albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) Secondary endpoints at day 90: ● Change in IgG & IgA biomarkers |
| African Americans with CKD |
SC |
Phase 2 |
Enrollment complete |
Primary endpoint at day 95: ● Safety & tolerability ● Albuminuria and eGFR Secondary endpoints at day 90: ● Change in blood pressure |
Supporting Data for Use of DM199 (KLK1):
We have identified several hundred papers supporting the clinical use of urinary and porcine derived KLK1 from China, Japan and Korea. We estimate that over 20 companies are marketing porcine KLK1 and 1 company marketing human urinary KLK1 in these countries.
Studies have shown that lower KLK1 levels are also a predictor of stroke recurrence. As shown in the graph below, the red line represents patients in the lowest KLK1 quartile who are at the highest risk for recurrence of stroke. (2,478 stroke patients and event free survival over 5 years).
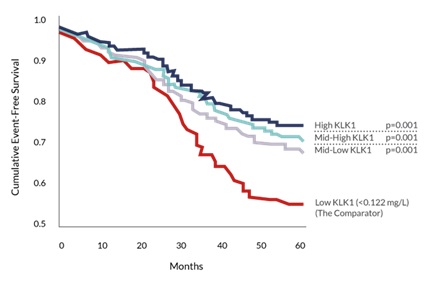
Source: Annals of Neurology (2011) 70:265-73
For patients with chronic kidney disease, studies have shown that KLK1 excretion, or levels of KLK1 in the urine, were significantly decreased. This decrease was more pronounced in patients with severe renal failure requiring dialysis, as illustrated in the graph below.
Low KLK1 Levels Are Associated With Chronic Kidney Disease
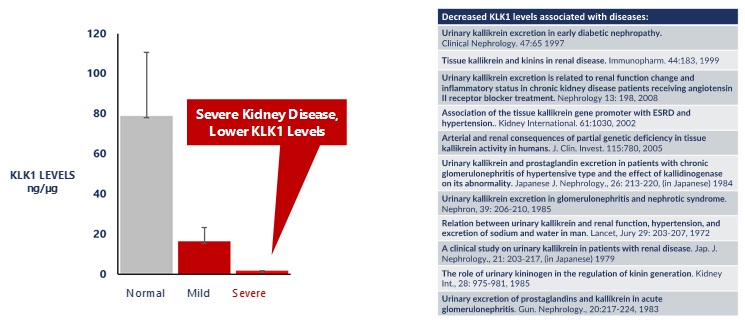
Source: Immunopharmacology 44 1999. 183–192
Our Strategy
Our mission is to improve the lives of people suffering from serious diseases. Our near-term goal is to principally focus on executing our recently initiated ReMEDy2 Phase 2/3 trial of DM199 in AIS and to complete patient follow-up in our REDUX Phase 2 trial of DM199 in CKD. Key elements of our strategy include:
| ● |
DM199 for AIS – execute our ongoing ReMEDy2 Phase 2/3 trial; |
| ● |
DM199 for CKD – complete patient follow-up in our REDUX Phase 2 trial; |
| ● |
Continue manufacturing process development to support applications for commercial approval of DM199; and |
|
| ● | Identify a strategic partner(s) to assist with future clinical development and commercialization of DM199.
|
AIS Background and Disease Pathology
Acute Ischemic Stroke Background
Stroke is characterized by the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to a blockage of blood flow in the brain. As a result, the affected tissues of the brain become inactive and may eventually die. Strokes can be classified into two major categories: AIS and hemorrhagic stroke. AIS is characterized by interruption of the blood supply by a blood clot (ischemia), while a hemorrhagic stroke results from rupture, or bleeding, of a blood vessel in the brain. Risk factors for stroke include, among other things, advanced age, hypertension (high blood pressure), previous stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), diabetes, high cholesterol, cigarette smoking, atrial fibrillation, physical inactivity and obesity.
More specifically, with respect to an ischemic stroke, at the site of a blood flow blockage in the brain, there exist two major ischemic zones - the core ischemic zone with nearly complete loss of blood flow (blood flow below 10% to 25%), and the surrounding ischemic penumbra, a rim of mild to moderately ischemic tissue surrounding the core ischemic zone. Within minutes, the significant lack of blood flow in the core ischemic zone deprives these cells of glucose and oxygen which rapidly depletes energy stores and triggers the loss of ion gradients, ultimately leading to neuronal cell death, or apoptosis. The ischemic penumbra zone, however, may remain viable for several hours via collateral arteries that branch from the main occluded artery in the core ischemic zone. Unfortunately, the penumbra is at great risk of delayed tissue damage due to inflammation which may also lead to neuronal cell death. As time goes on, a lack of blood flow in the core ischemic zone (infarct) may lead to fluid buildup (edema) and swelling which creates intracranial pressure. This pressure on the brain leads to tissue compression resulting in additional ischemia. Additional events in AIS include vascular damage to the blood vessel lining or endothelium, loss of structural integrity of brain tissue and blood vessels and inflammation. A stroke can lead to permanent damage with memory loss, speech problems, reading and comprehension difficulties, physical disabilities and emotional/behavioral problems. The long-term costs of stroke are substantial, with many patients requiring extended hospitalization, extended physical therapy or rehabilitation and/or long-term institutional or family care. However, provided the extended window of viability in the penumbra, next generation stroke therapies are being developed to protect valuable brain tissue during the hours to a week after a stroke.
Unmet Medical Need in AIS
According to the World Health Organization, each year approximately 1.7 million people in the U.S., Europe and Japan and approximately 15 million people worldwide suffer a stroke, of which 5 million will die and 5 million will be permanently disabled people. According to the U.S. Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) approximately 87% of all strokes are ischemic in nature, meaning a blockage of blood flow in/to the brain. We believe that stroke represents an area of significant unmet medical need and a KLK1 therapy (such as DM199) could provide a significant patient benefit, in particular given its proposed treatment window of up to 24 hours after the first sign of symptoms. Currently, the only FDA-approved pharmacological intervention for AIS is tPA, which is approved to be given within 3 hours of symptom onset; however, we understand that based upon supplemental clinical research and common practice, it is administered up to 4.5 hours from symptom onset. Treating patients with tPA during this time window can be challenging because it is difficult to determine precisely when symptoms began and a patient must undergo complex brain imaging before treatment to rule out a hemorrhagic stroke, a ruptured blood vessel causing bleeding within the brain. Mechanical thrombectomy, a procedure in which the clot is removed using catheter-based tools, is also available to certain patients. Despite the availability of these treatments, we believe they are relevant to approximately 10% of ischemic stroke patients due to the location of the clot, the elapsed time after the stroke occurred or other safety considerations. Thus, we believe DM199 may offer significant advantages over the current treatment options in that it fills a serious, unmet need for patients who cannot receive tPA or mechanical thrombectomy. Additionally, we believe DM199 may also offer a complimentary follow-on treatment for patients who initially receive tPA or mechanical thrombectomy treatments by enabling sustained blood flow improvements to the brain during the critical weeks and months after a stroke, reducing the risk of stroke recurrence.
Specifically with respect to the United States, and according to the CDC:
| ● |
Every year in the United States, approximately 800,000 people experience a stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic). Approximately 600,000 of these are first events and approximately 25%, or 200,000, are recurrent stroke events. |
|
| ● |
Approximately one of every 20 deaths in the United States is caused by stroke and is the fifth leading cause of death. On average, someone in the United States has a stroke every 40 seconds and someone dies from a stroke every four minutes. |
|
| ● |
Stroke is the leading cause of serious long-term disability and reduces mobility in more than half of stroke survivors aged 65 and over. |
|
| ● |
Risk of having a first stroke is nearly twice as high for African Americans as for Caucasians, and African Americans have the highest rate of death due to stroke. |
Stroke costs in the United States, as reported by the American Heart Association, averaged nearly $46 billion in 2014 and 2015, including the cost of health care services, medications and lost productivity.
Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment Options

DM199 – Our Novel Solution for the Treatment of AIS
We believe DM199 has the potential to preserve “at risk” brain tissue by increasing cerebral blood flow, establishing better collateral circulation, decreasing inflammation, reducing cell death, or apoptosis, and facilitating improved blood flow to at-risk brain tissue in the ischemic penumbra. Immediate actions include activation of the KKS to release nitric oxide and improve microcirculation in ischemic tissue along with improvements in the balance between blood flow and brain activity (neurovascular coupling). Longer term (days following the stroke) actions include the restoration of the blood brain barrier through increases in regulatory T cells (Tregs), a subpopulation of regulatory T cells that modulate the immune system and prevent pathologic autoimmune response, and inhibition of neuronal cell death, or apoptosis.
DM199 Acute Ischemic Stroke: Proposed Mechanism
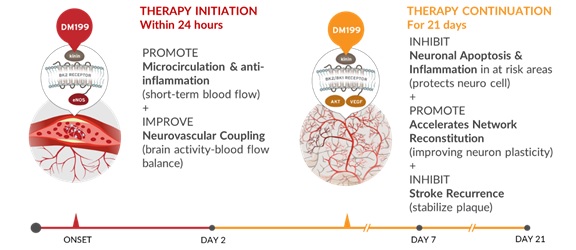
In January 2019, we published a paper titled “Human Tissue Kallikrein in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke” in the peer reviewed journal, Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders. The paper reviews the scientific literature covering the biochemical role of KLK1 and presents the mechanistic rationale for using KLK1 as an additional pharmacological treatment for AIS. In addition to the biochemical mechanism of KLK1, the review highlights supporting results from human genetics and preclinical animal models of brain ischemia. It also reviews published clinical results for treatment of AIS by a form of KLK1 that is isolated from human urine. This form has been approved for post-infarct treatment of AIS in China and data has been published from clinical trials involving over 4,000 patients. The paper offers a series of testable therapeutic hypotheses for demonstrating the long-term beneficial effect of KLK1 treatment in AIS patients and the reasons for this action.
We are developing DM199 to treat AIS patients with a therapeutic window of up to 24 hours after the first sign of symptoms, well beyond the current window of up to 4.5 hours from sympton onset for tPA, thereby filling a large unmet need for those patients who cannot receive tPA under the currently available treatment window of tPA. This important attribute could potentially make therapy available to the millions of patients worldwide who currently have limited treatment options.
Supporting Data from the Use of Urine-derived KLK1 for the Treatment of AIS in China
In China, Kailikang® is approved and marketed by Techpool Bio-Pharma Inc., a company controlled by Shanghai Pharmaceuticals Holding Co. Ltd. Kailikang has been approved for the treatment of AIS in China. We believe the initial treatment window is up to 48 hours after stroke symptom onset. Based on IQVIA data, other publications and our own internal analysis, we estimate that over 600,000 stroke patients have been treated with Kailikang in China since its approval in 2005. More than 50 published clinical studies, covering over 4,000 stroke patients, have demonstrated a beneficial effect of Kailikang treatment in AIS including improvements in standard stroke scores, blood flow and biomarkers of inflammation. According to a publication in the China Journal of Neurology, in a double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of 446 patients treated with either Kailikang or a placebo with initial treatment administered up to 48 hours after symptom onset showed significantly better scores on the European Stroke Scale and Activities of Daily Living at three weeks post-treatment and after three months using the Barthel Index.
Additionally, a comprehensive meta-analysis covering 24 clinical studies involving 2,433 patients published in the Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine concluded that human urinary KLK1 appears to ameliorate neurological deficits for patients with AIS and improves long-term outcomes, though a few treated patients suffered from transient hypotension.
Furthermore, in a retrospective study covering 300 consecutive AIS patients, published in Brain and Behavior March 2018, patients treated with human urinary KLK1 experienced 39% (p=0.009) fewer recurrent strokes within one year.
CKD Background and Disease Pathology
Chronic Kidney Disease Background
CKD is characterized by a progressive decline in overall kidney function as measured by the eGFR, a test used to evaluate blood flow through the kidneys, and albuminuria, a marker for glomerular injury which is a measure of the amount of albumin protein excreted in your urine and an indicator for how well the kidneys are filtering excess fluid and waste products out of your blood. As glomerular filtration decreases, the body’s ability to continue to regulate its many functions, including the elimination of metabolic waste, is lost and ultimately, may result in severe physiologic consequences. Among multiple underlying causes, CKD often begins with an increase in blood glucose which leads to the thickening of the glomerular membrane, known as fibrosis. As the kidney function becomes impaired, eGFR decreases and albuminuria may increase. Increased albuminuria means that abnormal amounts of protein are released into the urine collecting tubules of the kidney through damaged capillary pores in the glomerular floor. Additionally, increased blood glucose leads to increased blood pressure, elevated reactive oxygen species, advanced glycation end product formation (harmful compounds that are formed when protein or fat combine with sugar in the bloodstream) and inflammation. As these continue, structural components of the kidney begin to collapse, resulting in cell ischemia and cell death. As the renal damage continues, a progressive thickening of the glomerular basement membrane is seen along with continued pathological changes in the cells and inflammation. Early stages of CKD are characterized as microalbuminuria (small amounts of protein leak into the urine). Late stages are characterized as macroalbuminuria (large amounts of protein leak into the urine). The rate of decline depends on a number of factors including the type of diabetes, genetic predisposition, glycemic controls and blood pressure. At the final stages of CKD, the kidneys fail completely and dialysis or a kidney transplant is needed.
Unmet Medical Need in CKD
CKD is a widespread health problem that generates significant economic burden throughout the world:
| ● |
According to the National Kidney Foundation, 37 million Americans have CKD and millions of others are at increased risk. |
|
| ● |
The primary causes of CKD are diabetes (Type 2 and Type 1) and hypertension. The Medical Clinics of North America estimates that over 40% of those with Type 2 diabetes and 20% of those with Type 1 diabetes will eventually develop CKD, making it one of the more common risks for diabetics. |
|
| ● |
Patients with CKD are at greater risk for hypertension and heart disease. |
Currently, there is no cure for CKD and treatment primarily involves management of the symptoms of the disease in order to reduce the rate of decline in kidney function. Blood pressure medications, such as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), are often prescribed to control hypertension, and hopefully, slow the progression of CKD. Recently sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2) have received approval to expand their label to treat diabetic kidney disease to reduce the rate of cardiovascular events. Nevertheless, according to the National Kidney Foundation, many of these patients continue to show declining kidney function and 3.6% of the overall population has a lifetime risk of developing end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where dialysis or a kidney transplant is needed. We believe DM199 offers a potentially novel approach for the treatment of CKD because KLK1 protein plays a vital role in normal kidney function.
DM199 – Our Novel Solution for the Treatment of CKD
We believe DM199 has the potential to offer meaningful therapeutic benefits for CKD patients. We believe that the KLK1 protein plays a vital role in maintaining normal kidney function, promoting the production of nitric oxide, prostacyclin and other anti-inflammatory mediators which are important for kidney health and integrity. Patients with moderate to severe CKD often excrete abnormally low levels of KLK1 in their urine, leading to the hypothesis that a KLK1 deficit contributes to disease progression. We believe that DM199, as a protein replacement therapy, can potentially replenish KLK1 levels and properly activate the KKS enabling or improving the production of nitric oxide, prostacyclin and other anti-inflammatory mediators which may protect the kidney from damage and possibly restore normal kidney function. In related preclinical testing, DM199 treatment in an animal model of Type 1 diabetes, a known cause of CKD, delayed the onset of the disease, attenuated the degree of insulitis (inflammation in the insulin producing islet cells of the pancreas) and improved pancreatic beta cell mass in a dose-dependent manner by increasing Tregs.
By providing additional KLK1, DM199 has the potential to:
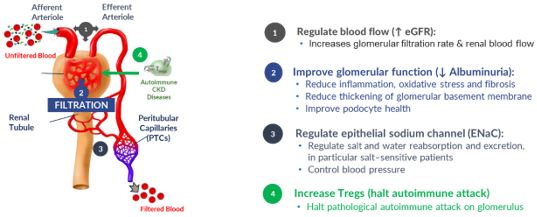
Further supporting the hypothesis that an intact KKS is critical for normal kidney function, a series of observational studies published in Immunopharmacology showed the amount of KLK1 released into the urine appears to be inversely correlated with the severity of disease in patients with CKD. Urinary KLK1 excretion was decreased in patients with both mild (not requiring dialysis) and severe (kidney failure/hemodialysis) renal disease compared to controls. Decreases in urinary KLK1 activity were seen especially when the reduction was associated with decreased glomerular filtration rate.
DM199 treatment is intended to directly replenish KLK1 levels to maintain, or possibly restore, kidney function. Current treatment options, especially ACEi drugs, primarily slow the rate of decline in kidney function and are associated with side effects. Importantly, it is becoming increasingly clear that part of the beneficial effect of ACEi drugs involves preventing the normal breakdown of BK leading to substantial increases in BK levels throughout the body. However, these effects can be unregulated and ACEi drugs therefore can generate excessive BK where it is not needed, potentially leading to side effects such as persistent cough, angioedema (swelling of skin and tissue) and hyperkalemia (abnormally high potassium levels that can lead to cardiac arrest and sudden death). We believe DM199 treatment could potentially restore normal KLK1 levels allowing the KKS to perform its normal physiological processes and release BK when and where it is needed, avoiding these side effects.
We intend to seek approval for use of DM199 as a novel and ground-breaking therapy for CKD. Protein replacement therapy with DM199, through the activation of the KKS, may complement the renin-angiotensin system, primarily targeted by ACEis and ARBs, and may potentially improve the function of the diseased renal system by improving blood flow and vasodilation, as well as reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Supporting Data from the Use of Porcine-Derived KLK1 for the Treatment of CKD in Japan, China and Korea
KLK1 derived from porcine pancreas is currently used to treat CKD in Japan, China and Korea. Specifically, porcine KLK1 is also used to treat hypertension and retinopathy. Based on data published by the data analytics company IQVIA and our own internal analysis, we estimate that millions of patients have been treated with porcine KLK1 for these and other vascular diseases. We have identified 17 clinical papers, published in China and Germany supporting the therapeutic activity of porcine KLK1 in CKD patients, whether given alone or in combination with an ARB or an ACEi. These unblinded studies involve treatment durations ranging from a few weeks up to six months and report improvement in kidney disease based on decreased urinary albumin excretion rates and other clinical endpoints of kidney disease.
Our Competition and Current Treatments for Acute Ischemic Stroke and Chronic Kidney Disease
The biopharmaceutical industry is highly competitive and characterized by rapidly advancing technologies that focus on rapid development of proprietary drugs. We believe that our DM199 product candidate, development capabilities, experience and scientific knowledge provide us with certain competitive advantages. However, we face significant potential competition from many different sources, including major pharmaceutical, specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic institutions, governmental agencies and other research institutions. Any product candidates that we successfully develop and commercialize will compete with existing therapies and new therapies that may become available in the future.
Many of our competitors, either alone or with their strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do, and experience in obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals of treatments and commercializing those treatments. Accordingly, our competitors may be more successful than us in obtaining approval for competitive products and achieving widespread market acceptance. Our competitors’ treatments may be more effectively marketed and sold than any products we may commercialize, thus limiting our market share and resulting in a longer period before we can recover the expenses of developing and commercializing our DM199 product candidate.
Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. Smaller or early stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies. These activities may lead to consolidated efforts that allow for more rapid development of competitive product candidates.
We also compete for staff, development and clinical resources. These competitors may impair our ability to recruit or retain qualified scientific and management personnel, our ability to work with specific advisors, or our ability to work with clinical contract organizations due to conflicts of interest or capacity constraints, and may also delay recruitment of clinical study sites and study volunteers, impeding progress in our development programs.
We expect any products that we develop and commercialize to compete on the basis of, among other things, efficacy, safety, price and the availability of reimbursement from government or other third-party payers. Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are viewed as safer, more effective or less expensive than any products that we may develop.
Acute Ischemic Stroke
Currently, there is one approved pharmaceutical treatment for AIS. That treatment is tPA (marketed under the brand name Activase®), and its therapeutic window is limited to up to 4.5 hours after the AIS. There are, however, a number of companies that are actively pursuing a variety of approaches to develop pharmaceutical products for the treatment of AIS including, among others:
| ● |
Stem cells (Athersys, Inc.) |
|
| ● |
tPA extended treatment window (Genentech) |
|
| ● |
Cerebral edema (Biogen Inc.) |
|
| ● |
Anti-inflammatory and clot dissolving (Biogen Inc.) |
|
| ● |
Cell protection and anti-inflammation (ZZ Biotech LLC) |
|
| ● |
Inhibiting platelet aggregation (Acticor Biotech SAS) |
|
| ● | Neuroprotector (Mitsubishi) |
There is a large unmet therapeutic need for AIS treatments that can be administered beyond the 4.5-hour time window of tPA. With this large unmet therapeutic need, there is significant competition to develop new therapeutic options. New therapeutic options in development include tissue protection focused therapies (deliverable from hours to days after the stroke) that preserve and protect brain cells beyond the tPA therapeutic window. Currently, the most advanced treatments involve the mechanical removal of blood clots in arteries supplying blood to the brain through sophisticated catheter-based approaches, or mechanical thrombectomy. According to published research, use of mechanical thrombectomy is growing and the window of time after a stroke where the procedure can be used is widening. The goal is to provide treatment options for the vast majority of AIS patients who do not receive hospital care early enough to qualify for tPA therapy. We believe there is a very significant market opportunity for a drug that has a therapeutic window beyond that of tPA and is able to obtain regulatory approval.
Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD is primarily associated with diabetes and hypertension along with other disease states. In the United States, we are aware of only two currently approved treatments for CKD. These treatments include an ACEi (marketed under the brand name Captopril®) which is approved for the treatment of patients with CKD caused by Type 1 diabetes and a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (marketed under the brand names INVOKANA® and Farxiga®) is approved to reduce the risk of ESRD, worsening of kidney function, cardiovascular (CV) death, and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease (nephropathy) with a certain amount of protein in the urine.
There are several pharmaceutical products for the treatment of CKD currently in clinical development, some of which include:
| ● |
Mineralcorticortisteroid receptor agonist (Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals LLC) |
|
| ● |
Chymase inhibitor (Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals LLC) |
|
| ● |
Transient receptor potential canonical channel 5 (Goldfinch Bio) |
|
| ● |
CCR2 receptor antagonists (ChemoCentryx, Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company) |
|
| ● |
Oxidative stress, cyclo-oxygenase 2 inhibitors (Reata Pharmaceuticals, Inc.) |
|
| ● |
Glycosylation inhibitors (Glycadia, Inc. aka Glycadia Pharmaceuticals) |
|
| ● |
Endothelin A receptor antagonists (Chinook therapeutics, Inc.) |
|
| ● |
Cyclin nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitor (Pfizer Inc.) |
|
| ● |
Aldosterone receptor antagonists (Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation) |
|
| ● |
Nitric oxide enzyme inhibitor (GenKyoTex SA) |
On December 15, 2021, the FDA granted accelerated approval to Calliditas Therapeutics AB’s “TARPEYO™” (budesonide) for the reduction of albuminuria in adult primary IgAN patients at risk of rapid disease progression, generally indicated by a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1.5g/g. TARPEYO (developed under the project name NEFECON) was specifically designed for and is the first and only FDA-approved treatment in this disease. It has not been established whether TARPEYO slows kidney function decline in patients with IgAN and continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory clinical trial. Additionally, there are several pharmaceutical products specifically for the treatment of IgAN currently in clinical development, some of which include:
| ● |
Dual acting ARB and endothelin receptor antagonist (Travere Therapeutics, Inc.) |
|
| ● |
Antibody MASP-2 inhibitor (Omeros Corporation) |
|
| ● |
Small-molecule inhibitor of complement factor B (Novartis AG) |
|
| ● |
Small-molecule inhibitor Nrf2 activator/NFkB inhibitor (Reata Pharmaceuticals, Inc.) |
|
| ● | APRIL inhibitor (Vera Therapeutics and Chinook Therapeutics) |
Current treatment strategies for CKD include the strict control of high blood pressure and high blood sugar. The ACEi drug Captopril® is approved for use in patients with CKD due to Type 1 diabetes and both ACEi and ARBs are widely prescribed to slow the progression of CKD. Furthermore, the treatment with ACEi has been linked to hyperkalemia (elevated blood potassium levels), which increases the risk for abnormal heart rhythms and sudden death. In fact, two clinical trials investigating the use of ACEi and ARB combination therapy in kidney disease were stopped prematurely because participants developed hyperkalemia. The added complication of hyperkalemia results in patients receiving smaller, or suboptimal, doses or patients being untreated because they cannot tolerate the treatment. Additional side effects with ACEi treatment are angioedema (swelling of skin tissue) and persistent cough.
INVOKANA® (canagliflozin) is approved for use in patients to reduce the risk of ESRD, worsening of kidney function, cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with Type 2 diabetes and DKD with a certain amount of protein in the urine. Potential side effects of INVOKANA include lower limb amputations, dehydration, diabetic ketoacidosis and genital mycotic infections. Farxiga (dapagliflozin) is approved for use in patients to reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure in adults with Type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease.
DM199 treatment is intended to directly replenish KLK1 levels, maintaining or potentially restoring kidney function. Current treatment options, especially ACEi drugs, only partially restore kidney function and are associated with high-risk side effects. ACEi drugs can generate excessive BK where it is not needed, potentially leading to side effects such as cough and angioedema. DM199 treatment may potentially allow KLK1 to follow its normal physiological processes and release BK when and where it is needed, avoiding these side effects.
DM199 Clinical Trials
AIS Phase 2/3 ReMEDy2 Trial
In September 2021, we announced the initiation of the first site for our pivotal ReMEDy2 trial, a Phase 2/3 clinical trial of DM199 for the treatment of AIS and the first patient was enrolled in November 2021. The ReMEDy2 trial is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 2/3 adaptive trial intended to enroll approximately 350 patients at 75 sites in the United States. Patients enrolled in the trial will be treated with either DM199 or placebo within 24 hours of the onset of AIS symptoms. The trial excludes patients treated with tPA, or any other thrombolytic, and those with large vessel occlusions. The study population is representative of the approximately 80% of AIS patients who do not have treatment options today, primarily due to the short treatment window - tPA must be administered within 4.5 hours from symptom onset.
The ReMEDy2 trial has two separate, independent, primary endpoints and is powered for success with either endpoint: 1) physical recovery from stroke as measured by the well-established modified Rankin Scale (mRS) at day 90, and 2) the rate of ischemic stroke recurrence through day 90. Recurrent strokes represent 25% of all ischemic strokes, often occuring in the first few weeks after an initial stroke and are typically more disabling, costly, and fatal than initial strokes. Secondary endpoints for the trial will evaluate, among other things, participant deaths, mRS shift (which shows the treatment effect on participants across the full spectrum of stroke severity) and additional standard stroke scores (NIHSS and Barthel Index).
In September 2021, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) granted Fast Track Designation to DM199 for the treatment of AIS where tPA and/or mechanical thrombectomy are not indicated or medically appropriate. Fast Track is a process intended to facilitate the development and expedite the review of investigational drugs for the treatment of serious or life-threatening conditions where there is an unmet medical need. Drugs that receive Fast Track Designation may be eligible for more frequent communications and meetings with the FDA to review the drug’s development plan, including the design of the proposed clinical trials, use of biomarkers and the extent of data needed for approval. Drugs with Fast Track Designation may also qualify for accelerated and priority review of new drug applications if relevant criteria are met.
AIS Phase 2 ReMEDy1 Trial
In May 2020, we announced top-line data from our Phase 2 ReMEDy1 trial assessing the safety, tolerability and markers of therapeutic efficacy of DM199 in patients suffering from AIS. We initiated treatment in this trial in February 2018 and completed enrollment in October 2019 with 92 participants. The study drug (DM199 or placebo) was administered as an intravenous (IV) infusion within 24 hours of stroke symptom onset, followed by subcutaneous injections later that day and once every 3 days for 21 days. The trial was designed to measure safety and tolerability along with multiple tests designed to investigate DM199’s therapeutic potential including plasma-based biomarkers and standard functional stroke measures assessed at 90 days post-stroke. Standard functional stroke measurements include the Modified Rankin Scale, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, the Barthel Index and C-reactive protein, a measure of inflammation. The trial met primary safety and tolerability endpoints and was generally safe and well tolerated. In addition, there was a demonstrated therapeutic effect on the rate of severe stroke recurrence inclusive of all participants and there was also a demonstrated therapeutic effect on the physical recoveries of participants that received tPA prior to enrollment but not in participants receiving mechanical thrombectomy prior to enrollment.
Prior to enrollment, 44 of the 91 evaluable patients (48%) received a mechanical thrombectomy, a catheter-based treatment indicated for those who have a large vessel occlusion and can be treated within 6 to 24 hours of the onset of stroke symptoms. While approximately 20% of AIS patients are believed to be eligible for a mechanical thrombectomy, currently only about 5% to 10% receive the treatment due to elapsed time post-stroke or unavailability of the therapy at the hospital where they present. DM199 is intended to treat the approximately 80% of AIS patients who are not eligible for either mechanical thrombectomy or tPA. Treatment for these patients is limited to supportive care. Due to the large volume of participants receiving mechanical thrombectomy prior to enrollment in the ReMEDy1 trial, and a disproportionate distribution of these participants between the active treatment and placebo groups, DM199 did not produce a therapeutic effect on physical recoveries in the overall trial analysis.
When participants treated with mechanical thrombectomy are excluded from the trial data set, which represents the group of participants most closely aligned with the target treatment population for DM199 in the ReMEDy2 trial, a positive therapeutic effect on participant physical recoveries was demonstrated. As shown in the table below, when evaluating the participants treated with DM199 (n=25) vs. supportive care and/or tPA (n=21), the results showed that 36% of participants receiving DM199 progressed to a full or nearly full recovery at 90 days (NIHSS: 0-1), compared to 14% of participants in the placebo group. This represents a 22% absolute increase in the proportion of participants achieving a full or nearly full recovery. Additionally, subject deaths decreased from 24% in the placebo group to 12% in the active therapy group, a 50% relative reduction. Note that the number of subjects in these subsets were insufficient for statistical significance.
DM199 vs. Supportive Care and/or tPA
| NIHSS Outcomes at 90 Days |
||||
| 0-1 |
2-8 |
≥ 9 |
Death |
|
| Placebo (n=21) |
14% |
57% |
5% |
24% |
| DM199 (n=25) |
36% |
36% |
16% |
12% |
In addition, in the evaluable participants (n=91), a significant reduction in the number of participants with recurrent ischemic stroke was noted in the active treatment group: 0 (0%) patient treated with DM199 vs. 6 (13%) on placebo (p=0.012), with 4 of the 6 resulting in participant death.
We believe these findings from our Phase 2 ReMEDy1 trial, which are consistent with the use of Kailikang in China, provide a signal that recombinant human KLK1 appears safe and may have promise as a new tool for physicians who have limited options for the treatment of patients suffering AIS.
CKD Phase 2 REDUX Trial
In October 2019, the FDA accepted our Phase 2 clinical trial protocol for the treatment of CKD caused by rare or significant unmet diseases. Enrollment commenced in December 2019 and was completed in December 2021. The trial named REDUX, Latin for restore, is a multi-center, open-label investigation of patients with mild or moderate CKD (Stage II or III) and albuminuria. The trial was conducted in the United States and was focused on participants with CKD: Cohort 1 was focused on non-diabetic, hypertensive African Americans (AA) with Stage II or III CKD. African Americans are at greater risk for CKD than Caucasians, and those African Americans who have the APOL1 gene mutation are at an even higher risk. Cohort 2 was focused on participants with IgA Nephropathy. Cohort 3 was focused on participants with Type 2 diabetes mellitus with CKD, hypertension and albuminuria (DKD). The trial evaluated two dose levels of DM199 within each cohort. Study participants received DM199 by subcutaneous injection twice weekly for 95 days. The primary study endpoints included safety, tolerability, blood pressure, albuminuria and kidney function, which are evaluated by changes from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria, as measured by the urinary albumin to creatinine ratio.
In June 2021, we announced interim results and in November 2021 we announced additional interim results from our Phase II REDUX trial. The interim results indicated that DM199 was demonstrating clinically meaningful improvements in kidney function in Cohorts 1 and 2, as measured by simultaneously stabilizing estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and decreasing urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR). Additionally, in patients who were hypertensive (Cohorts 1 and 3), DM199 also reduced blood pressure by clinically significant levels and importantly, there was no effect on participants who were not hypertensive (Cohort 2). We reported the following preliminary data:
| ● |
AA: Geometric mean decrease in UACR of -55% in moderate to severe albuminuria (baseline UACR >500 µg/mg) (n=3), Stable eGFR from baseline (n=12) and a mean decrease in systolic/diastolic blood pressure -19/-13 mmHg (n=8) at the 2 µg/kg dose level; |
| ● |
IgAN: UACR geometric mean decrease of -34% (p=0.002) (baseline UACR>500 µg/mg) (n=11), eGFR and blood pressure were stable (n=16) and mean decreases in the biomarkers April and IgA1 of 35% and 22% overall, respectively; and |
| ● |
DKD: No overall treatment effect was observed for UACR, however, reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (n=28) were observed. |
DM199 was generally safe and well tolerated across all cohorts. Adverse events (AEs) were generally mild to moderate in severity, with the most common being local injection site irritation that resolved without medical intervention.
We completed enrollment in REDUX with a total 79 subjects enrolled, including 21 African American subjects into Cohort 1, 25 subjects with IgAN into Cohort 2 and 33 subjects with Type 2 diabetes in Cohort 3. All subjects in Cohorts 1 and 3 have completed the trial. The last subjects in Cohort 2 will complete the treatment phase of the trial in March 2022.
CKD Phase 1b
In July 2019, we completed a Phase 1b clinical trial of DM199 in participants with moderate or severe CKD caused by Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. We initiated dosing patients in this trial in February 2019. The trial was performed to assess the pharmacokinetics (PK) of three dose levels of DM199 (3, 5 and 8 µg/kg), administered in a single subcutaneous dose, as well as the evaluation of safety, tolerability and secondary pharmacodynamic (PD) endpoints. The trial results demonstrated that at the 3µg/kg dose level, the PK profiles were similar between moderate and severe CKD patients, and consistent with healthy subjects (normal kidney function) tested previously. Additionally, DM199 was well tolerated with no dose-limiting tolerability observed. There were no deaths, no discontinuations due to a treatment-related adverse event (AE) and no treatment-related significant adverse events (SAEs). AEs were minor and consistent with standard treatment(s) in the CKD patient population. We announced favorable overall interim PD results from the first 28 subjects that included short-term improvements in NO, average increase of 35.2%, PGE2, average increase of 41.2%, eGFR, average increase of 4.08 mL/min/1732, and the urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) excluding subjects with normal UACR levels at baseline, average decrease of 18.7%. PD results appeared to be drug related in that the greatest improvements occurred approximately 24 hours after DM199 administration and subsequently declined.
Potential DM199 Commercial Advantages
Several researchers have studied the structural and functional properties of KLK1. This deep body of knowledge has revealed the potential clinical benefits of KLK1 treatments. Today, forms of KLK1 derived from human urine and porcine pancreas are sold in Japan, China and Korea to treat AIS, CKD, retinopathy, hypertension and related diseases. We are not aware of any recombinant version of KLK1 with regulatory approval for human use in any country, nor any recombinant version in development besides our drug candidate DM199 (recombinant human KLK1). We believe at least five companies have attempted, unsuccessfully, to create a recombinant version of KLK1.
The growing understanding of the role of KLK1 in human health and its use in Asia as an approved therapeutic highlight two important potential commercial advantages for DM199:
| ● |
KLK1 treatment is sold in Japan, China and Korea. Research has shown that patients with low levels of KLK1 are associated with a variety of diseases related to vascular dysfunction, such as AIS, CKD, retinopathy and hypertension. Clinical trial data with human urine and porcine derived KLK1 has demonstrated statistically significant clinical benefits in treating a variety of patients with KLK1 compared to placebo. These efficacy results are further substantiated by established markets in Japan, China and Korea for pharmaceutical sales of KLK1 derived from human urine and porcine pancreas. We estimate that millions of patients have been treated with these forms of KLK1 in Asia. Altogether, we believe this supports a strong market opportunity for a recombinant version of KLK1 such as DM199. |
| ● |
KLK1 treatment has had limited side effects and has been well tolerated in studies to date. KLK1 is naturally produced by the human body; and, therefore, the body’s own control mechanisms act to limit potential side effects. The side effect observed to limit patient tolerability in our clinical trials was orthostatic hypotension, or a sudden drop in blood pressure, which has been primarily seen at doses 10 to 20 times higher than our anticipated therapeutic dose levels. Moreover, routine clinical use of KLK1 treatment in Asia we understand has been well-tolerated by patients for several decades. In 2017, we completed a clinical trial comparing the pharmacokinetic profile of DM199 to the human urinary form of KLK1 (Kailikang), which showed DM199, when administered in intravenous form, had a similar pharmacokinetic profile. Further, when DM199 was administered subcutaneously, DM199 demonstrated a longer acting pharmacokinetic profile, superior to the intravenously administered Kailikang and DM199. |
In addition, we believe that there are also significant formulation, manufacturing, regulatory and other advantages for recombinant human KLK1 drug candidate DM199:
| ● |
Potency and Impurity Considerations. KLK1 produced from human urine or porcine pancreas presents risks related to preventing impurities, endotoxins, and chemical byproducts due to the inherent variability of the isolation and purification process. We believe that this creates the risk of inconsistencies in potency and impurities from one production run to the next. However, we expect to produce a consistent formulation of KLK1 that is free of endotoxins and other impurities. |
| ● |
Cost and Scalability. Large quantities of human urine and porcine pancreas must be obtained to derive a small amount of KLK1. This creates potential procurement, cost and logistical challenges to source the necessary raw material, particularly for human urine sourced KLK1. Once sourced, the raw material is processed using chemicals and costly capital equipment and produces a significant amount of byproduct waste. Our novel recombinant manufacturing process utilizes widely available raw materials and can be readily scaled for commercial production. Accordingly, we believe our manufacturing process will have significant cost and scalability advantages. |
| ● |
Regulatory. We are not aware of any attempts by manufacturers of the urine or porcine based KLK1 products to pursue regulatory approvals in the United States. We believe that this is related to challenges presented by using inconsistent and potentially hazardous biomaterials, such as human urine and porcine pancreas, and their resulting ability to produce a consistent drug product. Our novel recombinant manufacturing process utilizes widely available raw materials which we believe provides a significant regulatory advantage, particularly in regions such as the United States, Europe and Canada, where safety standards are high. In addition, we believe that DM199 could qualify for 12 years of data exclusivity under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009, which was enacted as part of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010. |
From a strategic perspective, we continue to believe that strategic alternatives with respect to our DM199 product candidate, including licenses and business collaborations, with other regional and global pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies can be important in advancing the clinical development of DM199. Therefore, as a matter of course and from time to time, we engage in discussions with third parties regarding these matters.
Regulatory Approval
Securing regulatory approval for the manufacture and sale of human therapeutic products in the United States, Europe, Canada and other commercial territories is a long and costly process that is controlled by that particular territory’s national regulatory agency. The national regulatory agency in the United States is the FDA, in Europe it is the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and in Canada it is Health Canada. Other national regulatory agencies have similar regulatory approval processes, but each national regulatory agency has its own approval processes. Approval in the United States, Europe or Canada does not assure approval by other national regulatory agencies, although often test results from one country may be used in applications for regulatory approval in another country.
Prior to obtaining regulatory approval to market a drug product, every national regulatory agency has a variety of statutes and regulations which govern the principal development activities. These laws require controlled research and testing of products, governmental review, and approval of a submission containing preclinical and clinical data establishing the safety and efficacy of the product for each use sought, approval of manufacturing facilities including adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP) during production and storage, and control of marketing activities, including advertising, labeling and pricing approval.
None of our product candidates have been completely developed or tested; and, therefore, we are not yet in a position to seek regulatory approval in any territory to market any of our product candidates.
The clinical testing, manufacturing, labeling, storage, distribution, record keeping, advertising, promotion, import, export, and marketing, among other things, of our product candidates are subject to extensive regulation by governmental authorities in the United States and other countries. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals and the subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local, and foreign statutes and regulations require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources. Failure to comply with the applicable requirements at any time during the product development process, approval process, or after approval may subject us to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, including refusal by the applicable regulatory authority to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, imposition of a clinical hold, issuance of warning letters and other types of letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, refusals of government contracts, restitution, disgorgement of profits, or civil or criminal investigations and penalties brought by the FDA and the Department of Justice or other governmental entities.
U.S. Approval Process
In the United States, the FDA is responsible for the drug approval process. The FDA’s mission is to ensure that all medications on the market are safe and effective. The FDA’s approval process examines and thoroughly reviews potential new drugs; only those that are in compliance with the Code of Regulations, 21 CFR 312 and 21 CFR 314 are approved.
The U.S. food and drug regulations require licensing of manufacturing facilities, carefully controlled research and testing of products, governmental review and approval of test results prior to marketing of therapeutic products, and adherence to GMP, as defined by each licensing jurisdiction, during production.
A description of the different stages in the drug approval process in the United States follows.
Stage 1: Preclinical Research. After an experimental drug is discovered, research is conducted to help determine its potential for treating or curing an illness. This is called preclinical research. Animal and/or bench studies are conducted to determine if there are any harmful effects of the drug and to help understand how the drug works. Information from these experiments is submitted to the FDA as part of an IND application. The FDA reviews the information in the IND and decides if the drug is safe to study in humans.
Stage 2: Clinical Research. The experimental drug is studied in humans. The studies are known as clinical trials. Clinical trials are carefully designed and controlled experiments in which the experimental drug is administered to patients to test its safety and to determine the effectiveness of an experimental drug. The four general phases of clinical research are described below.
| ● |
Phase 1 Clinical Studies. Phase 1 clinical studies are generally conducted with healthy volunteers who are not taking other medicines; patients with the illness that the drug is intended to treat are not tested at this stage. Ultimately, Phase 1 studies demonstrate how an experimental drug affects the body of a healthy individual. Phase 1 consists of a series of small studies consisting of tens of volunteers. Tests are done on each volunteer throughout the study to see how the person’s body processes, responds to, and is affected by the drug. Low doses and high doses of the drug are usually studied, resulting in the determination of the safe dosage range in volunteers by the end of Phase 1. This information will determine whether the drug proceeds to Phase 2. |
| ● |
Phase 2 Clinical Studies. Phase 2 clinical studies are conducted in order to determine how an experimental drug affects people who have the disease to be treated. Phase 2 usually consists of a limited number of studies that help determine the drug’s short-term safety, side effects, and general effectiveness. The studies in Phase 2 often are controlled investigations involving comparison between the experimental drug and a placebo, or between the experimental drug and an existing drug. Information gathered in Phase 2 studies will determine whether the drug proceeds to Phase 3. |
| ● |
Phase 3 Clinical Studies. Phase 3 clinical studies are expanded controlled and uncontrolled trials that are used to more fully investigate the safety and effectiveness of the drug. These trials differ from Phase 2 trials because a larger number of patients are studied (sometimes in the thousands) and because the studies are usually double blinded, placebo controlled and of longer duration. As well, Phase 3 studies can include patients who have more than one illness and are taking medications in addition to the experimental drug used in the study. Therefore, the patients in Phase 3 studies more closely reflect the general population. The information from Phase 3 forms the basis for most of the drug’s initial labeling, which will guide physicians on how to use the drug. |
| ● |
Phase 4 Clinical Studies. Phase 4 clinical studies are conducted after a drug is approved. Phase 4 studies may be required by the FDA or conducted by companies to more fully understand how their drug compares to other drugs. FDA-required Phase 4 studies often investigate the drug in specific types of patients that may not have been included in the Phase 3 studies and can involve very large numbers of patients to further assess the drug’s safety. |
Stage 3: FDA Review for Approval. Following the completion of Phase 3 clinical studies, the pharmaceutical company prepares an electronic common technical document reporting all clinical nonclinical and chemistry, manufacturing and control studies conducted on the drug that is transmitted to the FDA as a New Drug Application (NDA). The FDA reviews the information in the NDA to determine if the drug is safe and effective for its intended use. An advisory panel meeting is scheduled for a new drug allowing the FDA to gain feedback from experts. If the FDA determines that the drug is safe and effective, the drug will be approved.
Stage 4: Marketing. After the FDA has approved the experimental drug, the pharmaceutical company can make it available to physicians and their patients. A company also may continue to conduct research to discover new uses for the drug. Each time a new use for a drug is discovered, the drug once again is subject to the entire FDA approval process before it can be marketed for that purpose.
Any FDA approved pharmaceutical products are subject to continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, record-keeping requirements, reporting of adverse experiences with the product, providing the FDA with updated safety and efficacy information, product sampling and distribution requirements, complying with certain electronic records and signature requirements and complying with FDA guidance documents, and promotion and advertising requirements, which include, among others, standards for direct-to-consumer advertising, promoting pharmaceutical products for uses or in patient populations that are not described in the pharmaceutical product’s approved labeling (known as “off-label use”), industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities and promotional activities involving the internet or social media. Failure to comply with FDA requirements is likely to have negative consequences, including adverse publicity, warning or enforcement letters from the FDA or the Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”), mandated corrective advertising or communications with doctors, product seizures or recalls and state or federal civil or criminal prosecution, injunctions and penalties.
The FDA also may require post-marketing testing, known as Phase 4 testing, risk evaluation and mitigation strategies and surveillance to monitor the effects of an approved product or place conditions on an approval that could restrict the distribution or use of the product.
DM199 may qualify for 12 years of data exclusivity under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 (the BPCIA), which was enacted as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Under the BPCIA, an application for a biosimilar product (BLA) cannot be submitted to the FDA until four years, or if approved by the FDA, until 12 years, after the original brand product identified as the reference product is approved under a BLA. The BPCIA provides an abbreviated pathway for the approval of biosimilar and interchangeable biological products. The new abbreviated regulatory pathway establishes legal authority for the FDA to review and approve biosimilar biologics, including the possible designation of a biosimilar as “interchangeable” based on its similarity to an existing brand product. The new law is complex and is only beginning to be interpreted and implemented by the FDA.
European Approval Process
The EMA is roughly parallel to the FDA in terms of the drug approval process and the strict requirements for approval. The EMA was set up in 1995 in an attempt to harmonize, but not replace, the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies in individual European countries. As with the FDA, the EMA drug review and approval process follows similar stages from preclinical testing through clinical testing in Phase 1, 2, and 3. There are some differences between the FDA and EMA review process, specifically the review process in individual European countries. Such differences may allow certain drug products to be tested in patients at an earlier stage of development.
Other Healthcare Laws and Compliance Requirements
In the United States, our activities are potentially subject to regulation by various federal, state and local authorities in addition to the FDA, including the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and other divisions of the U.S. government, including, the Department of Health and Human Services, the Department of Justice and individual U.S. Attorney offices within the Department of Justice, and state and local governments. For example, if a drug product is reimbursed by Medicare, Medicaid, or other federal or state healthcare programs, a company, including its sales, marketing and scientific/educational grant programs, must comply with the federal Food, Drug & Cosmetic Act as it relates to advertising and promotion of drugs, the federal False Claims Act, as amended, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, as amended, the Physician Payments Sunshine Act, the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), and similar state laws. If a drug product is reimbursed by Medicare or Medicaid, pricing and rebate programs must comply with, as applicable, the Medicaid rebate requirements of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 (OBRA), and the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003. Among other things, OBRA requires drug manufacturers to pay rebates on prescription drugs to state Medicaid programs and empowers states to negotiate rebates on pharmaceutical prices, which may result in prices for our future products being lower than the prices we might otherwise obtain. Additionally, the ACA substantially changes the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers. There may continue to be additional proposals relating to the reform of the U.S. healthcare system, in the future, some of which could further limit coverage and reimbursement of drug products. If drug products are made available to authorized users of the Federal Supply Schedule of the General Services Administration, additional laws and requirements may apply.
Pharmaceutical Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement
In the United States and markets in other countries, sales of any products for which we receive regulatory approval for commercial sale will depend in part on the availability of coverage and adequate reimbursement from third-party payers, including government health administrative authorities, managed care providers, private health insurers and other organizations. In the United States, private health insurers and other third-party payers often provide reimbursement for products and services based on the level at which the government (through the Medicare and/or Medicaid programs) provides reimbursement for such treatments. Third-party payers are increasingly examining the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of medical products and services in addition to their safety and efficacy; and, accordingly, significant uncertainty exists regarding the coverage and reimbursement status of newly approved therapeutics. In particular, in the United States, the European Union and other potentially significant markets for our product candidates, government authorities and third-party payers are increasingly attempting to limit or regulate the price of medical products and services, particularly for new and innovative products and therapies, which has resulted in lower average selling prices. Further, the increased emphasis on managed healthcare in the United States and on country and regional pricing and reimbursement controls in the European Union will put additional pressure on product pricing, reimbursement and usage, which may adversely affect our future product sales and results of operations. These pressures can arise from rules and practices of managed care groups, judicial decisions and governmental laws and regulations related to Medicare, Medicaid and healthcare reform, pharmaceutical reimbursement policies and pricing in general. As a result, coverage and adequate third party reimbursement may not be available for our products to enable us to realize an appropriate return on our investment in research and product development.
The market for our product candidates for which we may receive regulatory approval will depend significantly on access to third-party payers’ drug formularies or lists of medications for which third-party payers provide coverage and reimbursement. The industry competition to be included in such formularies often leads to downward pricing pressures on pharmaceutical companies. Also, third-party payers may refuse to include a particular branded drug in their formularies or may otherwise restrict patient access to a branded drug when a less costly generic equivalent or another alternative is available. In addition, because each third-party payer individually approves coverage and reimbursement levels, obtaining coverage and adequate reimbursement is a time-consuming and costly process. We would be required to provide scientific and clinical support for the use of any product candidate to each third-party payer separately with no assurance that approval would be obtained, and we may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies to demonstrate the cost-effectiveness of our product candidates. This process could delay the market acceptance of any of our product candidates for which we may receive approval and could have a negative effect on our future revenues and operating results. We cannot be certain that our product candidates will be considered cost-effective. If we are unable to obtain coverage and adequate payment levels for our product candidates from third-party payers, physicians may limit how much or under what circumstances they will prescribe or administer them and patients may decline to purchase them. This in turn could affect our ability to successfully commercialize our products and impact our profitability, results of operations, financial condition, and future success.
Research and Development
We have devoted substantially all of our efforts to research and development (R&D) which therefore comprises the largest component of our operating costs. Our primary focus over the past approximately nine years has been our lead product candidate, DM199, which is currently in clinical development for the treatment of AIS and CKD.
We expect our R&D expenses will continue to increase in the future as we advance our initial product candidate, DM199, through clinical trials in AIS and CKD and seek to expand our product candidate portfolio. The process of conducting the necessary clinical research to obtain regulatory approval is costly and time-consuming and we consider the active management and development of our clinical pipeline to be integral to our long-term success. The actual probability of success for each product candidate, clinical indication and preclinical program may be affected by a variety of factors including, among other things, the safety and efficacy data for each product candidate, amounts invested in their respective programs, competition and competitive developments, manufacturing capability and commercial viability.
R&D expenses include:
| ● |
expenses incurred under contract research agreements and other agreements with third parties; |
|
| ● |
expenses incurred under agreements with clinical trial sites that conduct research and development activities on our behalf; |
|
| ● |
laboratory and vendor expenses related to the execution of clinical trials and non-clinical studies; |
|
| ● |
the cost of acquiring, developing, manufacturing, and distributing clinical trial materials; |
|
| ● |
employee and consultant-related expenses, which include salaries, benefits, travel and share-based compensation; and |
|
| ● |
facilities and other expenses, which include direct and allocated expenses for rent and maintenance of facilities, insurance, and other supply costs. |
R&D costs are expensed as incurred. Costs for certain development activities such as clinical trials are recognized based on an evaluation of the progress to completion of specific tasks using information and data provided to us by our vendors and our clinical sites.
We expect that it will be at least three to five years, if ever, before we have any product candidates ready for commercialization.
Manufacturing
We do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of clinical quantities of DM199 nor do we have plans to develop our own manufacturing operations in the foreseeable future. We rely on Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC (Catalent), a contract manufacturing organization (CMO) with proven GMP experience in the manufacturing of recombinant proteins for clinical trials, for all of our required raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients for our clinical trials. We have licensed certain gene expression technology and we contract with Catalent for the manufacture of DM199. We currently employ internal resources and third-party consultants to manage our manufacturing relationship with Catalent.
Sales and Marketing
We have not yet defined our sales, marketing or product distribution strategy for our initial product candidate, DM199, or any future product candidates. We currently expect to partner with a large pharmaceutical company for sales execution. However, our future commercial strategy may include the use of distributors, a contract sales force or the establishment of our own commercial and specialty sales force, as well as similar strategies for regions and territories outside the United States.
Intellectual Property
We view patents and other means of intellectual property protection, including trade secrets, as an important component of our core business. We focus on translating our innovations into intangible property protecting our proprietary technology from infringement by competitors. To that end, patents are reviewed frequently and continue to be sought in relation to those components or concepts of our preclinical and clinical products to provide protection. Our strategy, where possible, is to file patent applications to protect our product candidates, as well as methods of manufacturing, administering and using a product candidate. Prior art searches of both patent and scientific databases are performed to evaluate novelty, inventiveness and freedom-to-operate. We require all employees, consultants and parties to a collaborative research agreement to execute confidentiality agreements upon the commencement of employment, consulting relationships or a collaboration with us. These agreements require that all confidential information developed or made known during the course of the engagement with us is to be kept confidential. We also maintain agreements with our scientific staff and all parties contracted in a scientific capacity affirming that all inventions resulting from work performed for us, using our property or relating to our business and conceived or completed during the period covered by the agreement are the exclusive property of DiaMedica.
Our DM199 patent portfolio includes three granted U.S. patents, a granted European patent and pending applications in Australia, Canada, China, Europe, India, Japan, Korea and the United States. Granted or pending claims offer various forms of protection for DM199 including claims to compositions of matter, pharmaceutical compositions, specific formulations and dosing levels and methods for treating a variety of diseases, including chronic kidney disease, stroke and related disorders. These U.S. patents and applications, and their foreign equivalents, are described in more detail below.
Issued patents held by us cover the DM199 composition of matter based on an optimized combination of closely-related isoforms that differ in the extent of glycosylation (process by which sugars are chemically attached to proteins). Issued claims in this patent family cover the most pharmacologically active variants of DM199 and methods of using the same for treating ischemic conditions and these patents are due to expire in 2033. A second patent family includes an issued U.S. patent with claims directed to methods of treating subjects by administering a SC formulation of DM199 or related recombinant kallikrein-1 (KLK1) polypeptides and is predicted to expire in 2033. The pending applications are directed to a range of dose levels and dosing regimens of DM199 that are potentially useful for treating a wide range of diseases including, e.g. pulmonary arterial hypertension, cardiac ischemia, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, stroke and vascular dementia which, if granted, are predicted to expire in 2038.
As previously discussed, we do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of clinical or commercial quantities of DM199. We are contracting with Catalent for the manufacture of DM199. We have licensed certain gene expression technology and we contract with Catalent for the manufacture of DM199. Under the terms of this license, certain milestone and royalty payments may become due and are dependent upon, among other factors, performing clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals and ultimately the successful commercialization of a new drug, the outcome and timing of which is uncertain. The royalty term is indefinite but the license agreement may be canceled by us on 90 days’ prior written notice. The license may not be terminated by Catalent unless we fail to make required milestone and royalty payments.
Methods and reagents required for commercial scale manufacture of DM199 are subject to a series of patents issued to Catalent. We license these patents from Catalent, and such license is exclusive as it relates to the production of DM199 or any human KLK1 protein.
We believe that our proprietary technology along with trade secrets and specialized knowledge of the manufacturing process will provide substantial protection from third-party competitors. We also believe that DM199 cannot be easily reverse engineered for the production of a copycat version.
We believe that the most relevant granted patents and applications with composition of matter or method of use claims covering DM199 are listed below, along with their projected expiration dates exclusive of any patent term extension:
| Patent/Application Number |
Title |
Geography |
Predicted Expiration |
|||
| Issued patents |
||||||
| US 9,364,521 |
Human Tissue Kallikrein 1 Glycosylation Isoforms |
US |
2033 |
|||
| US 9,839,678 |
Human Tissue Kallikrein 1 Glycosylation Isoforms |
US |
2033 |
|||
| EP 2 854 841 |
Human Tissue Kallikrein 1 Glycosylation Isoforms |
Europe |
2033 |
|||
| US 9,616,015 |
Formulations for Human Tissue Kallikrein-1 for Parenteral Delivery and Related Methods |
US |
2033 |
|||
| Pending applications |
||||||
| AU 2018230478 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
Australia |
2038 |
|||
| CA 3054962 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
Canada |
2038 |
|||
| CN 201880016380.4 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
China |
2038 |
|||
| EP 18763243.5 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
Europe |
2038 |
|||
| IN 201917037712 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
India |
2038 |
|||
| JP 2019-548655 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
Japan |
2038 |
|||
| KR 10-2019-7026369 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
Korea |
2038 |
|||
| US 16/492,059 |
Dosage Forms of Tissue Kallikrein 1 |
US |
2038 |
The base term of a U.S. patent is 20 years from the filing date of the earliest-filed non-provisional patent application from which the patent claims priority. The term of a U.S. patent can be lengthened by patent term adjustment, which compensates the owner of the patent for administrative delays at the U.S. PTO. In some cases, the term of a U.S. patent is shortened by terminal disclaimer that reduces its term to that of an earlier-expiring patent.
The term of a U.S. patent may also be eligible for patent term extension under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, referred to as the Hatch-Waxman Act, to account for at least some of the time the drug is under development and regulatory review after the patent is granted. With regard to a drug for which FDA approval is the first permitted marketing of the active ingredient, the Hatch-Waxman Act allows for extension of the term of one U.S. patent that includes at least one claim covering the composition of matter of an FDA-approved drug, an FDA-approved method of treatment using the drug, and/or a method of manufacturing the FDA-approved drug. The extended patent term cannot exceed the shorter of five years beyond the non-extended expiration of the patent or 14 years from the date of the FDA approval of the drug. Some foreign jurisdictions, including Europe and Japan, also have patent term extension provisions, which allow for extension of the term of a patent that covers a drug approved by the applicable foreign regulatory agency. In the future, if and when our pharmaceutical products receive FDA approval, we expect to apply for patent term extension on patents covering those products, their methods of use, and/or methods of manufacture.
In addition to patents, we rely on trade secrets and know-how to develop and maintain our competitive position. Companies typically rely on trade secrets to protect aspects of their business that are not amenable to, or that they do not consider appropriate for, patent protection. We protect trade secrets, if any, and know-how by establishing confidentiality agreements and invention assignment agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors, contractors and partners. These agreements provide that all confidential information developed or made known during the course of an individual or entity’s relationship with us must be kept confidential during and after the relationship. These agreements also generally provide that all relevant inventions resulting from work performed for us or relating to our business and conceived or completed during the period of employment or assignment, as applicable, shall be our exclusive property. In addition, we take other appropriate precautions, such as physical and technological security measures, to guard against misappropriation of our proprietary information by third parties.
Employees
As of December 31, 2021, we had 15 employees, 14 of which were full-time employees. We have never had a work stoppage and none of our employees are covered by collective bargaining agreements. We believe our employee relations are good.
Information About Our Executive Officers
The following table sets forth information as of March 10, 2022 regarding each of our current executive officers:
| Name |
Age |
Positions |
||
| Rick Pauls |
50 |
President and Chief Executive Officer, Director |
||
| Scott Kellen |
56 |
Chief Financial Officer and Secretary |
||
| Kirsten Gruis, M.D. |
49 |
Chief Medical Officer |
||
| Harry Alcorn, Pharm.D. |
65 |
Senior Vice President, Clinical Operations |
||
| Dominic Cundari |
71 |
Chief Commercial Officer |
The present principal occupations and recent employment history of each of our executive officers are set forth below.
Rick Pauls was appointed our President and Chief Executive Officer in January 2010. Mr. Pauls has served as a member of our Board of Directors since April 2005 and the Chairman of the Board from April 2008 to July 2014. Prior to joining DiaMedica, Mr. Pauls was the Co-Founder and Managing Director of CentreStone Ventures Inc., a life sciences venture capital fund, from February 2002 until January 2010. Mr. Pauls was an analyst for Centara Corporation, another early stage venture capital fund, from January 2000 until January 2002. From June 1997 until November 1999, Mr. Pauls worked for General Motors Acceptation Corporation specializing in asset-backed securitization and structured finance. Mr. Pauls previously served as an independent member of the board of directors of LED Medical Diagnostics, Inc. Mr. Pauls received his Bachelor of Arts in Economics from the University of Manitoba and his M.B.A. in Finance from the University of North Dakota.
Scott Kellen joined DiaMedica as our Vice President of Finance in January 2018 and was appointed our Chief Financial Officer and Secretary in April 2018. Prior to joining DiaMedica, Mr. Kellen served as Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Panbela Therapeutics, Inc., formerly known as Sun BioPharma, Inc., a publicly traded clinical stage drug development company, from October 2015 until April 2018. From February 2010 to September 2015, Mr. Kellen served as Chief Financial Officer and Secretary of Kips Bay Medical, Inc., a publicly traded medical device company, and became Chief Operating Officer of Kips Bay in March 2012. From November 2007 to May 2009, Mr. Kellen served as Finance Director of Transoma Medical, Inc. From 2005 to October 2007, Mr. Kellen served as Corporate Controller of ev3 Inc. From March 2003 to April 2005, Mr. Kellen served as Senior Manager, Audit and Advisory Services of Deloitte & Touche, LLP. Altogether, Mr. Kellen has spent more than 25 years in the life sciences industry, focusing on publicly traded early stage and growth companies. Mr. Kellen has a Bachelor of Science degree in Business Administration from the University of South Dakota and is a Certified Public Accountant (inactive).
Kirsten Gruis, M.D. was appointed our Chief Medical Officer effective as of January 3, 2022. Prior to joining DiaMedica, Dr. Gruis served as an independent clinical development consultant for several biotech companies. Prior to these consulting engagements, from March 2020 to January 2021, Dr. Gruis served as Chief Medical Officer for Edgewise Therapeutics, Inc., a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company that is developing orally bioavailable, small molecule therapies for musculoskeletal diseases. Prior to Edgewise, Dr. Gruis served as Franchise Head, Neuromuscular at F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche, a Swiss multinational healthcare company, from November 2018 to December 2019, and as Chief Medical Officer of Agilis Biotherapeutics, Inc., a biotechnology company, from April 2017 to August 2018. Prior to Agilis, Dr. Gruis served in various clinical development positions with the following biopharmaceutical companies: Wave Life Sciences Ltd., Idera Pharmaceutics, Inc., Alynylam Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Pfizer Inc. Prior Pfizer, Dr. Gruis was Associate Professor at SUNY Upstate from March 2012 to July 2013 and prior to that position was an Assistant/Associate Professor at the University of Michigan where she was practicing neurologist and neuromuscular specialist. Dr. Gruis earned her Medical Doctorate from the University of Iowa College of Medicine, has a Master of Science in Clinical Trial Design and Statistical Analysis from the University of Michigan, School of Public Health, and earned her Bachelor of Science in Microbiology from Iowa State University.
Dominic Cundari was appointed our Chief Commercial Officer effective as of February 1, 2022. Mr. Cundari has over 30 years of pharmaceutical experience in various commercial roles in high growth markets. Prior to joining DiaMedica, Mr. Cundari served as an independent commercial strategy and development consultant for Genentech, a global biotechnology company, since February 2009. From January 1988 to January 2009, Mr. Cundari held a variety of sales and marketing management positions across multiple medical specialties at Genentech. As Senior Director for the Vascular Franchise, Mr. Cundari was responsible for shaping commercial strategies, leading product launches in cardiology, pulmonary and neurology specialties and establishing strategic partnerships with telemedicine companies. Mr. Cundari holds both a Master of Science and Bachelor of Arts in Psychology from Villanova University.
Harry Alcorn Jr. Pharm.D. was appointed Senior Vice President of Clinical Operations in August 2018 and served as our Chief Medical Officer until Dr. Gruis joined us in January 2022. Prior to joining DiaMedica, Dr. Alcorn served as Chief Scientific Officer at DaVita Clinical Research (DCR), a company that provides clinical research services for Pharmaceutical and Biotech companies, from October 1997 to June 2018. While at DCR, Dr. Alcorn was responsible for clinical research operations, including the formation and management of the early clinical and late phase research services. Dr. Alcorn also founded the U.S. Renal Network, the first network of Phase 1 renal research sites in the United States. Dr. Alcorn developed DCR’s site management organization for clinical trials. Dr. Alcorn also served as an Executive Director, a Pharmacist and an Investigator at DCR. During this time, from January 2013 to December 2014, he also served on the Board of Directors for the Association of Clinical Pharmacology Units, an association of Phase 1 clinical trial sites. Dr. Alcorn has over 30 years of clinical research experience working with biotech and pharmaceutical companies, both public and private, in conducting research in renal, hepatic and cardiovascular disease. Dr. Alcorn has written and consulted on the development of several protocols and has served as Principal Investigator or Sub Investigator in numerous studies and, for several of these studies, presented study design and results to the FDA. Currently he holds clinical faculty appointments with the University of Minnesota, Creighton University, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Virginia Commonwealth and the University of Colorado, Denver. Dr. Alcorn graduated from Creighton University with a Bachelor of Pharmacy and went on to earn his Doctor of Pharmacy degree from University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Available Information
We are a corporation governed under British Columbia’s Business Corporations Act (BCBCA). Our company was initially incorporated pursuant to The Corporations Act (Manitoba) by articles of incorporation dated January 21, 2000. Our articles were subsequently amended several times, including on April 11, 2016 to continue the Company from The Corporations Act (Manitoba) to the Canada Business Corporations Act (CBCA) and on May 31, 2019, to continue our existence from a corporation incorporated under the CBCA into British Columbia under the BCBCA.
Our registered office is located at 301-1665 Ellis Street, Kelowna, British Columbia, Canada V1Y 2B3 and our principal executive office is located at our wholly owned subsidiary, DiaMedica USA Inc., located at Two Carlson Parkway, Suite 260, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA 55447. Our telephone number is 763-496-5454. Our internet website address is http://www.diamedica.com. Information contained on our website does not constitute part of this report.
We make available, free of charge and through our Internet web site, our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments to any such reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Reports filed with the SEC may be viewed at www.sec.gov.
Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company
We are an emerging growth company as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (JOBS Act), and we may remain an emerging growth company for up to five years from December 31, 2018. However, if certain events occur prior to the end of such five-year period, including if we become a large accelerated filer, our annual gross revenue exceeds $1.07 billion, or we issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt in any three-year period, we will cease to be an emerging growth company prior to the end of such five-year period. For so long as we remain an emerging growth company, we are permitted and intend to rely on exemptions from certain disclosure and other requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. In particular, in this report, we have provided only two years of audited financial statements and have not included certain other information that would be required if we were not an emerging growth company. Accordingly, the information contained herein may be different than the information you receive from other public companies in which you hold equity interests. However, we have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards, and, therefore, we are subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
The following are the material factors known to us that could materially adversely affect our business, operating results or financial condition.
Risk Factors Summary
This summary is not complete and should be read in conjunction with the risk factors that follow.
Risks Related to Our DM199 Product Candidate and Clinical Trials
| ● |
Our prospects depend on the clinical success and commercial potential of DM199, which is in the clinical stage of development. |
|
| ● |
We are required to conduct clinical trials and if these trials fail to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of DM199, or any future product candidate, we will not obtain the approvals required to market and commercialize the product. |
|
| ● |
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in delays in clinical trial site activations and patient enrollments and hospital and medical facility staffing shortages, which will likely continue to adversely affect our clinical trials during 2022. |
|
| ● |
The adaptive design of our ReMEDy2 trial could result in the trial being required to enroll more patients than anticipated increasing the time and costs to complete the trial, which may require additional funding that may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. |
|
| ● |
We may be required to suspend, repeat or terminate our clinical trials if they are not conducted in accordance with regulatory requirements, the results are negative or inconclusive or the trials are not well designed. |
Risks Related to Governmental and Regulatory Compliance and Approvals
| ● |
The regulatory approval process is expensive, time-consuming and uncertain and may prevent us or any future partner or collaborator from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate. |
|
| ● |
Any product candidate for which we, or any future partner or collaborator, obtain marketing approval could be subject to post-marketing restrictions or recall or withdrawal from the market and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with the product candidate. |
Risks Related to Our Reliance on Third Parties
| ● |
We rely on contract manufacturers over whom we have limited control. |
|
| ● |
We rely on third parties to plan, conduct and/or monitor our clinical trials, and their failure to perform could cause delays in completing our product development. |
|
| ● |
Future development collaborations are expected to be important to us. |
Risks Related to the Future Commercialization of DM199 or Any Future Product Candidate
| ● |
The successful commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate, if approved, will depend on market acceptance and coverage and adequate reimbursement for the product. |
|
| ● |
We, or any future partner, will likely face competition from other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, many of which have substantially greater resources and our DM199 product candidate may face competition sooner than expected. |
Risks Related to Intellectual Property
| ● |
We may be unable to adequately protect our technology and enforce our intellectual property rights. |
|
| ● |
We, or a future partner, may require additional third-party licenses to effectively develop, manufacture and commercialize DM199 or any future product candidate, and such license might not be available on commercially-acceptable terms, or at all. |
|
| ● |
Changes in patent law and its interpretation could diminish the value of our patents. |
|
| ● |
Intellectual property litigation may be expensive, time consuming and cause delays in the development, manufacturing and commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate. |
|
| ● |
We could lose important intellectual property rights that we currently license from a third party if we fail to comply with our obligations under the license agreement or otherwise experience disruptions to our relationship with this third party. |
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and Need for Additional Capital
| ● |
We have incurred and expect to continue to incur substantial losses and may never become profitable. |
|
| ● |
Since we have no revenue from product sales and do not expect any revenue from product sales for at least three or four years, we will need additional funding to continue our R&D activities and other operations, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. |
Risks Related to Human Capital Management
| ● |
We heavily rely on the capabilities and experience of our key executives and scientists and the loss of any of them could affect our ability to develop DM199 or any future product candidate. |
|
| ● |
We will likely need to expand our operations and increase the size of our company and we may experience difficulties in managing growth. |
Risks Related to Our Common Shares
| ● |
Our common share price has been and may continue to be volatile and no assurance can be provided that an active trading market for our shares will continue. |
|
| ● |
We may issue additional common shares resulting in share ownership dilution, and if there are substantial sales of our common shares or the perception that such sales may occur, the market price of our common shares could decline. |
Risks Related to Our Jurisdiction of Organization
| ● |
We are governed by the corporate laws of British Columbia, which in some cases have a different effect on shareholders than the corporate laws in effect in the United States. |
|
| ● |
We may be classified as a “passive foreign investment company” in future taxable years, which may have adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences for U.S. shareholders and adversely affect the level of interest in our common shares by U.S. investors. |
Risks Related to Our DM199 Product Candidate
Our prospects depend on the clinical and commercial success of our DM199 product candidate which is in the clinical stage of development.
We are highly dependent on the success of DM199 and we may not be able to successfully obtain regulatory or marketing approval for, or successfully commercialize, this product candidate. To date, we have expended significant time, resources and effort on the development of DM199, including conducting preclinical and clinical trials, for the treatment of AIS and CKD. DM199 requires significant additional clinical testing and investment prior to seeking marketing approval. A commitment of substantial resources by ourselves and any potential partner or collaborator to continue to conduct the clinical trials for DM199 will be required to obtain required regulatory approvals and successfully commercialize this product candidate. Although we intend to study the use of DM199 to treat multiple diseases, we have no other product candidates in our current clinical development pipeline, with the exception of our new product candidate, DM300, which is in the early, pre-clinical stage of development and is intended to treat other inflammatory diseases. Our ability to generate revenue from product sales and to achieve commercial success with DM199 will depend almost entirely on our ability to demonstrate sufficient safety and efficacy to obtain regulatory approval for DM199. We may fail to complete required clinical trials successfully, obtain regulatory approvals, or commercialize DM199. Competitors may develop alternative products and methodologies to treat the diseases or indications that we are pursuing, thus reducing or eliminating the anticipated competitive advantages of DM199. We do not know whether any of our product development efforts will prove to be effective, meet applicable regulatory standards required to obtain the requisite regulatory approvals, be capable of being manufactured at a reasonable cost or be successfully marketed. DM199 is not expected to be commercially viable for at least three or four years. In addition, although no significant adverse events have occurred to date in our clinical trials, it is possible that DM199 may be observed to cause undesirable side effects. Results of early preclinical and clinical research may not be indicative of the results that will be obtained in later stages of clinical research. If regulatory authorities do not approve DM199 for the treatment of AIS and/or CKD or any other indications, or if we fail to maintain regulatory compliance, we would be unable to commercialize DM199 and our business and results of operations would be harmed. If we do succeed in developing viable products from DM199, we will face many potential future obstacles, such as the need to develop or obtain manufacturing, sales and marketing and distribution capabilities.
The clinical success and commercial potential of our DM199 product candidate will depend on a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control.
The clinical success and commercial potential of our DM199 product candidate will depend on a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control, including, among others:
| ● |
the timely initiation, continuation and completion of our currently ongoing Phase 2 and Phase 2/3 clinical trials and future clinical trials for DM199, which will depend substantially upon requirements for such trials imposed by the FDA and other regulatory agencies and bodies; |
|
| ● |
our ability to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of DM199 to the satisfaction of the relevant regulatory authorities or third-party payers; |
|
| ● |
whether we are required by the FDA or other regulatory authorities to conduct additional clinical trials, and the scope and nature of such clinical trials, prior to or after approval to market our DM199 product candidate; |
|
| ● |
the timely receipt of necessary marketing approvals from the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities, as well as pricing and reimbursement determinations; |
|
| ● |
the ability to successfully commercialize DM199, if approved by the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities, whether alone or in collaboration with others; |
|
| ● |
our ability and the ability of third-party manufacturers to manufacture the quantities of DM199, with quality attributes necessary to meet regulatory requirements, sufficient to meet anticipated demand and at a cost that allows us or a future partner to achieve profitability; |
|
| ● |
acceptance of DM199, if approved, as safe and effective by patients and the healthcare providers; |
|
| ● |
the achievement and maintenance of compliance with all regulatory requirements applicable to DM199 by us and our third-party manufacturers and supporting vendors; |
|
| ● |
the maintenance of an acceptable safety profile of DM199 following any approval; |
|
| ● |
the availability, perceived advantages, relative cost, relative safety and relative efficacy of alternative and competitive treatments; |
|
| ● |
our ability to provide approved product with a convenient and patient-friendly administration method; |
|
| ● |
our ability or the ability of a future partner to successfully enforce our intellectual property rights for DM199 and against the products of potential competitors; and |
|
| ● |
our ability to avoid or succeed in defending any third-party patent interference or patent infringement claims. |
No assurance can be provided that we will ever be able to achieve profitability through the sale of, or royalties from, our DM199 product candidate. If we or any future partners or collaborators are not successful in obtaining approval for and commercializing DM199, or are delayed in completing those efforts, our business and operations would be substantially harmed.
Risks Related to Our Clinical Trials
If clinical trials of DM199, or any future product candidate, fail to demonstrate safety and efficacy to the satisfaction of regulatory authorities or do not otherwise produce positive results, we would incur additional costs and experience delays in completing, or may ultimately be unable to complete, the development of DM199 or any future product candidate and therefore be unable to commercialize it.
Before obtaining marketing approval from regulatory authorities for the sale of DM199 or any future product candidate, we must conduct preclinical trials and extensive clinical trials in humans to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our product candidate. Clinical testing is expensive and difficult to design and implement, can take many years to complete and has uncertain outcomes. The outcome of preclinical trials and early clinical trials may not predict the success of later clinical trials, and interim results of a clinical trial may not necessarily predict final results. A number of companies in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials due to lack of efficacy or unacceptable safety profiles, including the emergence of undesirable side effects, notwithstanding promising results in earlier trials. We do not know whether the clinical trials we are currently conducting or may conduct in the future will demonstrate adequate efficacy and safety to support regulatory approval to market DM199 or any future product candidate in any jurisdiction. A product candidate may fail for safety or efficacy reasons at any stage of the testing process. In addition, the patient populations in our clinical trials for DM199 often have co-morbidities that may cause severe illness or death, which may be attributed to DM199 in a manner that negatively affects the safety profile of our DM199 product candidate. If the results of our ongoing or future clinical trials for DM199 are inconclusive with respect to efficacy, if we do not meet our clinical endpoints with statistical significance, or if there are unanticipated safety concerns or adverse events that emerge during clinical trials, we may be prevented from or delayed in obtaining marketing approval, and even if we obtain marketing approval, any sales of DM199 may be limited.
If we have difficulty engaging clinical trial sites for, or enrolling patients in, our clinical trials or experience other delays in clinical testing, we will be delayed in commercializing DM199 or any future product candidate, and our business may be substantially harmed.
We cannot predict whether any clinical trials will begin as planned, will need to be restructured or will be completed on schedule, or at all. Our product development costs will increase if we experience delays in clinical testing. Significant clinical trial delays could shorten any periods during which we or a future partner may have the exclusive right to commercialize DM199 or any future product candidate or allow our competitors to bring products to market before us, which would impair the ability to successfully commercialize DM199 or any future product candidate and may harm our financial condition, results of operations and prospects. The commencement and completion of clinical trials for DM199 or any future product candidate may be delayed for a number of reasons, including among others:
| ● |
patients choosing an alternative treatment for the indications for which we are developing our product candidate or participating in competing clinical trials; |
| ● |
competing clinical trials and scheduling conflicts with participating clinicians; |
|
| ● |
suspension or termination of clinical trials by regulators for many reasons, including concerns about patient safety or failure of our contract manufacturers to comply with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) requirements; |
|
| ● |
any changes to our manufacturing process that may be necessary or desired which affect our ability to produce adequate or timely clinical drug supply; |
|
| ● |
delays or failure to obtain clinical drug supply from contract manufacturers of our product candidate necessary to conduct clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
the product candidate demonstrating a lack of safety or efficacy during clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
patients failing to enroll or complete clinical trials at the rates and within the timelines we expect due to dissatisfaction with the treatment, side effects, or other reasons; |
|
| ● |
clinical investigators not performing our clinical trials on their anticipated schedule, dropping out of a trial or employing methods not consistent with the clinical trial protocol, regulatory requirements or other third parties not performing data collection and analysis in a timely or accurate manner; |
|
| ● |
inspections of clinical trial sites by regulatory authorities, Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or ethics committees finding regulatory violations that require us to undertake corrective action, resulting in suspension or termination of one or more sites or the imposition of a clinical hold on the entire trial; or |
|
| ● |
public health crises, epidemics and pandemics, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, which adversely impact and may continue to adversely impact our ability to engage clinical trial sites, recruit or enroll subjects for our clinical trials and obtain the requisite staffing for our clinical trials. |
Our product development costs will increase if we experience delays in clinical testing or approval or if we need to perform more or larger clinical trials than planned. Additionally, changes in regulatory requirements and policies may occur, and we may need to amend trial protocols or alter our manufacturing processes to reflect these changes. Amendments may require us to resubmit our trial protocols to regulatory authorities or IRBs or ethics committees for re-examination, which may impact the cost, timing or successful completion of any current or future trial. Delays or increase product development costs, any of which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and prospects.
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in delays in clinical trial site activations and patient enrollments and hospital and medical facility staffing shortages which will likely continue during 2022 and continue to adversely affect our clinical trials.
The COVID-19 pandemic, especially in light of the Delta and Omicron, is having a severe effect on the clinical trials of many drug candidates. Some trials have been merely delayed, while others have been cancelled. We have experienced slower than expected site activations and enrollments in our clinical trials due to the reduction or suspension of activities at our clinical trial sites, staffing shortages and patient concerns related to visiting clinical trial sites. We anticipate that the COVID-19 pandemic, and variants of COVID-19, will likely continue to adversely affect our ability to recruit or enroll subjects and initiate new clinical trial sites, and we cannot provide any assurance as to when these issues will resolve.
The extent to which the COVID-19 pandemic may impact our ongoing and planned clinical trials will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted with confidence, such as the emergence of new variants, the duration and severity of each variant and the overall the pandemic, and the effectiveness of actions to contain, treat and prevent COVID-19, including the availability, effectiveness and acceptance of vaccines and vaccine booster shots. The resurgence of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the Delta and Omicron variants, or the emergence of any new variants in the future, could cause us to experience continued and/or additional disruptions that could severely impact our business and clinical trials, including:
| ● |
continued or additional delays or difficulties in enrolling or retaining participants in our clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
delays or difficulties in the identification and initiation of a sufficient number of investigators and clinical sites to recruit sufficient participants at an acceptable rate due to pandemic related restrictions or inadequate clinical site staff; |
|
| ● |
changes in local regulations as part of a response to the pandemic, which may require us to change the ways in which our clinical trials are conducted, which may result in unexpected costs, or require us to discontinue the clinical trials altogether; |
|
| ● |
inability or unwillingness of participants to comply with clinical trial protocols; |
|
| ● |
interruption of key clinical trial activities, such as clinical trial site monitoring, due to limitations on travel imposed or recommended by federal or state governments, employers and others, or interruption of clinical trial subject visits and trial procedures, the occurrence of which could affect the integrity of clinical trial data; |
|
| ● |
risk that participants enrolled in our clinical trials will contract COVID-19 while the clinical trial is ongoing, which could result in participants dropping out of the trial, missing scheduled doses or follow-up visits or failing to follow protocol or otherwise impact the results of the clinical trial, including by increasing the number of observed adverse events; |
|
| ● |
delays in receiving authorizations from local regulatory authorities to initiate our planned clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
delays in necessary interactions with local regulatory authorities, ethics committees and other important agencies and contractors due to limitations in employee resources or forced furlough of employees; and |
|
| ● |
limitations in employee resources that would otherwise be focused on the conduct of our clinical trials, including because of sickness of employees or their families, required quarantines or the desire of employees to avoid contact with large groups of people. |
As a result, the expected timeline for our ReMEDy2 trial and the full data readout of our REDUX trial has been and may continue to be negatively impacted, which has also adversely affected the timing of certain regulatory filings and our ability to initiate required follow-on trials, obtain regulatory approval for and to commercialize our DM199 product candidate.
The adaptive design of our ReMEDy2 trial could result in the trial being required to enroll more patients than anticipated increasing the time and costs to complete the trial, which may result in a need additional funding that may not be available to us on favorable terms or at all.
Our ReMEDy2 trial is currently targeted to enroll approximately 350 patients at 75 sites in the United States. However, with the trial’s adaptive design, it is possible that the number of patients required to complete the trial may increase significantly. If we are required enroll more patients than currently anticipated, it will increase the time and costs to complete the trial, which may result in a need for additional funding that may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
We may be required to suspend, repeat or terminate our clinical trials if they are not conducted in accordance with regulatory requirements, the results are negative or inconclusive or the trials are not well designed.
Clinical trials must be conducted in accordance with the FDA’s current Good Clinical Practices (cGCP) requirements, or analogous requirements of applicable foreign regulatory authorities. Clinical trials are subject to oversight by the FDA, other foreign governmental agencies and IRBs or ethics committees at the trial sites where the clinical trials are conducted. In addition, clinical trials must be conducted with product candidates produced in accordance with applicable cGMP. Clinical trials may be suspended by us or by the FDA, other foreign regulatory authorities, or by an IRB or ethics committee with respect to a particular clinical trial site, for various reasons, including:
| ● |
deficiencies in the conduct of the clinical trials, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or trial protocols; |
|
| ● |
deficiencies in the clinical trial operations or trial sites; |
|
| ● |
unforeseen adverse side effects or the emergence of undue risks to trial subjects; |
|
| ● |
deficiencies in the trial design necessary to demonstrate efficacy; |
|
| ● |
the product candidate may not appear to offer benefits over current therapies; or |
|
| ● |
the quality or stability of the product candidate may fall below acceptable standards. |
The design and implementation of clinical trials is a complex process. As a Company, we have limited experience designing and implementing clinical trials. We may not successfully or cost-effectively design and implement clinical trials that achieve our desired clinical endpoints efficiently, or at all. A clinical trial that is not well designed may delay or even prevent initiation of the trial, can lead to increased difficulty in enrolling patients, may make it more difficult to obtain regulatory approval for the product candidate on the basis of the trial results or, even if a product candidate is approved, could make it more difficult to commercialize the product successfully or obtain reimbursement from third party payers. Additionally, a trial that is not well-designed could be delayed and more expensive than it otherwise would have been, or we may incorrectly estimate the costs to implement the clinical trial, which could lead to a shortfall in funding.
We have conducted and may in the future conduct clinical trials for our product candidates outside the United States, and the FDA may not accept data from such trials.
We have conducted and may in the future conduct clinical trials for our product candidates outside the United States. Clinical trial conducted outside the United States must be conducted in accordance with cGCP requirements, and the FDA must be able to validate the data from the clinical trial through an onsite inspection if it deems such an inspection necessary. If the FDA does not accept data from clinical trials we conduct outside the United States, it would likely result in the need for additional clinical trials, which would be costly and time-consuming and delay aspects of our business plan, including the development and commercial launch of our DM199 product candidate for the treatment of AIS. In addition, the conduct of clinical trials outside the United States also exposes us to additional risks, including risks associated with the following:
| ● |
foreign regulatory requirements that could burden or limit our ability to conduct our clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
administrative burdens of conducting clinical trials under multiple foreign regulatory schemes; |
|
| ● |
foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations; |
|
| ● |
compliance with foreign manufacturing, customs, shipment, and storage requirements; |
|
| ● |
cultural differences in medical practice and clinical research; and |
|
| ● |
diminished protection of intellectual property in some countries. |
Future legislation in the United States, Europe or other countries, and/or regulations and policies adopted by the FDA, the EMA or comparable regulatory authorities, may increase the time and cost required for us or any future partners or collaborators to conduct and complete clinical trials of our current or any future product candidates.
The FDA and the EMA have each established regulations to govern the product development and approval process, as have other foreign regulatory authorities. The policies of the FDA, the EMA and other regulatory authorities may change. For example, in December 2016, the 21st Century Cures Act (Cures Act) was signed into law. The Cures Act, among other things, is intended to modernize the regulation of drugs and spur innovation, but not all of its provisions have yet been implemented. Additionally, in August 2017, the FDA issued final guidance setting forth its current thinking with respect to development programs and clinical trial designs for antibacterial drugs to treat serious bacterial diseases in patients with an unmet medical need. We cannot predict what if any effect the Cures Act or any existing or future guidance from the FDA or other regulatory authorities will have on the development of DM199 or any future product candidate.
Risks Related to Governmental and Regulatory Compliance and Approvals
We may not be able to obtain FDA acceptance of INDs to commence future clinical trials in the United States or on the timelines we expect, and even if we are able to, the FDA may not permit us to proceed in a timely manner.
Prior to commencing additional clinical trials in the United States for DM199 or any future product candidate, we will be required to have an accepted IND for each product candidate and for each targeted indication. In April 2021, we filed, and in May 2021, the FDA accepted, an IND for the Phase 2/3 ReMEDy2 trial in patients with AIS. A submission of an IND may not necessarily result in the FDA allowing further clinical trials to begin and, once begun, issues may arise that will require us to suspend or terminate such clinical trials. Additionally, even if relevant regulatory authorities agree with the design and implementation of the clinical trials set forth in an IND, these regulatory authorities may change their requirements in the future. Failure to submit or obtain acceptance of INDs may cause the development of DM199 or any future product candidate to be delayed or terminated, which could materially and adversely affect our business and prospects.
Even if we complete the necessary preclinical trials and clinical trials, the regulatory approval process is expensive, time-consuming and uncertain and may prevent us or any future partner or collaborator from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate.
The process of obtaining marketing approvals, both in the United States and abroad, is expensive and may take many years, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon a variety of factors, including the type, complexity and novelty of the product candidate involved. Our DM199 or any future product candidate, and the activities associated with their development and commercialization, including design, research, testing, manufacture, quality control, recordkeeping, labeling, packaging, storage, approval, advertising, promotion, sale, distribution, import, export and reporting of safety and other post-market information, are subject to comprehensive regulation by the FDA, the EMA and other similar foreign regulatory agencies. Failure to obtain marketing approval for DM199 or any future product candidate will prevent us or any future partner or collaborator from commercializing the product candidate. We have only limited experience in filing and supporting the applications necessary to gain marketing approvals and expect to rely on third-parties to assist us in this process. Securing marketing approval requires the submission of extensive preclinical and clinical data and supporting information to regulatory authorities for each therapeutic indication to establish the product candidate’s safety and efficacy. Securing marketing approval also requires the submission of information about the product manufacturing process to, and inspection of manufacturing facilities by, the regulatory authorities. The FDA, EMA or other regulatory authorities may determine that DM199 or any future product candidate may not be effective, may be only moderately effective or may prove to have undesirable or unintended side effects, toxicities or other characteristics that may preclude our obtaining marketing approval or prevent or limit its commercial use. As a result, any marketing approval we ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that render the approved product not commercially viable. Our inability to obtain regulatory approval for DM199 or any future product candidate, or if such approval is limited, could substantially harm our business.
We have received Fast Track Designation for DM199 for the treatment of AIS, and we may seek such designation for other uses of DM199 or future product candidates. Fast Track Designation may not actually lead to a faster FDA review and approval process, and there is no guarantee we will be able to maintain such designation.
In September 2021, we received Fast Track Designation from the FDA for DM199 for the treatment of AIS where tPA and/or mechanical thrombectomy are not indicated or medically appropriate. Additionally, in the future, we may seek Fast Track Designation for other uses of DM199 or future product candidates, though we cannot guarantee the FDA will grant such designation. Fast Track is a process intended to facilitate the development and expedite the review of investigational drugs for the treatment of serious or life-threatening conditions where there is an unmet medical need. Drugs that receive Fast Track Designation may be eligible for more frequent communications and meetings with FDA to review the drug’s development plan, including the design of the proposed clinical trials, use of biomarkers and the extent of data needed for approval. Drugs with Fast Track Designation may also qualify for accelerated and priority review of new drug applications if relevant criteria are met. However, Fast Track Designation may not actually lead to a faster review process, and a delay in the review process or in the approval of DM199 will delay revenue from potential sales and will increase the capital necessary to fund our development programs and operations. Additionally, Fast Track Designation is within the discretion of the FDA and may be withdrawn if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
Any product candidate for which we or any future partner or collaborator obtains marketing approval could be subject to post-marketing restrictions or recall or withdrawal from the market, and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with the product candidate, when and if it is approved.
The FDA and other federal and state agencies, including the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), closely regulate compliance with all requirements governing prescription drug products, including requirements pertaining to marketing and promotion of drugs in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling and manufacturing of products. The FDA and DOJ impose stringent restrictions on manufacturers’ communications regarding off-label use, and if we do not market our products for their approved indications, we may be subject to enforcement action for off-label marketing. Violations of such requirements may lead to investigations alleging violations of the FDCA and other statutes, including the False Claims Act and other federal and state health care fraud and abuse laws, as well as state consumer protection laws.
Our failure to comply with all regulatory requirements, or the later discovery of previously unknown adverse events or other problems with our products, manufacturers or manufacturing processes, may yield various results, including:
| ● |
litigation involving patients using our products; |
|
| ● |
restrictions on such products, manufacturers or manufacturing processes; |
|
| ● |
restrictions on the labeling or marketing of a product; |
|
| ● |
restrictions on product distribution or use; |
|
| ● |
requirements to conduct post-marketing studies or clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
warning or untitled letters; |
|
| ● |
withdrawal of the products from the market; |
|
| ● |
refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications that we submit; |
|
| ● |
recall of products; |
| ● |
fines, restitution or disgorgement of profits or revenues; |
|
| ● |
suspension or withdrawal of marketing approvals; |
|
| ● |
damage to relationships with any then current or potential partners; |
|
| ● |
unfavorable press coverage and damage to our or any future partner’s reputation; |
|
| ● |
refusal to permit the import or export of our products; |
|
| ● |
product seizure; or |
|
| ● |
injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
Non-compliance by us or any future partner or collaborator with regulatory requirements regarding ongoing safety monitoring, or pharmacovigilance, and with requirements related to the development of products, can also result in significant financial penalties. Similarly, failure to comply with regulatory requirements regarding the protection of personal information can also lead to significant penalties and sanctions.
Current and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost for us and any future partner or collaborator to obtain marketing approval of and commercialize DM199 or any future product candidate and affect the prices we may obtain.
In the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of DM199 or any future product candidate, restrict or regulate post-approval activities and affect our ability to profitably sell DM199 or any future product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval.
Among policy makers and payers in the United States and elsewhere, there is significant interest in promoting changes in healthcare systems with the stated goals of containing healthcare costs, improving quality and/or expanding access. For example, the ACA includes measures to change health care delivery, decrease the number of individuals without insurance, ensure access to certain basic health care services, and contain the rising cost of care. This healthcare reform movement, including the enactment of the ACA, has significantly changed health care financing by both governmental and private insurers in the United States. With respect to pharmaceutical manufacturers, the ACA increased the number of individuals with access to health care coverage, including prescription drug coverage, but it simultaneously imposed, among other things, increased liability for rebates and discounts owed to certain entities and government health care programs, fees for the manufacture or importation of certain branded drugs and transparency reporting requirements under the Physician Payments Sunshine Act. In addition to the ACA, other federal health reform measures have been proposed and adopted in the United States. We expect that the ACA, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in more rigorous coverage criteria and additional downward pressure on the price that we may receive for any product, if approved. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare or other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payers.
The 117th United States Congress has closely monitored drug pricing and healthcare spending in the United States. Many members of Congress have prioritized policies targeting reducing drug prices and healthcare spending and are committed to lowering spending in federal government programs. Pending legislation, such as the Prescription Drug Pricing Reduction Act and the Elijah E. Cummings Lower Drug Costs Now Act, could significantly change healthcare spending. Additionally, the current U.S. presidential administration has prioritized reducing drug pricing and price transparency in the healthcare industry. On July 9, 2021, an Executive Order was signed directing federal agencies to develop and implement policies to lower drug prices. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us or a future partner from being able to generate sufficient revenue, attain profitability or even commercialize at all DM199 or any future product candidate.
Risks Related to Our Reliance on Third Parties
We rely on contract manufacturers over whom we have limited control. If we are subject to quality, cost or delivery issues with the materials supplied by these or future contract manufacturers, we may be unable to produce adequate supplies of DM199 or any future product candidate, and our clinical and business operations could suffer significant harm.
Completion of our clinical trials and commercialization of our DM199 product candidate and any future product candidate require access to, or development of, facilities to manufacture our product candidates at sufficient yields and, ultimately, at commercial scale. Clinical and commercial drug product must be produced under applicable cGMP regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations may require us to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process. We rely on CMOs to manufacture DM199. We rely on CMOs for manufacturing, filling, labeling, packaging, storing and shipping DM199 in compliance applicable cGMP regulations. The FDA ensures the quality of drug products by carefully monitoring drug manufacturers’ compliance with cGMP regulations.
As a company, we have no direct experience in manufacturing or managing third parties in manufacturing our DM199 product candidate in the volumes that are expected to be necessary to support commercialization, if DM199 is approved. Our efforts to establish these capabilities may not meet our requirements as to scale-up, timeliness, yield, cost or quality in compliance with applicable cGMP regulations. We or any future partner or collaborator or our CMOs may encounter difficulties in production, which may include the following, among others:
| ● |
costs and challenges associated with scale-up and attaining sufficient manufacturing yields; |
|
| ● |
supply chain issues, including the timely availability and shelf life requirements of raw materials and supplies and the lack of redundant and backup suppliers; |
|
| ● |
quality control and assurance; |
|
| ● |
shortages of qualified personnel and capital required to manufacture large quantities of our product candidate; |
|
| ● |
competing capacity needs at CMOs supporting product development as quantities for supply increase; |
|
| ● |
establishment of commercial supply capacity through binding supply agreements; |
|
| ● |
compliance with regulatory requirements that vary in each country where a product might be sold; |
|
| ● |
capacity limitations and scheduling availability in contracted facilities; and |
|
| ● |
natural disasters, cyberattacks or other force majeure events that affect facilities and possibly limit production or loss of product inventory maintained in third party storage facilities. |
There can be no assurances that our current CMOs or any future CMOs will be able to meet our timetable and requirements for our DM199 product candidate or any future product candidate. If we are unable to arrange for alternative third-party manufacturing sources on commercially reasonable terms or in a timely manner, we may be delayed in the development of DM199 or any future product candidate. Further, CMOs failing to operate in compliance with cGMP regulations could result in, among other things, the disruption of product supplies. Our dependence upon our current CMOs and any future CMOs for the manufacture of our product candidates may adversely affect our ability to develop our product candidates in a timely and competitive basis and, if we or a future partner are able to commercialize our product candidates, may adversely affect our revenues from product sales and significantly harm our business.
We rely and will continue to rely on third parties to plan, conduct and monitor our preclinical and clinical trials, and their failure to perform as required could cause delays in completing our product development and substantial harm to our business.
We rely and will continue to rely on third parties to conduct a significant portion of our preclinical and clinical development activities. Preclinical activities include in vivo studies in specific disease models, pharmacology and toxicology studies and assay development. Clinical development activities include trial design, regulatory submissions, clinical patient recruitment, clinical trial monitoring, clinical data management and analysis, safety monitoring and project management. If there is any dispute or disruption in our relationship with third parties, or if they are unable to provide quality services in a timely manner and at a feasible cost, our development programs may face delays. Further, if any of these third parties fail to perform as we expect or if their work fails to meet regulatory requirements, our clinical testing could be delayed, cancelled or rendered ineffective. This happened to us in the past and resulted in us commencing litigation against Pharmaceutical Research Associates Group B.V. (PRA Netherlands) as a result of its handling of a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, single-dose and multiple-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and proof of concept of DM199 in healthy subjects and in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus, as described later in this report, and could happen again.
Our inability to maintain contractual relationships with physicians could have a negative impact on our research and development.
We maintain contractual relationships with respected physicians in hospitals and universities who assist us in the design of our clinical trials and interpretation of trial results. If we are unable to enter into and maintain these relationships, our ability to develop, obtain required regulatory approvals for, and market our DM199 or any future product candidate could be adversely affected. In addition, it is possible that U.S. federal and state and international laws requiring us to disclose payments or other transfers of value, such as gifts or meals, to surgeons and other healthcare providers could have a chilling effect on the relationships with individuals or entities that may, among other things, want to avoid public scrutiny of their financial relationships with us.
Future development collaborations are expected to be important to us. If we are unable to enter into or maintain these collaborations, or if these collaborations are not successful, our business could be adversely affected.
In the future, we intend to seek to collaborate with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for the development and/or commercialization of DM199. We face significant competition in seeking appropriate collaborators or partners. Our ability to reach a definitive agreement for any collaboration will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator’s or partner’s resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed collaborator’s or partner’s evaluation of a number of factors. If we are unable to reach agreements with suitable collaborators or partners on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all, we may have to curtail the development of our DM199 product candidate and take certain actions including, among other things, reducing or delaying its development program, delaying its potential development schedule or reducing the scope of research activities. If we fail to enter into one or more collaborations and do not have sufficient funds or expertise to undertake the necessary development or clinical trial activities, we may not be able to continue or further develop DM199 and our business may be materially and adversely affected.
Future collaborations we may enter into may involve the following risks, among others:
| ● |
collaborators may have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to the collaboration; |
|
| ● |
collaborators may not perform their obligations as expected; |
|
| ● |
changes in the collaborators’ strategic focus or available funding, or external factors, such as an acquisition, may divert resources or create competing priorities; |
|
| ● |
collaborators may delay nonclinical or clinical development, provide insufficient funding for product development of targets selected by us, stop or abandon nonclinical or clinical development for a product candidate, or repeat or conduct new nonclinical and clinical development for a product candidate; |
|
| ● |
collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, products that compete directly or indirectly with our products or product candidates if the collaborators believe that competitive products are more likely to be successfully developed than our products; |
|
| ● |
product candidates discovered in collaboration with us may be viewed by our future collaborators as competitive with their own product candidates or products, which may cause collaborators to cease to devote resources to the development of our product candidates; |
|
| ● |
disagreements with collaborators, including disagreements over proprietary rights, contract interpretation or the preferred course of development, might cause delays or termination of the preclinical or clinical development or commercialization of product candidates, might lead to additional responsibilities for us with respect to product candidates, or might result in litigation or arbitration, any of which would be time-consuming and expensive; |
|
| ● |
collaborators may not properly maintain or defend our intellectual property rights or intellectual property rights licensed to us or may use our proprietary information in such a way as to invite litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our intellectual property or proprietary information or expose us to potential litigation; |
|
| ● |
collaborators may infringe the intellectual property rights of third parties, which may expose us to litigation and potential liability; and |
|
| ● |
collaborations may be terminated for the convenience of the collaborator and, if terminated, we could be required to raise additional capital to pursue further development or commercialization of the applicable product candidates. |
If a collaborator terminates its agreement with us, we may find it more difficult to attract new collaborators and the way we are perceived in the business and financial communities could be adversely affected.
If our collaborations do not result in the successful development of DM199 or any future product candidate, development could be delayed and we may need additional resources to develop DMI99 or any future product candidates. All of the risks relating to product development, regulatory approval and commercialization described in this report also apply to the activities of our future collaborators.
Risks Related to the Future Commercialization of DM199 or Any Future Product Candidate
The successful commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate, if approved, will depend on achieving market acceptance and we may not be able to gain sufficient acceptance to generate significant revenue.
Even if DM199 or any future product candidate is successfully developed and receives regulatory approval, it may not gain market acceptance among physicians, patients, healthcare payers such as private insurers or governments and other funding parties. The degree of market acceptance for DM199 or any product candidate we develop will depend on a number of factors including, among others:
| ● |
demonstration of sufficient clinical efficacy and safety; |
|
| ● |
the prevalence and severity of any adverse side effects; |
|
| ● |
limitations or warnings contained in the product’s approved labeling; |
| ● |
cost-effectiveness and availability of acceptable pricing; |
|
| ● |
the availability of alternative treatment methods and the superiority of alternative treatment methods; |
|
| ● |
the effectiveness of marketing and distribution methods and support for the product; and |
|
| ● |
coverage and reimbursement policies of government and third-party payers to the extent that the product could receive regulatory approval but not be approved for coverage by or receive adequate reimbursement from government and quasi-government agencies or other third-party payers. |
If we fail to obtain coverage and adequate reimbursement for DM199 or any future product candidate, its revenue-generating ability will be diminished and there is no assurance that the anticipated market for the product will develop or be sustained.
Our or a future partner’s ability to successfully commercialize DM199 or any future product candidate will depend, in part, on the extent to which coverage of and adequate reimbursement for such product and related treatments will be available from governmental health payer programs at the federal and state levels, including Medicare and Medicaid, private health insurers, managed care plans and other organizations. No assurance can be given that third-party coverage or adequate reimbursement will be available that will allow us or a future partner to obtain or maintain price levels sufficient for the realization of an appropriate return on our investment in product development. Coverage and adequate reimbursement is critical to new product acceptance by healthcare providers. There is no uniform coverage and reimbursement policy among third-party payers in the United States; however, private third-party payers may follow Medicare coverage and reimbursement policy in setting their own coverage policy and reimbursement rates. Additionally, coverage decisions may depend upon clinical and economic standards that disfavor new drug products when more established or lower cost therapeutic alternatives are already available or subsequently become available. Even if coverage is obtained for DM199 or any future product candidate, the related reimbursement rates might not be adequate to make the product attractive to providers, or may require patient cost sharing (e.g., copayments/deductibles) that patients find unacceptably high. In addition, healthcare reform and controls on healthcare spending may limit coverage of the product and the price we charge and get paid for the product and the volumes thereof that we can sell. Patients are unlikely to use DM199 or any future product candidate unless coverage is provided and reimbursement is adequate to cover a significant portion of its cost.
Outside of the United States, the successful commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate will depend largely on obtaining and maintaining government coverage, because in many countries, patients are unlikely to use prescription drugs that are not covered by their government healthcare programs. Negotiating coverage and reimbursement with governmental authorities can delay commercialization by 12 months or more. Coverage and reimbursement policies may adversely affect our or a future partner’s ability to sell DM199 or any future product candidate on a profitable basis. In many international markets, governments control the prices of prescription pharmaceuticals, including through the implementation of reference pricing, price cuts, rebates, revenue-related taxes and profit control, and we expect prices of prescription pharmaceuticals to decline over the life of the product or as volumes increase.
We or a future partner face competition from other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies and our financial condition and operations will suffer if we fail to compete effectively.
Technological competition is intense in the industry in which we operate. Development of new, potentially competitive therapies comes from pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and universities, as well as companies that offer non-pharmaceutical solutions. Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial and technical resources; more extensive R&D capabilities; and greater marketing, distribution, production and human resources than we do. Moreover, competitors may develop products more quickly than us and may obtain regulatory approval for such products more rapidly than we do. Products and processes which are more effective than those that we intend to develop may be developed by our competitors. R&D by others may render our product candidates non-competitive or obsolete.
Our DM199 product candidate may face competition sooner than expected.
We believe that DM199 could qualify for 12 years of data exclusivity in the United States under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 (BPCIA), which was enacted as part of the ACA. Under the BPCIA, an application for a biosimilar product, or BLA, cannot be submitted to the FDA until four years, or if approved by the FDA, until 12 years, after the original brand product identified as the reference product is approved under a BLA. The BPCIA provides an abbreviated pathway for the approval of biosimilar and interchangeable biological products. The new abbreviated regulatory pathway establishes legal authority for the FDA to review and approve biosimilar biologics, including the possible designation of a biosimilar as “interchangeable” based on its similarity to an existing brand product. This law is complex and is only beginning to be interpreted and implemented by the FDA. While it is uncertain when any such processes may be fully adopted by the FDA, any such processes could have a material adverse effect on the future commercial prospects for DM199 or any future product candidate that is a biologic. There is also a risk that the U.S. Congress could repeal or amend the BPCIA to shorten this exclusivity period, potentially creating the opportunity for biosimilar competition sooner than anticipated after the expiration of our patent protection. Moreover, the extent to which a biosimilar, once approved, will be substituted for any reference product in a way that is similar to traditional generic substitution for non-biological products is not yet clear, and will depend on a number of marketplace and regulatory factors that are still developing.
Even if, as we expect, our DM199 product candidate is considered to be a reference product eligible for 12 years of exclusivity under the BPCIA, another company could market competing products if the FDA approves a full BLA for such product containing the sponsor’s own preclinical data and data from adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to demonstrate the safety, purity and potency of the products. Moreover, an amendment or repeal of the BPCIA could result in a shorter exclusivity period for our DM199 product candidate, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Risks Related to Intellectual Property
If we are unable to adequately protect our technology and enforce our intellectual property rights, our competitors may take advantage of our development efforts or acquired technology and compromise our prospects of marketing and selling DM199 or any future product candidate.
We believe that patents and other proprietary rights are key to our business. Our policy is to file patent applications to protect technology, inventions and improvements that may be important to the development of DM199 or any future product candidate. We also rely upon trade secrets, know-how and continuing technological innovations to develop and maintain our competitive position. We plan to enforce our issued patents and our rights to proprietary information and technology. We review third-party patents and patent applications, both to refine our own patent strategy and to monitor the landscape related to our technology.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to secure and protect our intellectual property rights and to operate without infringing on the proprietary rights of others or having third parties circumvent the rights owned or licensed by us. We have a number of patents, patent applications and rights to patents related to our compounds, product candidates and technology, but we cannot be certain that they will be enforceable or provide adequate protection or that pending patent applications will result in issued patents.
To the extent that development, manufacturing and testing of our product candidates is performed by third party contractors, such work is performed pursuant to fee for service contracts. Under the contracts, all intellectual property, technology know-how and trade secrets arising under such agreements are our exclusive property and must be kept confidential by the contractors. It is not possible for us to be certain that we have obtained from the contractors all necessary rights to such technologies. Disputes may arise as to the scope of the contract or possible breach of contract. No assurance can be given that our contracts would be enforceable or would be upheld by a court.
The patent positions of pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms, ourselves included, are uncertain and involve complex questions of law and fact for which important legal issues remain unresolved. Therefore, it is not clear whether our pending patent applications will result in the issuance of patents or whether we will develop additional proprietary products which are patentable. Part of our strategy is based on our ability to secure a patent position to protect our technology. There is no assurance that we will be successful in this approach and failure to secure patent protection may have a material adverse effect upon us and our financial condition. Also, we may fail in our attempt to commercialize products using currently patented or licensed technology without having to license additional patents. Moreover, it is not clear whether the patents issued or to be issued will provide us with any competitive advantages or if any such patents will be the target of challenges by third parties, whether the patents of others will interfere with our ability to market our products, or whether third parties will circumvent our patents by means of alternate processes. Furthermore, it is possible for others to develop products that have the same effect as our product candidates or technologies on an independent basis or to design around technologies patented by us. Patent applications relating to or affecting our business may have been filed by pharmaceutical or biotechnology companies or academic institutions. Such applications may conflict with our technologies or patent applications and such conflict could reduce the scope of patent protection that we could otherwise obtain or even lead to the rejection of our patent applications. There is no assurance that we can enter into licensing arrangements on commercially reasonable terms or develop or obtain alternative technology in respect of patents issued to third parties that incidentally cover our products or production technologies. Any inability to secure licenses or alternative technology could result in delays in the introduction of some of our product candidates or even lead to us being prevented from pursuing the development, manufacture or sale of certain products. Moreover, we could potentially incur substantial legal costs in defending legal actions that allege patent infringement, or by initiating patent infringement suits against others. It is not possible for us to be certain that we are the creator of inventions covered by pending patent applications or that we were the first to invent or file patent applications for any such inventions. While we have used commercially reasonable efforts to obtain assignments of intellectual property from all individuals who may have created materials on our behalf (including with respect to inventions covered by our patent and pending patent applications), it is not possible for us to be certain that we have obtained all necessary rights to such materials. No assurance can be given that our patents, if issued, would be upheld by a court, or that a competitor’s technology or product would be found to infringe on our patents. Moreover, much of our technology know-how that is not patentable may constitute trade secrets. Therefore, we require our employees, consultants, advisors and collaborators to enter into confidentiality agreements either as stand-alone agreements or as part of their employment or consulting contracts. However, no assurance can be given that such agreements will provide meaningful protection of our trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information in the event of any unauthorized use or disclosure of confidential information. Also, while we have used commercially reasonable efforts to obtain executed copies of such agreements from all employees, consultants, advisors and collaborators, no assurance can be given that executed copies of all such agreements have been obtained.
We or a future partner may require additional third-party licenses to effectively develop, manufacture and commercialize DM199 or any future product candidate and are currently unable to predict the availability or cost of such licenses.
A substantial number of patents have already been issued to other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies. To the extent that valid third-party patent rights cover our product candidates, we or our strategic collaborators would be required to seek licenses from the holders of these patents in order to manufacture, use or sell these product candidates, and payments under them would reduce our profits from these product candidates. We are currently unable to predict the extent to which we may wish or be required to acquire rights under such patents, the availability and cost of acquiring such rights, and whether a license to such patents will be available on acceptable terms, or at all. There may be patents in the United States or in foreign countries or patents issued in the future that are unavailable to license on acceptable terms. Our inability to obtain such licenses may hinder or eliminate our ability to develop, manufacture and market our product candidates.
Changes in patent law and its interpretation could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect DM199 or any future product candidate.
As is the case with other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, our success is heavily dependent on intellectual property rights, particularly patents. Obtaining and enforcing patents in the biopharmaceutical industry involves technological and legal complexity, and obtaining and enforcing biopharmaceutical patents is costly, time consuming, and inherently uncertain. The U.S. Supreme Court has ruled on several patent cases in recent years, either narrowing the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances or weakening the rights of patent owners in certain situations. In addition to increasing uncertainty with regard to our and our licensors’ or collaborators’ ability to obtain patents in the future, this combination of events has created uncertainty with respect to the value of patents once obtained. Depending on decisions by the U.S. Congress, the federal courts, and the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that would weaken our and our licensors’ or collaborators’ ability to obtain new patents or to enforce existing patents and patents we and our licensors or collaborators may obtain in the future. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the United States or other countries could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of patent applications and the enforcement or defense of issued patents.
Assuming that other requirements for patentability are met, prior to March 2013, in the United States, the first to invent the claimed invention was entitled to the patent, while outside the United States, the first to file a patent application was entitled to the patent. After March 2013, under the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act, or the America Invents Act, enacted in September 2011, the United States transitioned to a first inventor to file system in which, assuming that other requirements for patentability are met, the first inventor to file a patent application will be entitled to the patent on an invention regardless of whether a third party was the first to invent the claimed invention. A third party that files a patent application in the USPTO after March 2013, but before us could, therefore, be awarded a patent covering an invention of ours even if we had made the invention before it was made by such third party. This will require us to be cognizant of the time from invention to filing of a patent application. Since patent applications in the United States and most other countries are confidential for a period of time after filing or until issuance, we cannot be certain that we or our licensors were the first to either (i) file any patent application related to our product candidates or (ii) invent any of the inventions claimed in our or our licensor’s patents or patent applications.
The America Invents Act also includes a number of significant changes that affect the way patent applications will be prosecuted and also may affect patent litigation. These include allowing third party submission of prior art to the USPTO during patent prosecution and additional procedures to attack the validity of a patent in USPTO-administered post-grant proceedings, including post-grant review, inter partes review, and derivation proceedings. Because of a lower evidentiary standard in USPTO proceedings compared to the evidentiary standard in United States federal courts necessary to invalidate a patent claim, a third party could potentially provide evidence in a USPTO proceeding sufficient for the USPTO to hold a claim invalid even though the same evidence would be insufficient to invalidate the claim if first presented in a district court action. Accordingly, a third party may attempt to use the USPTO procedures to invalidate our patent claims that would not have been invalidated if first challenged by the third party as a defendant in a district court action. Therefore, the America Invents Act and its implementation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our owned or in-licensed patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our owned or in-licensed issued patents, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects.
The U.S. Supreme Court has ruled on several patent cases in recent years, either narrowing the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances or weakening the rights of patent owners in certain situations. In addition to increasing uncertainty with regard to our and our licensors’ or collaborators’ ability to obtain patents in the future, this combination of events has created uncertainty with respect to the value of patents, once obtained. Depending on decisions by the U.S. Congress, the federal courts, and the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, and similar legislative, judicial, and administrative bodies in other countries, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that would weaken our and our licensors’ or collaborators’ ability to obtain new patents or to enforce existing patents and patents we and our licensors or collaborators may obtain in the future.
Litigation regarding patents, patent applications, and other proprietary rights is generally expensive, time consuming and may cause delays in the development, manufacturing and commercialization of DM199 or any future product candidate.
Third parties may claim that we are using their proprietary information without authorization. Third parties may also have or obtain patents and may claim that technologies licensed to or used by us infringe their patents. If we are required to defend patent infringement actions brought by third parties, or if we sue to protect our own patent rights or otherwise to protect our proprietary information and to prevent its disclosure, we may be required to pay substantial litigation costs and managerial attention may be diverted from business operations even if the outcome is in our favor. In addition, any legal action that seeks damages or an injunction to stop us from carrying on our commercial activities relating to the affected technologies could subject us to monetary liability (including treble damages and attorneys’ fees if we are found to have willfully infringed) and require us or any third-party licensors to obtain a license to continue to use the affected technologies. We cannot predict whether we would prevail in any of these types of actions or that any required license would be available on commercially acceptable terms or at all. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than we can because they have substantially greater resources.
Competitors may infringe our patents or other intellectual property. If we were to initiate legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent covering our product candidates, the defendant could counterclaim that the patent covering our product candidate is invalid and/or unenforceable. In patent litigation in the United States, defendant counterclaims alleging invalidity and/or unenforceability are commonplace. Grounds for a validity challenge could be an alleged failure to meet any of several statutory requirements, including lack of novelty, obviousness, written description or non-enablement. Grounds for an unenforceability assertion could be an allegation that someone connected with prosecution of the patent withheld relevant information from the USPTO, or made a misleading statement, during prosecution. The outcome following legal assertions of invalidity and unenforceability is unpredictable. Moreover, similar challenges may be made by third parties outside the context of litigation, e.g., via administrative proceedings such as post grant or inter partes review in the United States or via oppositions or other similar proceedings in other countries/regions.
Interference or derivation proceedings provoked by third parties or brought by us or declared by the USPTO may be necessary to determine the priority of inventions with respect to our patents or patent applications. An unfavorable outcome could require us to cease using the related technology or to attempt to license rights to it from the prevailing party. Our business could be harmed if the prevailing party does not offer us a license on commercially reasonable terms or at all, or if a non-exclusive license is offered and our competitors gain access to the same technology. Our defense of litigation, validity or enforceability, interference or derivation proceedings may fail and, even if successful, may result in substantial costs and distract our management and other employees. In addition, the uncertainties associated with litigation or such other proceedings could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our clinical trials, continue our research programs, license necessary technology from third parties, or enter into development partnerships that would help us bring our product candidates to market.
Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation or administrative proceedings, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure. There could also be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments. If securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common shares.
If we fail to comply with our obligations in the agreements under which we license intellectual property rights from third parties or otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our licensors, we could lose intellectual property rights that are important to our business.
We are a party to a license agreement relating to an expression system and cell line for use in the production of DM199 or any human KLK1, and we may need to obtain additional licenses from others to advance our R&D activities or allow the commercialization of DM199 or any other product candidates we may identify and pursue. Future license agreements may impose various development, diligence, commercialization and other obligations on us. If any of our in-licenses are terminated, or if the underlying patents fail to provide the intended exclusivity, competitors or other third parties may gain access to technologies that are material to our business, and we may be required to cease our development and commercialization of DM199 or other product candidates that we may identify or to seek alternative manufacturing methods. However, suitable alternatives may not be available or the development of suitable alternatives may result in a significant delay in our commercialization of DM199. Any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Moreover, disputes may arise regarding intellectual property subject to a licensing agreement, including, among others:
| ● |
the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues; |
|
| ● |
the extent to which our product candidates, technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject to the licensing agreement; |
|
| ● |
the sublicensing of patent and other rights under our collaborative development relationships; |
|
| ● |
our diligence obligations under the license agreement and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations; |
|
| ● |
the inventorship and ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by our licensors and us and our partners; and |
|
| ● |
the priority of invention of patented technology. |
In addition, the agreements under which we currently license intellectual property or technology from third parties are complex, and certain provisions in such agreements may be susceptible to multiple interpretations. The resolution of any contract interpretation disagreement that may arise could narrow what we believe to be the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology, or increase what we believe to be our financial or other obligations under the relevant agreement, either of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects. Moreover, if disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on commercially acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize the affected product candidates, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects.
Our reliance on third parties requires us to share our trade secrets, which increases the possibility that a competitor will discover them.
Because we rely on third parties to develop our DM199 product candidate, we must share trade secrets with them. We seek to protect our proprietary technology in part by entering into confidentiality agreements and, if applicable, material transfer agreements, collaborative research agreements, employment or consulting agreements or other similar agreements with our collaborators, advisors, employees, and consultants prior to beginning research or disclosing proprietary information. These agreements typically restrict the ability of our collaborators, advisors, employees, and consultants to publish data potentially relating to our trade secrets. In the future, we may also conduct joint R&D programs which may require us to share trade secrets under the terms of R&D collaboration or similar agreements. We cannot be certain that our current or any future agreements have been or will be entered into with all relevant parties. Moreover, despite our efforts to protect our trade secrets, our competitors may discover our trade secrets, either through breach of these agreements, independent development or publication of information including our trade secrets in cases where we do not have proprietary or otherwise protected rights at the time of publication. Trade secrets can be difficult to protect. If the steps taken to maintain our trade secrets are deemed inadequate, we may have insufficient recourse against third parties for misappropriating any trade secrets. A competitor’s discovery of our trade secrets may impair our competitive position and could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
Patent terms may be inadequate to protect the competitive position of DM199 or any future product candidate for an adequate amount of time.
Patents have a limited lifespan. In the United States, if all maintenance fees are timely paid, the natural expiration of a patent is generally 20 years from its earliest U.S. non-provisional filing date. Certain extensions may be available, but the life of a patent, and the protection it affords, is limited. Even if patents covering our product candidates are obtained, once the patent life has expired, we may be open to competition from competitive products, including generics or biosimilars. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. As a result, our owned and licensed patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours.
We may be subject to claims that our employees, consultants or independent contractors have wrongfully used or disclosed confidential information of third parties or that our employees have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged trade secrets of their former employers.
As is common in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry, we employ individuals who were previously employed at universities or other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. Although we try to ensure that our employees, consultants and independent contractors do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or our employees, consultants or independent contractors have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed intellectual property, including trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any of our employees’ former employers or other third parties. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel, which could adversely impact our business. Even if we are successful in defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management and other employees.
Obtaining and maintaining our patent protection depends on compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment and other requirements imposed by governmental patent agencies, and our patent protection could be reduced or eliminated for non-compliance with these requirements.
Periodic maintenance fees, renewal fees, annuity fees and various other governmental fees on patents and/or applications will be due to be paid to the USPTO and various governmental patent agencies outside of the United States in several stages over the lifetime of the patents and/or applications. We have systems in place to remind us to pay these fees, and we employ an outside firm and rely on our outside counsel to pay these fees due to non-U.S. patent agencies. The USPTO and various non-U.S. governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other similar provisions during the patent application process. We employ reputable law firms and other professionals to help us comply, and in many cases, an inadvertent lapse can be cured by payment of a late fee or by other means in accordance with the applicable rules. However, there are situations in which non-compliance can result in abandonment or lapse of the patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. In such an event, our competitors might be able to enter the market and this circumstance would have a material adverse effect on our business.
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting and defending patents on our product candidates in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the United States can be less extensive than those in the United States. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and state laws in the United States. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in all countries outside the United States, or from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the United States or other jurisdictions. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patent protection to develop their own products and may also export infringing products to territories where we have patent protection, but enforcement is not as strong as that in the United States. These products may compete with our products and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents, trade secrets, and other intellectual property protection, particularly those relating to biotechnology products, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or marketing of competing products in violation of our proprietary rights generally. Proceedings to enforce our patent rights in foreign jurisdictions, whether or not successful, could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and could put our patent applications at risk of not issuing and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we develop or license.
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and Need for Additional Capital
We have incurred substantial losses since our inception and expect to continue to incur substantial losses for at least three or four years and may never become profitable.
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of our DM199 product candidate. Investment in biopharmaceutical product development is highly speculative because it entails substantial upfront capital expenditures and significant risk that a product candidate will fail to prove effective, gain regulatory approval or become commercially viable. We do not have any products approved by regulatory authorities and have not generated any revenues from product sales to date, and do not expect to generate any revenue from the sale of products for at least three or four years. We have incurred significant R&D and other expenses related to our ongoing operations and expect to continue to incur such expenses. As a result, we have not been profitable and have incurred significant operating losses in every reporting period since our inception. For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, we incurred a net loss of $13.6 million and $12.3 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2021, we had an accumulated deficit of $82.5 million. Our prior losses, combined with expected future losses, have had and will continue to have an adverse effect on our shareholders’ equity and working capital. We expect to continue to incur substantial operating losses as we continue our R&D activities, planned clinical trials, regulatory activities and otherwise develop DM199 or any future product candidate to a point where it receives required regulatory approvals and may be commercially sold and we begin to recognize future product sales, or receive royalty payments, licensing fees and/or milestone payments sufficient to generate revenues to fund our continuing operations. We expect our operating losses to increase in the near term as we continue the research, development and clinical trials of, and seek regulatory approval for DM199 or any future product candidate. We are unable to predict the extent of any future losses or when we will become profitable, if ever. Our failure to become and remain profitable may depress the market price of our common shares and could impair our ability to raise capital, continue to develop DM199 or any future product candidate, expand our business and product offerings or continue our operations. Even if we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on an ongoing basis.
Since we currently have no revenue from product sales and do not expect any revenue from product sales for at least three or four years, we will need additional funding to continue our R&D activities and other operations, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
We expect we will need substantial additional capital to further our R&D activities, planned clinical trials and regulatory activities and to otherwise develop our DM199 product candidate to a point where it may be commercially sold. We expect our current cash resources of $45.1 million in cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities as of December 31, 2021 to be sufficient to allow us to complete patient follow-up in our REDUX Phase 2 trial in patients with CKD, to continue our Phase 2/3 trial in patients with AIS and to otherwise fund our planned operations for at least the next twelve months from the date of issuance of the financial statements included in this report. However, the amount and timing of our future funding requirements will depend on many factors, including, among others:
| ● |
the rate of progress in the development of and the conduct of clinical trials with respect to DM199 or any future product candidates; |
|
| ● |
the timing and results of our ongoing development efforts, including in particular our current Phase 2 and Phase 2/3 clinical trials; |
|
| ● |
the costs of our development efforts, including the conduct of clinical trials with respect to DM199 or any future product candidates; |
|
| ● |
the costs associated with identifying additional product candidates and the potential expansion of our current development programs or potential new development programs; |
|
| ● |
the costs necessary to obtain regulatory approvals for DM199 or any future product candidates; |
| ● |
the costs of developing and validating manufacturing processes for DM199 or any future product candidates; |
|
| ● |
the costs associated with being a U.S. public reporting company with shares listed on The Nasdaq Capital Market; |
|
| ● |
the costs we incur in the filing, prosecution, maintenance and defense of our intellectual property; and |
|
| ● |
the costs related to general and administrative support. |
We may require significant additional funds earlier than we currently expect, and there is no assurance that we will not need or seek additional funding prior to such time. We may elect to raise additional funds even before we need them if market conditions for raising additional capital are favorable.
Since our inception, we have financed our operations primarily from public and private sales of equity securities, the exercise of warrants and stock options, interest income on funds available for investment, and government grants and tax incentives, and we expect to continue this practice for the foreseeable future. We do not have any existing credit facilities under which we could borrow funds. We may seek to raise additional funds through various sources, such as equity and debt financings, or through strategic collaborations and license agreements. We can give no assurances that we will be able to secure additional sources of funds to support our operations, or if such funds are available to us, that such additional financing will be sufficient to meet our needs or on terms acceptable to us. This is particularly true if our clinical data is not positive or economic and market conditions deteriorate.
Although we have previously been successful in obtaining financing through our equity securities offerings, there can be no assurance that we will be able to do so in the future. To the extent we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interests of our shareholders will be diluted. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include conversion discounts or covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through government or other third-party funding, marketing and distribution arrangements or other collaborations or strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. It is possible that financing will not be available or, if available, may not be on favorable terms. The availability of financing will be affected by the results of our clinical trials and other scientific and clinical research; our ability to obtain regulatory approvals; market acceptance of DM199 or any future product candidates; the state of the capital markets generally with particular reference to pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical companies, and which could be affected by various events outside our control,
including without limitation geopolitical events, such as the current conflict between Russia and Ukraine; the status of strategic alliance agreements; and other relevant commercial considerations. If adequate funding is not available, we may be required to implement cost reduction strategies; delay, reduce or eliminate one or more of our product development programs; relinquish significant rights to DM199 or any future product candidates or obtain funds on less favorable terms than we would otherwise accept; and/or divest assets or cease operations through a merger, sale or liquidation of our company.
Risks Related to Human Capital Management
We rely heavily on the capabilities and experience of our key executives, clinical personnel and advisors and the loss of any of them could affect our ability to develop DM199 or any future product candidate.
We depend heavily on members of our management team and certain other key personnel, including in particular our clinical personnel. We also depend on our clinical collaborators and advisors, all of whom have outside commitments that may limit their availability to us. In addition, we believe that our future success will depend in large part upon our ability to attract and retain highly skilled scientific, managerial, medical, clinical and regulatory personnel, particularly as we continue to expand our activities and seek regulatory approvals for clinical trials and eventually our DM199 product candidate. We enter into agreements with scientific and clinical collaborators and advisors, key opinion leaders and academic partners in the ordinary course of our business. We also enter into agreements with physicians and institutions that will recruit patients into our clinical trials on our behalf in the ordinary course of our business. Notwithstanding these arrangements, we face significant competition for these types of personnel from other companies, research and academic institutions, government entities and other organizations. We cannot predict our success in hiring or retaining the personnel we require for our continued growth. The loss of the services of any of our key executive officers, clinical personnel and advisors could potentially harm our business, operating results or financial condition.
We will likely need to expand our operations and increase the size of our Company and we may experience difficulties in managing our growth.
As we advance our DM199 product candidate through preclinical testing and clinical trials, or develop any future product candidates, we will need to increase our product development, scientific, clinical, regulatory and compliance and administrative headcount to manage these programs. In furtherance of these efforts, we recently hired a new Chief Medical Officer and Chief Commercial Officer. In addition, to continue to meet our obligations as a U.S. public reporting company, we will likely need to increase our general and administrative capabilities. Our management, personnel and systems currently in place may not be adequate to support this future growth. Our need to effectively manage our operations, growth and various projects requires that we:
| ● |
successfully attract and recruit new employees with the expertise and experience we will require; |
|
| ● |
manage our clinical programs effectively, which have been and will continue to be conducted at numerous clinical sites; |
|
| ● |
develop a marketing, distribution and sales infrastructure if we seek to market our products directly; and |
|
| ● |
continue to improve our operational, manufacturing, quality assurance, financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures. |
If we are unable to successfully manage this growth and increased complexity of operations, our business may be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Our Common Shares
Our common share price has been volatile and may continue to be volatile.
Our common shares trade on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the trading symbol “DMAC.” During 2021, the sale price of our common shares ranged from $3.00 to $10.88 per share. A number of factors could influence the volatility in the trading price of our common shares, including changes in the economy or in the financial markets, industry related developments and the impact of material events and changes in our operations, such as our clinical results, operating results and financial condition. Each of these factors could lead to increased volatility in the market price of our common shares. In addition, the market prices of the securities of our competitors may also lead to fluctuations in the trading price of our common shares.
We do not have a history of a very active trading market for our common shares.
During 2021, the daily trading volume of our common shares ranged from 25,600 shares to 4.8 million shares. Although we anticipate a more active trading market for our common shares in the future, we can give no assurance that a more active trading market will develop or be sustained. If we do not have an active trading market for our common shares, it may be difficult for you to sell our common shares at a favorable price or at all.
We may issue additional common shares resulting in share ownership dilution.
Future dilution will likely occur due to anticipated future equity issuances by us. To the extent we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interests of our shareholders will be diluted. In addition, as of December 31, 2021, we had outstanding warrants to purchase 265,000 common shares, options to purchase 1,896,600 common shares, deferred stock units representing 67,659 common shares and 1,507,651 common shares reserved for future issuance in connection with future grants under the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2019 Omnibus Incentive Plan and the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2021 Employment Inducement Incentive Plan. If these or any future outstanding warrants, options or deferred stock units are exercised or otherwise converted into our common shares, our shareholders will experience additional dilution.
If there are substantial sales of our common shares or the perception that such sales may occur, the market price of our common shares could decline.
Sales of substantial numbers of our common shares, or the perception that such sales may occur, could cause a decline in the market price of our common shares. Any sales by existing shareholders or holders who exercise their warrants or stock options may have an adverse effect on our ability to raise capital and may adversely affect the market price of our common shares.
We are an “emerging growth company” and a “smaller reporting company,” and because we have opted to use the reduced disclosure requirements available to us, certain investors may find investing in our common shares less attractive.
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012. We may remain an emerging growth company until December 31, 2023, the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of our first sale of common shares pursuant to a registration statement under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until such earlier time as we have more than $1.07 billion in annual revenue, the market value of our common shares held by non-affiliates is more than $700 million or we issue more than $1 billion of non-convertible debt over a three-year period. For so long as we remain an emerging growth company, we are permitted and intend to rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. These exemptions include not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Section 404), not being required to comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation and exemptions from the requirements of holding a non-binding advisory vote on executive compensation and shareholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved.
We are also a “smaller reporting company” under the federal securities laws and, as such, are subject to scaled disclosure requirements afforded to such companies. For example, as a smaller reporting company, we are subject to reduced executive compensation disclosure requirements.
Our shareholders and investors may find our common shares less attractive as a result of our status as an “emerging growth company” and “smaller reporting company” and our reliance on the reduced disclosure requirements afforded to these companies. If some of our shareholders or investors find our common shares less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common shares and the market price of our common shares may be more volatile.
We have never paid dividends and do not expect to do so in the foreseeable future.
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our common shares to date. The payment of dividends in the future will be dependent on our earnings and financial condition and on such other factors as our Board of Directors considers appropriate. Unless and until we pay dividends, shareholders may not receive a return on their common shares. There is no present intention by our Board of Directors to pay dividends on our common shares. We currently intend to retain all of our future earnings, if any, to finance the growth and development of our business. In addition, the terms of any future debt agreements may preclude us from paying dividends. As a result, appreciation, if any, in the market price of our common shares will be your sole source of gain for the foreseeable future.
Risks Related to Our Jurisdiction of Organization
We are governed by the corporate laws of British Columbia, which in some cases have a different effect on shareholders than the corporate laws in effect in the United States.
We are a British Columbia corporation. Our corporate affairs and the rights of holders of our common shares are governed by British Columbia’s Business Corporations Act (BCBCA) and applicable securities laws, which laws may differ from those governing a company formed under the laws of a United States jurisdiction. The provisions under the BCBCA and other relevant laws may affect the rights of shareholders differently than those of a company governed by the laws of a United States jurisdiction and may, together with our Notice of Articles and Articles, have the effect of delaying, deferring or discouraging another party from acquiring control of our company by means of a tender offer, proxy contest or otherwise, or may affect the price an acquiring party would be willing to offer in such an instance. The material differences between the BCBCA and the Delaware General Corporation Law (DGCL), by way of example, that may be of most interest to shareholders include the following:
| ● |
for material corporate transactions (such as mergers and amalgamations, other extraordinary corporate transactions or amendments to our Notice of Articles), the BCBCA, subject to the provisions of our Articles, generally requires two-thirds majority vote by shareholders; whereas, the DGCL generally only requires a majority vote of shareholders; |
| ● |
under the BCBCA, a holder of 5% or more of our common shares can requisition a special meeting at which any matters that can be voted on at our annual meeting can be considered; whereas, the DGCL does not give this right; |
| ● |
our Articles require two-thirds majority vote by shareholders to pass a resolution for one or more directors to be removed; whereas, the DGCL only requires the affirmative vote of a majority of the shareholders; and |
| ● |
our Articles may be amended by resolution of our directors to alter our authorized share structure, including to (a) subdivide or consolidate any of our shares and (b) create additional classes or series of shares; whereas, under the DGCL, a majority vote by shareholders is generally required to amend a corporation’s certificate of incorporation and a separate class vote may be required to authorize alternations to a corporation’s authorized share structure. |
We cannot predict if investors find our common shares less attractive because of these material differences. If some investors find our common shares less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common shares and our share price may be more volatile.
We may be classified as a “passive foreign investment company” in future taxable years, which may have adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences for U.S. shareholders.
General Rule. For any taxable year in which 75% or more of our gross income is passive income, or at least 50% of the value of our assets (where the value of our total assets is determined based upon the market value of our common shares at the end of each quarter) are held for the production of, or produce, passive income, we would be characterized as a passive foreign investment company (PFIC) for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The percentage of a corporation’s assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income generally is determined based upon the average ratio of passive assets to total assets calculated at the end of each measuring period. Calculation of the value of assets at the end of each measuring period is generally made at the end of each of the four quarters that make up the company’s taxable year, unless an election is made to use an alternative measuring period (such as a week or month). The “weighted average” of those periodic values is then used to determine the value of assets for the passive asset test for the taxable year. In proposed regulations section 1.1297-1(d)(2), a limited exception to the passive asset test valuation rules is provided for the treatment of working capital in order to take into account the short-term cash needs of operating companies. This new rule provides that an amount of cash held in a non-interest bearing account that is held for the present needs of an active trade or business and is no greater than the amount reasonably expected to cover 90 days of operating expenses incurred in the ordinary course of the trade or business of the foreign corporation (for example, accounts payable for ordinary operating expenses or employee compensation) is not treated as a passive asset. The Treasury Department and the IRS indicated that they continue to study the appropriate treatment of working capital for purposes of the passive asset test.
PFIC Status Determination. The tests for determining PFIC status for any taxable year are dependent upon a number of factors, some of which are beyond our control, including the value of our assets, the market price of our common shares, and the amount and type of our gross income. Based on these tests (i) we believe that we were a PFIC for the taxable year ended December 31, 2016, and (ii) we do not believe that we were a PFIC for any of the taxable years ended thereafter through December 31, 2021. Our status as a PFIC is a fact-intensive determination made for each taxable year, and we cannot provide any assurance regarding our PFIC status for the taxable year ending December 31, 2022 or for future taxable years. U.S. shareholders who own our common shares for any period during which we are a PFIC (which we believe would currently only be those shareholders that held our common shares in the taxable year ended December 31, 2016) will be required to file IRS Form 8621 for each tax year during which they hold our common shares, unless, after we are no longer a PFIC, any such shareholder makes the “purging election” discussed below.
PFIC Consequences. If we are a PFIC for any year during a non-corporate U.S. shareholder’s holding period of our common shares, and the U.S. shareholder does not make a Qualified Electing Fund election (QEF Election) or a “mark-to-market” election, both as described below, then such non-corporate U.S. shareholder generally will be required to treat any gain realized upon a disposition of our common shares, or any so-called “excess distribution” received on our common shares, as ordinary income, rather than as capital gain, and the preferential tax rate applicable to dividends received on our common shares would not be available. This income generally would be allocated over a U.S. shareholder’s holding period with respect to our common shares and the amount allocated to prior years will be subject to tax at the highest tax rate in effect for that year and an interest charge would be imposed on the amount of deferred tax on the income allocated to prior taxable years. Pursuant to the specific provisions of the PFIC rules, a taxpayer may realize gain on the disposition of common shares if the securities are disposed of by a holder whose securities are attributed to the U.S. shareholder, if the securities are pledged as security for a loan, transferred by gift or death, or are subject to certain corporate distributions. Additionally, if we are a PFIC, a U.S. shareholder who acquires our common shares from a decedent would be denied normally available step-up in tax basis for our common shares to fair market value at the date of death but instead would have a tax basis equal to the lower of the fair market value of such common shares or the decedent’s tax basis in such common shares. Newly proposed regulations, that are not yet effective, address domestic partnerships and S corporations that own stock in a PFIC for which a QEF election or "mark-to-market" election could be made. Currently, only the domestic partnership or S corporation (and not the partners or S corporation shareholders) can make these elections. The proposed regulations would reverse the current rule so that only the partners or S corporation shareholders — not the partnership or S corporation — could make the elections. These proposed regulations would only apply to partnership or S corporation shareholders' tax years beginning on or after the date they are issued in final form.
QEF Election. A U.S. shareholder may avoid the adverse tax consequences described above by making a timely and effective QEF election. A U.S. shareholder who makes a QEF election generally must report, on a current basis, its share of our ordinary earnings and net capital gains, whether or not we distribute any amounts to our shareholders, and would be required to comply with specified information reporting requirements. Any gain subsequently recognized upon the sale by that U.S. shareholder of the common shares generally would be taxed as capital gain and the denial of the basis step-up at death described above would not apply. The QEF election is available only if the company characterized as a PFIC provides a U.S. shareholder with certain information regarding its earnings and capital gains, as required under applicable U.S. Treasury regulations. We intend to provide all information and documentation that a U.S. shareholder making a QEF election is required to obtain for U.S. federal income tax purposes (e.g., the U.S. shareholder’s pro rata share of ordinary income and net capital gain, and a “PFIC Annual Information Statement” as described in applicable U.S. Treasury regulations).
Mark-to-Market Election. As an alternative to a QEF Election, a U.S. shareholder may also mitigate the adverse tax consequences of PFIC status by timely making a “mark-to-market” election. A U.S. shareholder who makes the mark-to-market election generally must include as ordinary income each year the increase in the fair market value of the common shares and deduct from gross income the decrease in the value of such shares during each of its taxable years. Losses would be allowed only to the extent of the net mark-to-market gain accrued under the election. If a mark-to-market election with respect to our common shares is in effect on the date of a U.S. shareholder’s death, the tax basis of the common shares in the hands of a U.S. shareholder who acquired them from a decedent will be the lesser of the decedent’s tax basis or the fair market value of the common shares. A mark-to-market election may be made and maintained only if our common shares are regularly traded on a qualified exchange, including The Nasdaq Capital Market. Whether our common shares are regularly traded on a qualified exchange is an annual determination based on facts that, in part, are beyond our control. Accordingly, a U.S. shareholder might not be eligible to make a mark-to-market election to mitigate the adverse tax consequences if we are characterized as a PFIC.
Election Tax Risks. Certain economic risks are inherent in making either a QEF Election or a mark-to-market election. If a QEF Election is made, it is possible that earned income will be reported to a U.S. shareholder as taxable income and income taxes will be due and payable on such an amount. A U.S. shareholder of our common shares may pay tax on such “phantom” income, i.e., where income is reported to it pursuant to the QEF Election, but no cash is distributed with respect to such income. There is no assurance that any distribution or profitable sale will ever be made regarding our common shares, so the tax liability may result in a net economic loss. A mark-to-market election may result in significant share price gains in one year causing a significant income tax liability. This gain may be offset in another year by significant losses. If a mark-to-market election is made, this highly variable tax gain or loss may result in substantial and unpredictable changes in taxable income. The amount included in income under a mark-to-market election may be substantially greater than the amount included under a QEF election. Both the QEF and mark-to-market elections are binding on the U.S. shareholder for all subsequent years that the U.S. shareholder owns our shares unless permission to revoke the election is granted by the IRS.
Purging Election. Although we generally will continue to be treated as a PFIC as to any U.S. shareholder if we are a PFIC for any year during a U.S. shareholder’s holding period, if we cease to satisfy the requirements for PFIC classification, the U.S. shareholder may avoid PFIC classification for subsequent years if the U.S. shareholder elects to make a so-called “purging election,” by recognizing income based on the unrealized appreciation in the common shares through the close of the tax year in which we cease to be a PFIC. When a foreign corporation no longer qualifies as a PFIC (due to a change in facts or law), the foreign corporation nonetheless retains its PFIC status with respect to a shareholder unless and until the shareholder makes an election under Code section 1298(b)(1) and regulations section 1.1298–3 (purging election) on IRS Form 8621 attached to the shareholder’s tax return (including an amended return), or requests the consent of the IRS Commissioner to make a late election under Code section 1298(b)(1) and regulations section 1.1298–3(e) (late purging election) on Form 8621-A.
RULES RELATING TO A PFIC ARE VERY COMPLEX. YOU SHOULD CONSULT YOUR TAX ADVISER CONCERNING THE RELATIVE MERITS AND THE ECONOMIC AND TAX IMPACT OF THE PFIC RULES TO YOUR INVESTMENT IN OUR COMMON SHARES AS A NON-ELECTING U.S. SHAREHOLDER, A U.S. SHAREHOLDER MAKING A QEF ELECTION, A U.S. SHAREHOLDER MAKING A MARK-TO-MARKET ELECTION, OR A U.S. SHAREHOLDER MAKING ANY AVAILABLE PURGING ELECTION.
Should we be classified as a PFIC during a U.S. shareholder’s holding period for our common shares, each such U.S. shareholder should consult their own tax advisors with respect to the possibility of making these elections and the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of our common shares. In addition, the possibility of us being classified as a PFIC may deter certain U.S. investors from purchasing our common shares, which could have an adverse impact on the market price of our common shares and our ability to raise additional financing by selling equity securities, including our common shares.
It may be difficult for non-Canadian shareholders or investors to obtain and enforce judgments against us because of our organization as a British Columbia corporation.
We are a corporation governed under British Columbia’s Business Corporations Act (BCBCA). Two of our directors are residents of Canada, and all or a substantial portion of their assets, and a small portion of our assets, are located outside the United States. Consequently, it may be difficult for holders of our securities who reside in the United States to effect service within the United States upon those directors who are not residents of the United States. It may also be difficult for holders of our securities who reside in the United States to realize in the United States upon judgments of courts of the United States predicated upon our civil liability and the civil liability of our directors, and officers under the United States federal securities laws. Our shareholders and other investors should not assume that British Columbian or Canadian courts (i) would enforce judgments of United States courts obtained in actions against us or such directors, or officers predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the United States federal securities laws or the securities or “blue sky” laws of any state or jurisdiction of the United States, or (ii) would enforce, in original actions, liabilities against us or such directors, or officers predicated upon the United States federal securities laws or any securities or “blue sky” laws of any state or jurisdiction of the United States. In addition, the protections afforded by the securities laws of British Columbia or Canada may not be available to our shareholders or other investors in the United States.
General Risk Factors
We may not achieve our publicly announced milestones according to schedule, or at all.
From time to time, we may announce the timing of certain events we expect to occur, such as the anticipated timing of initiation or completion of or results from our clinical trials. These statements are forward-looking and are based on the best estimates of management at the time relating to the occurrence of such events. However, the actual timing of such events may differ significantly from what has been publicly disclosed. The timing of events such as the initiation or completion of a clinical trial, filing of an application to obtain regulatory approval or an announcement of additional clinical trials for a product candidate may ultimately vary from what is publicly disclosed. These variations in timing may occur as a result of different events, including the nature of the results obtained during a clinical trial or during a research phase, problems with a CMO or contract research organization, the COVID-19 pandemic or any other event having the effect of delaying the publicly announced timeline. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking information, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as otherwise required by law. Any variation in the timing of previously announced milestones could have a material adverse effect on our business plan, financial condition or operating results, and the trading price of our common shares.
If securities or industry analysts do not continue to publish research or reports about our business, or publish negative reports about our business, the market price of our common shares and trading volume could decline.
The market price and trading volume for our common shares will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. We do not have any control over these analysts. There can be no assurance that analysts will continue to cover us or provide favorable coverage. If one or more of the analysts who cover us downgrade our common shares or change their opinion of our common shares, the market price of our common shares would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease coverage of our company or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which could cause the market price of our common shares or trading volume to decline.
We could be subject to securities class action litigation, which is expensive and could divert management attention.
In the past, securities class action litigation has often been brought against a company following a decline or increase in the market price of its securities or certain significant business transactions. We may become involved in this type of litigation in the future, especially if our clinical trial results are not successful or we enter into an agreement for a significant business transaction. If we face such litigation, it could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and our resources, which could harm our business. This is particularly true in light of our limited securities litigation insurance coverage.
A variety of risks are associated with operating our business internationally which could materially adversely affect our business.
We have conducted R&D operations and/or clinical trials in the United States, Canada and Australia. In the future, we expect to conduct certain clinical trials, and plan to seek regulatory approval of DM199, or any future product candidates, outside of the United States. Accordingly, we are subject to risks related to operating in foreign countries including, among others:
| ● |
differing regulatory requirements for drug approvals; |
| ● |
different standards of care in various countries that could complicate the evaluation of our product candidates; |
|
| ● |
different reimbursement systems and different competitive drugs indicated to treat the indications for which our product candidates are or will be developed; |
|
| ● |
different United States and foreign drug import and export rules; |
|
| ● |
reduced protection for intellectual property rights in certain countries; |
|
| ● |
withdrawal from, or revision to or unexpected changes in international trade policies or agreements and the imposition or increases in import and export licensing and other compliance requirements, customs duties and tariffs, import and export quotas and other trade restrictions, license obligations, and other non-tariff barriers to trade; |
|
| ● |
the imposition of U.S. or international sanctions against a country, company, person or entity with whom we do business that would restrict or prohibit continued business with that country, company, person or entity; |
|
| ● |
economic weakness, including inflation or political instability in particular foreign economies and markets; |
|
| ● |
compliance with tax, employment, immigration, and labor laws for employees living or traveling abroad; |
|
| ● |
compliance with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other anti-corruption and anti-bribery laws; |
|
| ● |
foreign taxes, including withholding of payroll taxes; |
|
| ● |
foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations, which could result in increased operating expenses and/or reduced revenue, and other obligations incident to doing business in another country; |
|
| ● |
difficulties in managing and staffing international operations and increases in infrastructure costs, including legal, tax, accounting, and information technology; |
|
| ● |
workforce uncertainty in countries where labor unrest is more common than in the United States; |
|
| ● |
production shortages resulting from any events affecting raw material supply or manufacturing capabilities abroad, such as recent supply chain disruptions, closures and slowdowns caused by the COVID-19 pandemic; |
|
| ● |
potential liability resulting from development work conducted by foreign partners or collaborators; |
|
| ● |
transportation delays and interruptions; |
|
| ● |
business interruptions resulting from natural disasters or geopolitical actions, including war, such as the current conflict between Russia and Ukraine, and terrorism or systems failure, including cybersecurity breaches; and |
|
| ● |
compliance with evolving and expansive international data privacy laws, such as the European Union General Data Protection Regulation. |
We face the risk of product liability claims, which could exceed our insurance coverage, deplete our cash resources and lead to clinical trial delays.
A risk of product liability claims, and related negative publicity, is inherent in the development of human therapeutics. We are exposed to the risk of product liability claims alleging that use of DM199 or any future product candidate caused an injury or harm. These claims can arise at any point in the development, testing, manufacture, marketing or sale of a product candidate and may be made directly by patients involved in clinical trials of our product candidate, by consumers or healthcare providers, or by individuals, organizations or companies selling our products, if and when approved. Product liability claims can be expensive to defend, even if the product or product candidate did not actually cause the alleged injury or harm, and could lead to clinical trial delays and could negatively impact existing or future collaborations.
Insurance covering product liability claims becomes increasingly expensive as a product candidate moves through the development pipeline to commercialization. To protect against potential product liability risks, we have $5.0 million product liability insurance coverage. However, there can be no assurance that such insurance coverage is or will continue to be adequate or available to us at a cost acceptable to us or at all. We may choose or find it necessary under our collaboration agreements to increase our insurance coverage in the future. We may not be able to secure greater or broader product liability insurance coverage on acceptable terms or at reasonable costs when needed. Any liability for damages resulting from a product liability claim could exceed the amount of our coverage, require us to pay a substantial monetary award from our own cash resources, and otherwise have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
If we are unable to maintain product liability insurance required by third parties, certain agreements, such as those with clinical trial sites, contract resource organizations and other supporting vendors, would be subject to termination, which could have a material adverse impact on our operations.
Some of our agreements with third parties require, and in the future will likely require, us to maintain product liability insurance in at least certain specified minimum amounts. If we cannot maintain acceptable amounts of coverage on commercially reasonable terms in accordance with the terms set forth in these agreements, the corresponding agreements would be subject to termination, which could have a material adverse impact on our operations.
Our insurance policies are expensive and protect us only from certain business risks, which could leave us exposed to significant uninsured liabilities. Additionally, future fluctuations in insurance cost and availability could adversely affect our operating results or risk management profile.
We hold a number of insurance policies, including product liability insurance, directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, property insurance and workers’ compensation insurance. The costs of maintaining adequate insurance coverage, most notably directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, have increased significantly recently and may continue to do so in the future, thereby adversely affecting our operating results. If such costs continue to increase, we may be forced to accept lower coverage levels and higher deductibles, which, in the event of a claim, could require significant, unplanned expenditures of cash, which could adversely affect our business. Future potential directors and officers could view our directors’ and officers’ liability insurance coverage as limited or even inadequate. Limited directors’ and officers’ liability insurance coverage, or the perception that our directors’ and officers’ liability insurance coverage is inadequate, may make it difficult to attract and retain directors and officers, and we may lose potential independent board members and management candidates to other companies that have more extensive directors’ and officers’ liability insurance coverage. In addition, if any of our current insurance coverages should become unavailable to us or become economically impractical, we would be required to operate our business without indemnity from commercial insurance providers.
Increasing scrutiny and evolving expectations from regulators, investors, and other stakeholders with respect to our environmental, social and governance practices may impose additional costs on us or expose us to new or additional risks.
Companies are facing increasing scrutiny from regulators, investors, and other stakeholders related to their environmental, social and governance (ESG) practices and disclosure. Investor advocacy groups, investment funds and influential investors are also increasingly focused on these practices, especially as they relate to the environment, climate change, health and safety, supply chain management, diversity, labor conditions and human rights, both in our own operations and in our supply chain. Increased ESG-related compliance costs could result in material increases to our overall operational costs. Our ESG practices may not meet the standards of all of our stakeholders and advocacy groups may campaign for further changes. A failure, or perceived failure, to adapt to or comply with regulatory requirements or to respond to investor or stakeholder expectations and standards could negatively impact our business and reputation and have a negative impact on the trading price of our common shares.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
This Item 1B is inapplicable to us as a smaller reporting company.
Item 2. Properties
Our principal executive offices, together with our research and development operations, are at the office of our wholly owned subsidiary, DiaMedica USA Inc., located at Two Carlson Parkway, Suite 260, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA 55447. We lease these premises, which consist of approximately 3,800 square feet, pursuant to a lease that expires in August 2022. We believe that our facilities are adequate for our current needs and that suitable additional space will be available as and when needed on acceptable terms.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
In March 2013, we entered into a clinical research agreement with Pharmaceutical Research Associates Group B.V. (PRA Netherlands) to perform a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, single-dose and multiple-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and proof of concept of DM199 in healthy subjects and in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. In one arm of this study, we enrolled 36 patients with Type 2 diabetes who were treated with two subcutaneous dose levels of DM199 over a 28-day period. This study achieved its primary endpoint and demonstrated that DM199 was well-tolerated. The secondary endpoints for this study, however, were not met. The secondary efficacy endpoints were confounded due to what we believe were significant execution errors caused by protocol deviations occurring at the clinical study site that were unable to be reconciled. To date, we have been unable to obtain the complete study records from PRA Netherlands and generate a final study report. On November 14, 2017, we initiated litigation with PRA Netherlands in the United States District Court, Southern District of New York,. The complaint alleged, among other things, that PRA failed to conduct the study in accordance with the study protocol and with generally accepted standards for conducting such clinical studies and that PRA further refused to provide us with all data, records and documentation, and/or access thereto, related to the study in accordance with the clinical trial study agreement. The complaint sought to compel PRA to comply with the terms of the clinical trial study agreement, including providing full study records and to recover damages. After PRA Netherlands objected to personal jurisdiction and venue, on August 24, 2018, we re-filed our complaint against both PRA Netherlands and its U.S. parent, PRA Health Sciences, Inc. (PRA USA and collectively with PRA Netherlands, PRA), in the United States District Court, District of Delaware. PRA again objected to the venue and personal jurisdiction. On November 19, 2018, PRA Netherlands and PRA USA filed motions to dismiss the lawsuit. On February 20, 2019, we filed a motion seeking to transfer the Delaware action to the United States District Court, District of Minnesota. PRA Netherlands and PRA USA filed an opposition to our motion. On September 21, 2020, the District Court judge issued a ruling denying our motion to transfer indicating that DiaMedica had not met the required standards to support a venue transfer and on November 2, 2020, a final dismissal order was issued by the District Court judge. Due to the uncertainty inherent in appealing this ruling, we have chosen to cease action in the United States and file our claims against PRA Netherlands directly in a Dutch Court. On November 13, 2020, PRA Netherlands was served with our complaint. PRA Netherlands and PRA USA filed their initial appearances with the Dutch Court on February 24, 2021, and are due to submit their defense, bringing forward all procedural and substances defenses. We have prepared a motion to move the case to the Netherlands Commercial Court (NCC), which specializes in handling international commercial disputes and provides more flexibility to accommodate the specific needs of an individual case and PRA has agreed to move to the NCC. We are currently evaluating pre-trial options prior to filing this motion. Once filed, the NCC will assign judges to this matter, and they will evaluate the adequacy of the documentation submitted in support of our claims and PRA’s response in order to determine the activities or additional information required and determine a schedule accordingly.
From time to time, we may be subject to other various ongoing or threatened legal actions and proceedings, including those that arise in the ordinary course of business, which may include employment matters and breach of contract disputes. Such matters are subject to many uncertainties and to outcomes that are not predictable with assurance and that may not be known for extended periods of time. Other than the PRA matter noted above, we are not currently engaged in or aware of any threatened legal actions.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
| Item 5. |
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information
Our common shares are listed on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the trading symbol “DMAC”.
Number of Record Holders
As of March 12, 2022, we had 37 holders of record of our common shares. This does not include persons whose common shares are in nominee or “street name” accounts through brokers or other nominees.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our common shares, and currently do not have any plans to do so in the foreseeable future. We expect to retain our future earnings, if any, for use in the operation and expansion of our business. Additionally, we may in the future become subject to contractual restrictions on, or prohibitions against, the payment of dividends. Subject to the foregoing, the payment of cash dividends in the future, if any, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon such factors as earnings levels, capital requirements, our overall financial condition and any other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors. As a result, our shareholders will likely need to sell their common shares to realize a return on their investment and may not be able to sell their shares at or above the price paid for them.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Company
We did not purchase any common shares or other equity securities of our company during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2021.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Equity Securities
We did not sell any unregistered equity securities of our company during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2021.
Exchange Controls
There are no governmental laws, decrees or regulations in Canada that restrict the export or import of capital, including foreign exchange controls, or that affect the remittance of dividends, interest or other payments to non-resident holders of the securities of DiaMedica, other than Canadian withholding tax.
Certain Canadian Federal Income Tax Considerations for U.S. Holders
The following is, as of March 1, 2022, a summary of the principal Canadian federal income tax considerations under the Income Tax Act (Canada) (Tax Act) generally applicable to a holder of our common shares who, for purposes of the Tax Act and at all relevant times, is neither resident in Canada nor deemed to be resident in Canada for purposes of the Tax Act and any applicable income tax treaty or convention, and who does not use or hold (and is not deemed to use or hold) common shares in the course of carrying on a business in Canada, deals at arm’s length with us, is not affiliated with us, is not a “specified shareholder” of us (within the meaning of subsection 18(5) of the Tax Act) and holds our common shares as capital property (Holder). A “specified shareholder” for these purposes generally includes a person who (either alone or together with persons with whom that person is not dealing at arm’s length for the purposes of the Tax Act) owns or has the right to acquire or control 25% or more of the common shares determined on a votes or fair market value basis. Generally, common shares will be considered to be capital property to a Holder thereof provided that the Holder does not hold common shares in the course of carrying on a business and such Holder has not acquired them in one or more transactions considered to be an adventure or concern in the nature of trade.
This summary does not apply to a Holder, (i) that is a “financial institution” for purposes of the mark-to-market rules contained in the Tax Act; (ii) that is a “specified financial institution” as defined in the Tax Act; (iii) that holds an interest which is a “tax shelter investment” as defined in the Tax Act; or (iv) that has elected to report its tax results in a functional currency other than Canadian currency. Special rules, which are not discussed in this summary, may apply to a Holder that is an “authorized foreign bank” within the meaning of the Tax Act, a partnership or an insurer carrying on business in Canada and elsewhere. Such Holders should consult their own tax advisors.
This summary is based upon the provisions of the Tax Act (including the regulations (Regulations) thereunder) in force as of March 1, 2022 and our understanding of the current administrative policies and assessing practices of the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) published in writing by the CRA prior to March 1, 2022. This summary takes into account all specific proposals to amend the Tax Act (and the Regulations) publicly announced by or on behalf of the Minister of Finance (Canada) prior to the date hereof (Tax Proposals) and assumes that the Tax Proposals will be enacted in the form proposed, although no assurance can be given that the Tax Proposals will be enacted in their current form or at all. This summary does not otherwise take into account any changes in law or in the administrative policies or assessing practices of the CRA, whether by legislative, governmental or judicial decision or action. This summary is not exhaustive of all possible Canadian federal income tax considerations and does not take into account other federal or any provincial, territorial or foreign income tax legislation or considerations, which may differ materially from those described in this summary.
This summary is of a general nature only and is not, and is not intended to be, and should not be construed to be, legal or tax advice to any particular Holder, and no representations concerning the tax consequences to any particular Holder are made. Holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the income tax considerations applicable to them having regard to their particular circumstances.
Dividends
Dividends paid or credited (or deemed to be paid or credited) to a Holder by us are subject to Canadian withholding tax at the rate of 25% unless reduced by the terms of an applicable tax treaty or convention. For example, under the Canada-United States Tax Convention (1980), as amended (US Treaty), the dividend withholding tax rate is generally reduced to 15% (or 5% in the case of a Holder that is a company that beneficially owns at least 10% of our voting shares) in respect of a dividend paid or credited to a Holder beneficially entitled to the dividend who is resident in the United States for purposes of the US Treaty and whose entitlement to the benefits of the US Treaty is not limited by the limitation of benefits provisions of the US Treaty. Holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors to determine their entitlement to relief under the US Treaty or any other applicable tax treaty as well as their ability to claim foreign tax credits with respect to any Canadian withholding tax, based on their particular circumstances.
Disposition of Common Shares
A Holder generally will not be subject to tax under the Tax Act in respect of a capital gain realized on the disposition or deemed disposition of a common share, unless the common share constitutes or is deemed to constitute “taxable Canadian property” to the Holder thereof for purposes of the Tax Act, and the gain is not exempt from tax pursuant to the terms of an applicable tax treaty or convention.
In general, provided the common shares are listed on a “designated stock exchange” (which currently includes The Nasdaq Capital Market) at the date of the disposition, the common shares will only constitute “taxable Canadian property” of a Holder if, at any time within the 60-month period preceding the disposition: (i) such Holder, persons with whom the Holder did not deal at arm’s length, partnerships in which the Holder or a person with whom the Holder did not deal at arm’s length holds a membership interest directly or indirectly through one or more partnerships, or any combination thereof, owned 25% or more of the issued shares of any class or series of the Company’s share capital; and (ii) more than 50% of the fair market value of the common shares was derived directly or indirectly from one or any combination of (A) real or immovable property situated in Canada, (B) Canadian resource properties, (C) timber resource properties, and (D) options in respect of, or interests in, or for civil law rights in, property described in any of subparagraphs (ii)(A) to (C), whether or not the property exists. However, and despite the foregoing, in certain circumstances the common shares may be deemed to be “taxable Canadian property” under the Tax Act.
Holders whose common shares may be “taxable Canadian property” should consult their own tax advisers.
Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following discussion is generally limited to certain material U.S. federal income tax considerations relating to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common shares by U.S. Holders (as defined below). This discussion applies to U.S. Holders that hold our common shares as capital assets. This summary is for general information purposes only and does not purport to be a complete analysis or listing of all potential U.S. federal income tax considerations that may apply to a U.S. Holder arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares. Accordingly, this summary is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, legal or U.S. federal income tax advice with respect to any U.S. Holder. Although this discussion is generally limited to the U.S. federal income tax considerations to U.S. Holders, the U.S. federal income tax treatment of dividends on and gain on sale or exchange of our common shares by certain “Non-U.S. Holders” (as defined below) is included below at “U.S. Federal Income Taxation of Non-U.S. Holders.”
No legal opinion from U.S. legal counsel or ruling from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has been requested, or will be obtained, regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. This summary is not binding on the IRS, and the IRS is not precluded from taking a position that is different from, and contrary to, the positions presented in this summary. In addition, because the guidance on which this summary is based are subject to various interpretations, the IRS and the U.S. courts could disagree with one or more of the positions described in this summary.
This discussion is based on the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (Code), U.S. Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder and administrative and judicial interpretations thereof, and the income tax treaty between the United States and Canada (Convention), all as in effect on the date hereof and all of which are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect. This summary is applicable to U.S. Holders who are residents of the United States for purposes of the Convention and who qualify for the full benefits of the Convention. This summary does not discuss the potential effects, whether adverse or beneficial, of any proposed legislation.
This discussion does not address all of the U.S. federal income tax considerations that may be relevant to specific U.S. Holders in light of their particular circumstances or to U.S. Holders subject to special treatment under U.S. federal income tax law (such as certain financial institutions, insurance companies, broker-dealers and traders in securities or other persons that generally mark their securities to market for U.S. federal income tax purposes, tax-exempt entities, retirement plans, regulated investment companies, real estate investment trusts, certain former citizens or residents of the United States, persons who hold common shares as part of a “straddle,” “hedge,” “conversion transaction,” “synthetic security” or integrated investment, persons that have a “functional currency” other than the U.S. dollar, persons that own (or are deemed to own) 10% or more (by voting power or value) of our common shares, persons that acquire their common shares as part of a compensation arrangement, corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax, partnerships and other pass-through entities, and investors in such pass-through entities). This discussion does not address any U.S. state or local or non-U.S. tax considerations or any U.S. federal estate, gift or alternative minimum tax considerations. In addition, except as specifically set forth below, this summary does not discuss applicable tax reporting requirements.
As used in this discussion, the term “U.S. Holder” means a beneficial owner of common shares that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (1) an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States, (2) a corporation (or entity treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes) created or organized in or under the laws of the United States, any state thereof, or the District of Columbia, (3) an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source or (4) a trust (x) with respect to which a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over its administration and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all of its substantial decisions or (y) that has elected under applicable U.S. Treasury regulations to be treated as a domestic trust for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
If an entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds the common shares, the U.S. federal income tax considerations relating to an investment in the common shares will depend in part upon the status and activities of such entity and the particular partner. Any such entity should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to it and its partners of the purchase, ownership and disposition of the common shares.
Persons holding common shares should consult their own tax advisors as to the particular tax considerations applicable to them relating to the purchase, ownership and disposition of common shares, including the applicability of U.S. federal, state and local tax laws and non-U.S. tax laws.
Distributions
Subject to the discussion below under “Passive Foreign Investment Company Considerations,” a U.S. Holder that receives a distribution with respect to the common shares generally will be required to include the gross amount of such distribution (before reduction for any Canadian withholding taxes) in gross income as a dividend when actually or constructively received to the extent of the U.S. Holder’s pro rata share of our current and/or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles). To the extent a distribution received by a U.S. Holder is not a dividend because it exceeds the U.S. Holder’s pro rata share of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, it will be treated first as a tax-free return of capital and reduce (but not below zero) the adjusted tax basis of the U.S. Holder’s common shares. To the extent the distribution exceeds the adjusted tax basis of the U.S. Holder’s common shares, the remainder will be taxed as capital gain. However, we cannot provide any assurance that we will maintain or provide earnings and profits determinations in accordance with U.S. federal income tax principles. Therefore, U.S. Holders should expect that a distribution will generally be treated as a dividend even if that distribution would otherwise be treated as a non-taxable return of capital or as capital gain under the rules described above.
The U.S. dollar value of any distribution on the common shares made in Canadian dollars generally should be calculated by reference to the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Canadian dollar in effect on the date of receipt (or deemed receipt) of such distribution by the U.S. Holder regardless of whether the Canadian dollars so received are in fact converted into U.S. dollars at that time. If the Canadian dollars received are converted into U.S. dollars on the date of receipt (or deemed receipt), a U.S. Holder generally should not recognize currency gain or loss on such conversion. If the Canadian dollars received are not converted into U.S. dollars on the date of receipt (or deemed receipt), a U.S. Holder generally will have a basis in such Canadian dollars equal to the U.S. dollar value of such Canadian dollars on the date of receipt (or deemed receipt). Any gain or loss on a subsequent conversion or other disposition of such Canadian dollars by such U.S. Holder generally will be treated as ordinary income or loss and generally will be income or loss from sources within the United States for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes. Different rules apply to U.S. Holders who use the accrual method of tax accounting. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own U.S. tax advisors regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of receiving, owning, and disposing of foreign currency.
Distributions on the common shares that are treated as dividends generally will constitute income from sources outside the United States for foreign tax credit purposes and generally will constitute “passive category income.” Because we are not a United States corporation, such dividends will not be eligible for the “dividends received” deduction generally allowed to corporate shareholders with respect to dividends received from U.S. corporations. Dividends paid by a “qualified foreign corporation” to a U.S. Holder who is an individual, trust or estate will generally be treated as “qualified dividend income” and are eligible for taxation at a reduced capital gains rate rather than the marginal tax rates generally applicable to ordinary income provided that a holding period requirement (more than 60 days of ownership, without protection from the risk of loss, during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the ex-dividend date) and certain other requirements are met. However, if we are a PFIC for the taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year (see discussion below under “Passive Foreign Investment Company Considerations”), we will not be treated as a qualified foreign corporation, and therefore the reduced capital gains tax rate described above will not apply. Each U.S. Holder is advised to consult its own tax advisors regarding the availability of the reduced tax rate on dividends.
If a U.S. Holder is subject to Canadian withholding tax on dividends paid on the holder’s common shares (see discussion above under “Material Canadian Federal Income Tax Considerations—Dividends”), the U.S. Holder may be eligible, subject to a number of complex limitations, to claim a credit against its U.S. federal income tax for the Canadian withholding tax imposed on the dividends. However, if U.S. persons collectively own, directly or indirectly, 50% or more of the voting power or value of our common shares it is possible that a portion of any dividends we pay will be considered U.S. source income in proportion to our U.S. source earnings and profits, which could limit the ability of a U.S. Holder to claim a foreign tax credit for the Canadian withholding taxes imposed in respect of such a dividend, although certain elections may be available under the Code and the Convention to mitigate these effects. A U.S. Holder may claim a deduction for the Canadian withholding tax in lieu of a credit, but only for a year in which the U.S. Holder elects to do so for all creditable foreign income taxes. The rules governing the foreign tax credit are complex. Each U.S. Holder is advised to consult its tax advisor regarding the availability of the foreign tax credit under its particular circumstances.
Sale, Exchange or Other Disposition of Common Shares
Subject to the discussion below under “Passive Foreign Investment Company Considerations,” a U.S. Holder generally will recognize capital gain or loss for U.S. federal income tax purposes upon the sale, exchange or other disposition of common shares. The amount of gain recognized will equal the excess of the amount realized (i.e., the amount of cash plus the fair market value of any property received) over the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the common shares sold or exchanged. The amount of loss recognized will equal the excess of the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the common shares sold or exchanged over the amount realized. Such capital gain or loss generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if, on the date of sale, exchange or other disposition, the common shares were held by the U.S. Holder for more than one year. Net long-term capital gain derived by a non-corporate U.S. Holder with respect to capital assets is currently subject to tax at reduced rates. The deductibility of a capital loss is subject to limitations. Any gain or loss recognized from the sale, exchange or other disposition of common shares will generally be gain or loss from sources within the United States for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes, except as otherwise provided in an applicable income tax treaty and if an election is properly made under the Code.
Passive Foreign Investment Company Considerations
General Rule. In general, a corporation organized outside the United States will be treated as a PFIC in any taxable year in which either (1) at least 75% of its gross income is “passive income” or (2) at least 50% of the average value of its assets is attributable to assets that produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income. Passive income for this purpose generally includes, among other things, dividends, interest, royalties, rents, and gains from commodities transactions and from the sale or exchange of property that gives rise to passive income. Assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income include cash, even if held as working capital or raised in a public offering, marketable securities and other assets that may produce passive income. The percentage of a corporation’s assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income generally is determined based upon the average ratio of passive assets to total assets calculated at the end of each measuring period. Calculation of the value of assets at the end of each measuring period is generally made at the end of each of the four quarters that make up the company’s taxable year, unless an election is made to use an alternative measuring period (such as a week or month). The “weighted average” of those periodic values is then used to determine the value of assets for the passive asset test for the taxable year. In proposed regulations section 1.1297-1(d)(2), a limited exception to the passive asset test valuation rules is provided for the treatment of working capital in order to take into account the short-term cash needs of operating companies. This working capital rule provides that an amount of cash held in a non-interest bearing account that is held for the present needs of an active trade or business and is no greater than the amount reasonably expected to cover 90 days of operating expenses incurred in the ordinary course of the trade or business of the foreign corporation (for example, accounts payable for ordinary operating expenses or employee compensation) is not treated as a passive asset. The Treasury Department and the IRS indicated that they continue to study the appropriate treatment of working capital for purposes of the passive asset test. In determining whether a foreign corporation is a PFIC, a proportionate share of the items of gross income and assets of each corporation in which it owns, directly or indirectly, at least a 25% interest (by value) are taken into account.
PFIC Status Determination. Although the tests for determining PFIC status for any taxable year are dependent upon a number of factors, some of which are beyond our control, including the value of our assets, the market price of our common shares, and the amount and type of our gross income, based on those tests: (i) we believe that we were a PFIC for the taxable year ended December 31, 2016, and (ii) we do not believe that we were a PFIC for any of the taxable years ended thereafter through December 31, 2021. Our status as a PFIC is a fact-intensive determination made on an annual basis, and we cannot provide any assurance regarding our PFIC status for the taxable year ending December 31, 2022 or for subsequent taxable years. U.S. Holders who own our common shares for any period during which we are a PFIC will be required to file IRS Form 8621 for each tax year during which they hold our common shares. No opinion of legal counsel or ruling from the IRS concerning our status as a PFIC has been obtained or is currently planned to be requested. However, the determination of our PFIC status is made annually after the close of each taxable year and it is difficult to predict before such determination whether we will be a PFIC for any given taxable year. Even if we determine that we are not a PFIC after the close of a taxable year, there can be no assurance that the IRS will agree with our conclusion. No assurance can be provided regarding our PFIC status, and neither we nor our United States counsel expresses any opinion with respect to our PFIC status.
PFIC Consequences. If we are a PFIC at any time when a non-corporate U.S. Holder owns common shares, and such U.S. Holder does not make a “qualified electing fund” election (QEF election) or a “mark-to-market” election, both as described below, such U.S. Holder will generally be subject to federal tax under the excess distribution rules (described below). Under such rules, additional taxes and interest charges would apply to certain distributions by us or to gain upon dispositions of our common shares. If neither of such elections are made, the excess distribution rules apply to (1) distributions paid during a taxable year that are greater than 125% of the average annual distributions paid in the three preceding taxable years, or, if shorter, the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares, and (2) any gain recognized on a sale, exchange or other disposition (which would include a pledge or transfer by gift or death) of common shares. Under the excess distribution rules, the non-corporate U.S. Holder’s tax liability will be determined by allocating such distribution or gain ratably to each day in the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares. The amount allocated to the current taxable year (i.e., the year in which the distribution occurs or the gain is recognized) and any year prior to the first taxable year in which we were a PFIC during such holding period will be taxed as ordinary income earned in the current taxable year and the preferential tax rate applicable to capital gains or dividends received on our common shares would not be available. The amount allocated to other taxable years (i.e., prior years in which we were a PFIC) will be taxed at the highest marginal rate in effect (for individuals or corporations as applicable) for ordinary income in each such taxable year, and an interest charge, generally applicable to the underpayment of tax, will be added to the tax and the preferential tax rate applicable to capital gains or dividends received on our common shares would not be available. These adverse tax consequences would not apply to a pension or profit-sharing trust or other tax-exempt organization that did not borrow funds or otherwise utilize leverage in connection with its acquisition of our common shares. In addition, if a non-electing U.S. Holder who is an individual dies while owning our common shares, such U.S. Holder's successor generally would not receive a step-up in tax basis with respect to such common shares, but instead would have a tax basis equal to the lower of the fair market value of such common shares or the decedent’s tax basis in such common shares. Newly proposed regulations, that are not yet effective, address domestic partnerships and S corporations that own stock in a PFIC for which a QEF election or "mark-to-market" election could be made. Currently, only the domestic partnership or S corporation (and not the partners or S corporation shareholders) can make these elections. The proposed regulations would reverse the current rule so that only the partners or S corporation shareholders — not the partnership or S corporation — could make the elections. These proposed regulations would only apply to partnership or S corporation shareholders' tax years beginning on or after the date they are issued in final form.
QEF Election. The tax considerations that would apply if we were a PFIC would be different from those described above if a U.S. Holder were able to make a valid QEF election. For each year that we meet the PFIC gross income test or asset test, an electing U.S. Holder would be required to include in gross income its pro rata share of our ordinary income and net capital gains, if any, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. The U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in our common shares would be increased by the amount of such inclusions. An actual distribution to the U.S. Holder out of such income generally would not be treated as a dividend and would decrease the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in our common shares. Gain realized from the sale of our common shares covered by a QEF election would be taxed as a capital gain and the denial of the basis step-up at death described above would not apply. Generally, a QEF election must be made by the U.S. Holder in a timely filed tax return for the first taxable year in which the U.S. Holder held our common shares that includes the close of our taxable year for which we met the PFIC gross income test or asset test. A separate QEF election would need to be made for any of our subsidiaries that are classified as a PFIC. A QEF election is made on IRS Form 8621. U.S. Holders will be eligible to make QEF elections only if we agree to provide U.S. Holders with the information they will need to comply with the QEF rules. In the event we become a PFIC, we intend to provide all information and documentation that a U.S. Holder making a QEF election is required to obtain for U.S. federal income tax purposes (e.g., the U.S. Holder’s pro rata share of ordinary income and net capital gain, and a “PFIC Annual Information Statement” as described in applicable U.S. Treasury regulations).
Mark-to-Market Election. As an alternative to a QEF election, a U.S. Holder may also mitigate the adverse tax consequences of PFIC status by timely making a “mark-to-market” election, provided the U.S. Holder completes and files IRS Form 8621 in accordance with the relevant instructions and related Treasury regulations. A U.S. Holder who makes the mark-to-market election generally must include as ordinary income each year the increase in the fair market value of the common shares and deduct from gross income the decrease in the value of such shares during each of its taxable years, but with losses limited to the amount of previously recognized net gains. The U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the common shares would be adjusted to reflect any income or loss recognized as a result of the mark-to-market election. If a mark-to-market election with respect to our common shares is in effect on the date of a U.S. Holder’s death, the tax basis of the common shares in the hands of a U.S. Holder who acquired them from a decedent will be the lesser of the decedent’s tax basis or the fair market value of the common shares. Any gain from a sale, exchange or other disposition of the common shares in any taxable year in which we are a PFIC (i.e., when we meet the gross income test or asset test described above) would be treated as ordinary income and any loss from a sale, exchange or other disposition would be treated first as an ordinary loss (to the extent of any net mark-to-market gains previously included in income) and thereafter as a capital loss. If we cease to be a PFIC, any gain or loss recognized by a U.S. Holder on the sale or exchange of the common shares would be classified as a capital gain or loss.
A mark-to-market election is available to a U.S. Holder only for “marketable stock.” Generally, stock will be considered marketable stock if it is “regularly traded” on a “qualified exchange” within the meaning of applicable U.S. Treasury regulations. A class of stock is regularly traded during any calendar year during which such class of stock is traded, other than in de minimis quantities, on at least 15 days during each calendar quarter. The common shares should be marketable stock as long as they are listed on The Nasdaq Capital Market and are regularly traded. A mark-to-market election will not apply to the common shares for any taxable year during which we are not a PFIC but will remain in effect with respect to any subsequent taxable year in which we again become a PFIC. Such election will not apply to any subsidiary that we own. Accordingly, a U.S. Holder may continue to be subject to the PFIC rules with respect to any lower-tier PFICs notwithstanding the U.S. Holder’s mark-to-market election. Whether our common shares are regularly traded on a qualified exchange is an annual determination based on facts that, in part, are beyond our control. Accordingly, a U.S. Holder might not be eligible to make a mark-to-market election to mitigate the adverse tax consequences if we are characterized as a PFIC.
Election Tax Risks. Certain economic risks are inherent in making either a QEF Election or a mark-to-market election. If a QEF Election is made, it is possible that earned income will be reported to a U.S. shareholder as taxable income and income taxes will be due and payable on such an amount. A U.S. shareholder of our common shares may pay tax on such “phantom” income, i.e., where income is reported to it pursuant to the QEF Election, but no cash is distributed with respect to such income. There is no assurance that any distribution or profitable sale will ever be made regarding our common shares, so the tax liability may result in a net economic loss. A mark-to-market election may result in significant share price gains in one year causing a significant income tax liability. This gain may be offset in another year by significant losses. If a mark-to-market election is made, this highly variable tax gain or loss may result in substantial and unpredictable changes in taxable income. The amount included in income under a mark-to-market election may be substantially greater than the amount included under a QEF election. Both the QEF and mark-to-market elections are binding on the U.S. shareholder for all subsequent years that the U.S. shareholder owns our shares unless permission to revoke the election is granted by the IRS.
Purging Election. If we are a PFIC at any time when a U.S. Holder holds our common shares, we will generally continue to be treated as a PFIC with respect to the U.S. Holder for all succeeding years during which the U.S. Holder holds our common shares even if we cease to meet the PFIC gross income test or asset test in a subsequent year. However, if we cease to meet these tests, a U.S. Holder can avoid the continuing impact of the PFIC rules by making a special election (a Purging Election) to recognize gain by making a “deemed sale” election with respect to all of the U.S. Holder’s common shares and have such common shares deemed to be sold at their fair market value on the last day of the last taxable year during which we were a PFIC. The shareholder makes a purging election under Code section 1298(b)(1) and regulations section 1.1298–3 on IRS Form 8621 attached to the shareholder’s tax return (including an amended return), or requests the consent of the IRS Commissioner to make a late election under Code section 1298(b)(1) and regulations section 1.1298–3(e) (late purging election) on Form 8621-A. In addition, for a U.S. Holder making such an election, a new holding period would be deemed to begin for our common shares for purposes of the PFIC rules. After the Purging Election, the common shares with respect to which the Purging Election was made will not be treated as shares in a PFIC unless we subsequently again become a PFIC.
Each U.S. person who is a shareholder of a PFIC generally must file an annual report (on IRS Form 8621) with the IRS containing certain information, and the failure to file such report could result in the imposition of penalties on such U.S. person and in the extension of the statute of limitations with respect to federal income tax returns filed by such U.S. person. Should we be classified as a PFIC during a U.S. Holder’s holding period for our common shares, each such U.S. Holder should consult their own tax advisors with respect to the possibility of making these elections and the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of our common shares. In addition, the possibility of us being classified as a PFIC may deter certain U.S. investors from purchasing our common shares, which could have an adverse impact on the market price of our common shares and our ability to raise additional financing by selling equity securities, including our common shares.
The U.S. federal income tax rules relating to PFICs are very complex. U.S. Holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors with respect to the purchase, ownership and disposition of common shares, the consequences to them of an investment in a PFIC, any elections available with respect to the common shares and the IRS information reporting obligations with respect to the purchase, ownership and disposition of common shares in the event we are considered a PFIC.
Additional Tax on Passive Income
Certain U.S. Holders that are individuals, estates or trusts (other than trusts that are exempt from tax) with adjusted income exceeding certain thresholds, will be subject to a 3.8% tax on all or a portion of their “net investment income,” which includes dividends on the common shares, and net gains from the disposition of the common shares. Further, excess distributions treated as dividends, gains treated as excess distributions, and mark-to-market inclusions and deductions are all included in the calculation of net investment income.
Treasury regulations provide, subject to the election described in the following paragraph, that solely for purposes of this additional tax, that distributions of previously taxed income will be treated as dividends and included in net investment income subject to the additional 3.8% tax. Additionally, to determine the amount of any capital gain from the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares that will be subject to the additional tax on net investment income, a U.S. Holder who has made a QEF election will be required to recalculate its basis in the common shares excluding any QEF election basis adjustments.
Alternatively, a U.S. Holder may make an election which will be effective with respect to all interests in controlled foreign corporations and PFICs that are subject to a QEF election and that are held in that year or acquired in future years. Under this election, a U.S. Holder pays the additional 3.8% tax on QEF election income inclusions and on gains calculated after giving effect to related tax basis adjustments. U.S. Holders that are individuals, estates or trusts should consult their own tax advisors regarding the applicability of this tax to any of their income or gains in respect of the common shares.
U.S. Federal Income Taxation of Non-U.S. Holders
A beneficial owner of our common shares, other than a partnership or entity treated as a partnership for U.S. Federal income tax purposes, that is not a U.S. Holder is referred to herein as a “Non-U.S. Holder”. Non-U.S. Holders generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax or withholding tax on dividends received from us with respect to our common shares, unless that income is effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business in the United States. In general, if the Non-U.S. Holder is entitled to the benefits of certain U.S. income tax treaties with respect to those dividends, that income is taxable only if it is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the Non-U.S. Holder in the United States.
Non-U.S. Holders generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax or withholding tax on any gain realized upon the sale, exchange or other disposition of our common shares, unless:
| ● |
the gain is effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business in the United States. In general, if the Non-U.S. Holder is entitled to the benefits of certain income tax treaties with respect to that gain, that gain is taxable only if it is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the Non-U.S. Holder in the United States; or |
| ● |
the Non-U.S. Holder is an individual who is present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year of disposition and other conditions are met. |
If the Non-U.S. Holder is engaged in a U.S. trade or business for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the income from the common shares, including dividends and the gain from the sale, exchange or other disposition of the stock, that is effectively connected with the conduct of that trade or business will generally be subject to regular U.S. federal income tax in the same manner as discussed above relating to the general taxation of U.S. Holders. In addition, if you are a corporate Non-U.S. Holder, your earnings and profits that are attributable to the effectively connected income, which are subject to certain adjustments, may be subject to an additional branch profits tax at a rate of 30%, or at a lower rate as may be specified by an applicable U.S. income tax treaty.
Information Reporting with Respect to Foreign Financial Assets
U.S. individuals that own “specified foreign financial assets” (as defined in Section 6038D of the Code) with an aggregate fair market value exceeding certain threshold amounts generally are required to file an information report on IRS Form 8938 with respect to such assets with their tax returns. Significant penalties may apply to persons who fail to comply with these rules. Specified foreign financial assets include not only financial accounts maintained in foreign financial institutions, but also, unless held in accounts maintained by certain financial institutions, any stock or security issued by a non-U.S. person, such as our common shares. Upon the issuance of future U.S. Treasury regulations, these information reporting requirements may apply to certain U.S. entities that own specified foreign financial assets. The failure to report information required under the current regulations could result in substantial penalties and in the extension of the statute of limitations with respect to federal income tax returns filed by a U.S. Holder. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the possible implications of these U.S. Treasury regulations for an investment in our common shares.
Special Reporting Requirements for Transfers to Foreign Corporations
A U.S. Holder that acquires common shares generally will be required to file IRS Form 926 with the IRS if (1) immediately after the acquisition such U.S. Holder, directly or indirectly, owns at least 10% of our common shares, or (2) the amount of cash transferred in exchange for common shares during the 12-month period ending on the date of the acquisition exceeds USD $100,000. Significant penalties may apply for failing to satisfy these filing requirements. U.S. Holders are urged to contact their tax advisors regarding these filing requirements.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
Dividends on and proceeds from the sale or other disposition of common shares may be reported to the IRS unless the U.S. Holder establishes a basis for exemption. Backup withholding may apply to amounts subject to reporting if (1) the U.S. holder fails to provide an accurate taxpayer identification number or otherwise establish a basis for exemption, (2) the U.S. Holder is notified by the IRS that backup withholding applies, or (3) the payment is described in certain other categories of persons.
If you sell your common shares through a U.S. office of a broker, the payment of the proceeds is subject to both U.S. backup withholding and information reporting unless you certify that you are a non-U.S. person, under penalties of perjury, or you otherwise establish an exemption. If you sell your common shares through a non-U.S. office of a non-U.S. broker and the sales proceeds are paid to you outside the United States, then information reporting and backup withholding generally will not apply to that payment. However, U.S. information reporting requirements, but not backup withholding, will apply to a payment of sales proceeds, even if that payment is made to you outside the United States, if you sell your common shares through a non-U.S. office of a broker that is a U.S. person or has certain other contacts with the United States, unless you certify that you are a non-U.S. person, under penalty of perjury, or you otherwise establish an exemption.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules generally will be allowed as a refund or a credit against a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability if the required information is furnished by the U.S. Holder on a timely basis to the IRS.
THE DISCUSSION ABOVE IS A GENERAL SUMMARY. IT DOES NOT COVER ALL TAX MATTERS THAT MAY BE OF IMPORTANCE TO A U.S. HOLDER. EACH U.S. HOLDER IS URGED TO CONSULT ITS OWN TAX ADVISOR ABOUT THE TAX CONSEQUENCES TO IT OF AN INVESTMENT IN COMMON SHARES IN LIGHT OF THE INVESTOR’S OWN CIRCUMSTANCES.
Item 6. [Reserved]
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations is based upon accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and discusses the financial condition and results of operations for DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. and subsidiaries for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020.
This discussion should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this report. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve numerous risks and uncertainties. Our actual results could differ materially from the forward-looking statements as a result of these risks and uncertainties. See “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” for additional cautionary information.
Business Overview
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company committed to improving the lives of people suffering from serious diseases. DiaMedica’s lead candidate DM199 is the first pharmaceutically active recombinant (synthetic) form of the human tissue kallikrein-1 (KLK1) protein to be studied in patients, an established therapeutic modality for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke and chronic kidney disease. Our goal is to use our patented and in-licensed technologies to establish our Company as a leader in the development and commercialization of therapeutic treatments from novel recombinant proteins. Our current focus is on the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). We plan to advance DM199, our lead drug candidate, through required clinical trials to create shareholder value by establishing its clinical and commercial potential as a therapy for AIS and CKD.
DM199 is a recombinant form of human tissue kallikrein-1 (KLK1). KLK1 is a serine protease (protein) produced primarily in the kidneys, pancreas and salivary glands, which plays a critical role in the regulation of local blood flow and vasodilation (the widening of blood vessels which decreases vascular resistance) in the body, as well as an important role in inflammation and oxidative stress (an imbalance between potentially damaging reactive oxygen species, or free radicals, and antioxidants in your body). We believe DM199 has the potential to treat a variety of diseases where healthy functioning requires sufficient activity of KLK1 and its system, the kallikrein-kinin system (KKS).
Our product development pipeline is as follows:
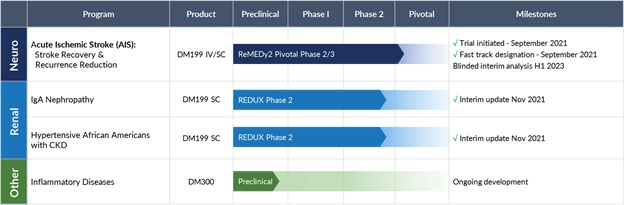
Current Clinical Trials
AIS Phase 2/3 ReMEDy2 Trial
Our ReMEDy2 trial is an adaptive design, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial intended to enroll approximately 350 patients at 75 sites in the United States. Patients enrolled in the trial will be treated with either DM199 or placebo within 24 hours of the onset of AIS symptoms. The trial excludes patients treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and those with large vessel occlusions. The study population is representative of the approximately 80% of AIS patients who do not have treatment options today, primarily due to the limitations on treatment with tPA or mechanical thrombectomy. DiaMedica believes that the proposed trial has the potential to serve as a pivotal registration study of DM199 in this patient population.
In April 2021, we submitted an Investigational New Drug (IND) application to the FDA for the trial, which was accepted in May 2021. In September 2021, the FDA granted Fast Track Designation to the Company’s lead candidate DM199 for the treatment of AIS where tPA and/or mechanical thrombectomy are not indicated or medically appropriate.
We initiated the first site for the Phase 2/3 trial in September and successfully dosed the first patient in November 2021. Additionally, in November 2021, the FDA accepted and concluded that DiaMedica “may proceed” with the proposed clinical investigation using our amended protocol adding stroke recurrence as a second independent primary endpoint to our Phase 2/3 ReMEDy2 trial. The FDA’s acceptance of the amendment allows the Company to evaluate the effects of DM199 on both physical recoveries post AIS and the rate of recurrent AIS, as two separate, independent, primary endpoints, with each statistically powered for success. There were no changes in treatment, duration, or study population of the trial as part of this protocol amendment.
Dosing the first patient in the ReMEDy2 trial triggered a $185,000 milestone payment due to Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC (Catalent) which was remitted during the fourth quarter of 2021. See Note 10 titled “Commitments and Contingencies” included elsewhere in this report.
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and the resurgence in cases caused by the Delta, Omicron and other variants, some clinical trials are experiencing delays and stoppages in site activations and enrollment due to staffing and other resource shortages. We have experienced slower than expected site activations and enrollment in our ReMEDy2 trial due to the reduction or suspension of activities and staffing shortages at our and/or potential clinical study sites. We anticipate that the continuing development of variants of COVID-19, will likely continue to adversely affect our ability to initiate new clinical trial sites and recruit or enroll patients into our ReMEDy2 trial, and we cannot provide any assurance as to when these issues will resolve.
CKD Phase 2 REDUX Clinical Trial
As of December 31, 2021, we completed enrollment in our Phase 2 clinical trial for the treatment of CKD with a total of 79 subjects enrolled, including 21 African American subjects into Cohort 1, 25 subjects with IgAN into Cohort 2 and 33 subjects with Type 2 diabetes in Cohort 3.
The trial named REDUX, Latin for restore, is a multi-center, open-label investigation which targeted enrollment of patients with mild or moderate CKD (Stage II or III) and albuminuria, enrolled in three equal cohorts. The trial was conducted in the United States and was focused on participants with CKD: Cohort 1 was focused on non-diabetic, hypertensive African Americans (AA) with Stage II or III CKD. African Americans are at greater risk for CKD than Caucasians, and those African Americans who have the APOL1 gene mutation are at an even higher risk. Cohort 2 was focused on participants with IgA Nephropathy. Cohort 3 was focused on participants with Type 2 diabetes mellitus with CKD, hypertension and albuminuria (DKD). The trial evaluated two dose levels of DM199 within each cohort. Study participants received DM199 by subcutaneous injection twice weekly for 95 days. The primary study endpoints include safety, tolerability, blood pressure, albuminuria and kidney function, which were evaluated by changes from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria, as measured by the urinary albumin to creatinine ratio. Participant enrollment and dosing for this trial commenced in December 2019 and in June 2021, we announced interim results and in November, we announced additional results.
REDUX is a multi-center, open-label investigation of with interim results indicating that DM199 is demonstrating clinically meaningful improvements in kidney function in Cohorts 1 and 2, as measured by simultaneously stabilizing estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and decreasing urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR). Additionally, in patients who were hypertensive (Cohorts 1 and 3), DM199 also reduced blood pressure by clinically significant levels and importantly, there was no effect on participants who were not hypertensive (Cohort 2). We reported the following preliminary data:
| ● |
AA: Geometric mean decrease in UACR of -55% in moderate to severe albuminuria (baseline UACR >500 µg/mg) (n=3), Stable eGFR from baseline (n=12) and a mean decrease in systolic/diastolic blood pressure -19/-13 mmHg (n=8) at the 2 µg/kg dose level; |
| ● |
IgAN: UACR geometric mean decrease of -34% (p=0.002) (baseline UACR>500 µg/mg) (n=11), eGFR and blood pressure were stable (n=16) and mean decreases in the biomarkers April and IgA1 of 35% and 22% overall, respectively; and |
| ● |
DKD: No overall treatment effect was observed for UACR, however, reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (n=28) were observed. |
DM199 was generally safe and well tolerated across all cohorts. Adverse events (AEs) were generally mild to moderate in severity, with the most common being local injection site irritation that resolved without medical intervention.
DM300
We have identified a potential novel new treatment for inflammatory diseases, DM300, currently in the pre-clinical stage of development.
Financial Overview
We have not generated any revenues from product sales. Since our inception, we have financed our operations from public and private sales of equity, the exercise of warrants and stock options, interest income on funds available for investment and government grants and tax credits. We have incurred losses in each year since our inception. Our net losses were $13.6 million and $12.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. As of December 31, 2021, we had an accumulated deficit of $82.5 million. Substantially all of our operating losses resulted from expenses incurred in connection with our product candidate development programs, our primary R&D activities, and general and administrative (G&A) support costs associated with our operations.
We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increased operating losses for at least the next several years. In the near term, we anticipate that our expenses will increase as compared to prior periods as we:
| ● |
continue site activation and enrollment of subjects in our pivotal ReMEDy2 Phase 2/3 trial of DM199 for AIS; |
|
| ● |
complete patient follow-up in our REDUX Phase 2 trial of DM199 for CKD; |
|
| ● |
expand our team to provide support for our operations; and |
|
| ● |
maintain, expand and protect our intellectual property portfolio. |
While we expect our rate of future negative cash flow per month will vary due to the timing of site activation and patient enrollment expenses, we expect our current cash resources will be sufficient to allow us to continue our ReMEDy2 Phase 2/3 trial in patients with AIS, complete patient follow-up in our REDUX Phase 2 trial in patients with CKD, and otherwise fund our planned operations for at least the next twelve months from the date of issuance of the consolidated financial statements included in this report. However, the amount and timing of future funding requirements will depend on many factors, including the timing and results of our ongoing development efforts, including site activations and enrollment in our clinical studies, the potential expansion of our current development programs, potential new development programs, related G&A support and the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. We may require significant additional funds earlier than we currently expect and there is no assurance that we will not need or seek additional funding prior to such time. We may elect to raise additional funds even before we need them if market conditions for raising additional capital are favorable.
Components of Our Results of Operations
Research and Development Expenses
R&D expenses consist primarily of fees paid to external service providers such as contract research organizations (CROs); contractual obligations for clinical development including clinical site costs, outside nursing services, laboratory testing, preclinical trials; development of manufacturing processes; costs for production runs of DM199; salaries, benefits and share-based compensation and other personnel costs. Over the past approximately ten years, our R&D efforts have been primarily focused on developing DM199. At this time, due to the risks inherent in the clinical development process and the clinical stage of our product development programs, we are unable to estimate with any certainty the costs we will incur in the continued development of DM199 or any of our preclinical development programs. The process of conducting clinical studies necessary to obtain regulatory approval and manufacturing scale-up to support expanded development and potential future commercialization is costly and time consuming. Any failure by us or delay in completing clinical studies, manufacturing scale-up or in obtaining regulatory approvals could lead to increased R&D expenses and, in turn, have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
General and Administrative Expenses
G&A expenses consist primarily of salaries and related benefits, including share-based compensation related to our executive, finance, business development and support functions. G&A expenses also include insurance, including directors and officers liability coverage, rent and utilities, travel expenses, patent costs, professional fees, including for auditing, tax and legal services and milestone payments under our technology license agreement with Catalent.
Other Income, Net
Other (income) expense consists primarily of interest income and foreign currency exchange gains and losses. In past years, governmental assistance – research incentives, which were associated with the ReMEDy1 Phase 2 stroke trial, were a significant component of this line item.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions for the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses and related disclosures. Our estimates are based on our historical experience and on various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions and any such differences may be material.
While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 3 to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report, we believe the following discussion addresses our most critical accounting policies, which are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results of operations and require our most difficult, subjective and complex judgments.
Research and Development Costs
R&D costs include expenses incurred in the conduct of human clinical trials, for third-party service providers performing various treatment, testing and data accumulation and analysis related to these clinical studies; non-clinical research studies; developing the manufacturing process necessary to produce sufficient amounts of the DM199 compound for use in our clinical studies; consulting resources with specialized expertise related to execution of our development plan for our DM199 product candidate; and personnel costs, including salaries, benefits and share-based compensation.
We charge R&D costs, including clinical trial costs, to expense when incurred. Our human clinical trials are performed at clinical trial sites and are generally administered by us with assistance from CROs, and include outside service providers such as outside nursing services, testing laboratories and data coordination and collection. Costs of setting up clinical trial sites are accrued upon execution of the trial agreement. Expenses related to the performance of clinical trials are accrued based on contracted amounts and the achievement of agreed upon milestones, such as patient enrollment, patient follow-up, etc. We monitor levels of performance under each significant contract, including the extent of patient enrollment and other activities through communications with the clinical trial sites, CROs and supporting vendors and adjust the estimates, if required, on a quarterly basis so that clinical expenses reflect the actual work performed at each clinical trial site and by each CRO or supporting vendor.
Clinical Trial Costs
Our clinical trials are performed at clinical trial sites and are administered by us with assistance from CROs or outside contractors as necessary. Clinical trial costs are recorded or accrued based on actual invoices received and estimates of work completed to date by CROs, outside contractors and clinical trial sites that manage and perform the trials. We obtain initial estimates of accrued costs based on the trial protocol and actual enrollment of subjects, trial duration, project and data management costs, patient treatment costs and other activities as required by the trial protocol. Additionally, non-patient related costs may be charged to us and are recognized as the tasks are completed by the clinical trial site. Accrued clinical trial costs may be subject to revisions as clinical trials progress and any revisions are recorded in the period in which the facts that give rise to the revisions become known.
Share-based Compensation
We account for all share-based compensation awards using a fair value method. The cost of employee and non-employee services received in exchange for awards of equity instruments is measured and recognized based on the estimated grant date fair value of those awards. Compensation cost is recognized ratably using the straight-line attribution method over the vesting period, which is considered to be the requisite service period. We record forfeitures in the periods in which they occur.
The fair value of share-based awards is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The determination of the fair value of share-based awards is affected by our common share price, as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. Risk-free interest rates are based upon United States Government bond rates appropriate for the expected term of each award. Expected volatility rates are based on the historical volatility equal to the expected life of the option. The assumed dividend yield is zero, as we do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future. The expected term of options is estimated considering the vesting period at the grant date, the life of the option and the average length of time similar grants have remained outstanding in the past.
The assumptions used in calculating the fair value under the Black-Scholes option valuation model are set forth in the following table for options issued by us for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| 2021 |
2020 |
|||||||||
| Common share fair value |
$3.64 |
– | $10.04 | $4.08 |
– | $6.91 | ||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
0.5 | – | 1.3% | 0.3 | – | 1.3% | ||||
| Expected dividend yield |
0% | 0% | ||||||||
| Expected option life (in years) |
5.0 | – | 5.5 | 5.0 | – | 5.2 | ||||
| Expected stock price volatility |
94.7 | – | 106.1% | 94.4 | – | 102.2% | ||||
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2021 and 2020
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 (in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2021 |
2020 |
|||||||
| Research and development expense |
$ | 8,765 | $ | 8,205 | ||||
| General and administrative expense |
4,881 | 4,494 | ||||||
| Other income, net |
(82 | ) | (434 | ) | ||||
Research and Development Expenses
R&D expenses increased slightly to $8.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, up from $8.2 million in the prior year. This increase was primarily due to a combination of costs incurred for our pivotal Phase 2/3 ReMEDy2 trial and increased personnel costs associated with adding staff to support R&D operations. This increase was partially offset by decreased costs incurred for our earlier ReMEDy1 Phase 2 trial, which completed during 2020, and decreased costs for our REDUX trial, as the number of enrollments in the REDUX trial declined throughout 2021 as the study neared completion. We expect that our R&D expenses will increase in the future as compared to prior periods as sites are activated and enrollment increases in the ReMEDy2 trial and as we incur costs to support the conduct of the ReMEDy2 trial.
General and Administrative Expenses
G&A expenses were $4.9 million and $4.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. This increase was due to a number of factors including increased costs associated with professional services, the payment to Catalent of a milestone obligation under our technology license agreement with Catalent, increased directors and officers liability insurance costs and increased personnel costs to support our expanding clinical programs. These increases were partially offset by reduced non-cash, share based compensation costs. We did not incur significant additional G&A expenses during the year ended December 31, 2021 related to the COVID-19 pandemic, nor do we expect to incur significant additional G&A expenses related to the COVID-19 pandemic going forward. We expect our G&A expenses will continue to increase in the future as compared to prior periods as we expand our development and operating activities.
Other Income, Net
Other income, net, was $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $0.4 million for 2020. This decrease was driven primarily by cessation of R&D incentive receivables from the Australian Government, paid for qualifying research work performed by our Australian subsidiary as the ReMEDy1 trial completed in 2020 and no costs were incurred for the ReMEDy1 trial during 2021. In addition, decreased interest income recognized during 2021 as compared to 2020 related to lower interest rates also contributed to the decrease.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The following tables summarize our liquidity and capital resources as of December 31, 2021 and 2020 and cash flows for each of the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, and are intended to supplement the more detailed discussion that follows (in thousands):
| Liquidity and Capital Resources |
December 31, 2021 |
December 31, 2020 |
||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities |
$ | 45,112 | $ | 27,507 | ||||
| Total assets |
45,551 | 28,095 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities |
1,524 | 2,028 | ||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity |
44,024 | 26,014 | ||||||
| Working capital |
43,915 | 25,893 | ||||||
| Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| Cash Flow Data |
2021 |
2020 |
||||||
| Cash flow provided by (used in): |
||||||||
| Operating activities |
$ | (12,252 | ) | $ | (9,185 | ) | ||
| Investing activities |
(20,537 | ) | (16,134 | ) | ||||
| Financing activities |
30,087 | 28,845 | ||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash |
$ | (2,702 | ) | $ | 3,526 | |||
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We had cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities of $45.1 million, current liabilities of $1.5 million and working capital of $43.9 million as of December 31, 2021, compared to $27.5 million in cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities, $2.0 million in current liabilities and $25.9 million in working capital as of December 31, 2020. The increases in our combined cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities and in our working capital were due to net proceeds from our September 2021 private placement, partially offset by cash used in operating activities during 2021.
On September 26, 2021, we issued and sold in a private placement an aggregate of 7,653,060 common shares at a purchase price of $3.92 per share to ten accredited investors, resulting in gross proceeds of $30.0 million and net proceeds to us of $29.8 million, after deducting offering expenses.
Cash Flows
Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2021 was $12.3 million compared to $9.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase relates primarily to the combination of the increase in the net loss and the effects of changes in operating assets and liabilities during 2021.
Investing Activities
Investing activities consist primarily of the net purchases of marketable securities. Net cash used in investing activities was $20.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $16.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase was primarily due to the investment of the net proceeds received in the September 2021 private placement in short-term marketable securities, partially offset by an increase in the maturities of marketable securities during 2021.
Financing Activities
Financing activities consist primarily of net proceeds from the sale of our common shares. Net cash provided by financing activities increased slightly to $30.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, up from $28.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase was due to greater net proceeds received from our September 2021 private placement as compared to the net proceeds received from our February 2020 and August 2020 public offerings, which involved customary underwriting fees and discounts.
Capital Requirements
Since our inception, we have incurred losses while advancing the R&D of our DM199 product candidate. We have not generated any revenues from product sales and do not expect to do so for at least three to five years. We do not know when or if, we will generate any revenues from product sales of our DM199 product candidate or any future product candidate. We do not expect to generate any revenue from product sales unless and until we obtain regulatory approval. We expect to continue to incur substantial operating losses until such time as any future product sales, royalty payments, licensing fees and/or milestone payments are sufficient to generate revenues to fund our continuing operations. We expect our operating losses to increase in the near term as compared to prior periods as we continue the research, development and clinical studies of, and seek regulatory approval for, our DM199 product candidate. In the long-term, subject to obtaining regulatory approval of our DM199 product candidate or any future product candidate, and in the absence of the assistance of a strategic partner, we expect to incur significant commercialization expenses for product sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution.
Accordingly, and notwithstanding the receipt of $29.8 million in net proceeds from our September 2021 private placement, we expect we will need substantial additional capital to further our R&D activities, planned clinical studies, regulatory activities and otherwise develop our product candidate, DM199, or any future product candidates, to a point where they may be commercially sold. Although we are striving to achieve these plans, there is no assurance these and other strategies will be achieved or that additional funding will be obtained on favorable terms or at all. While we expect our rate of future negative cash flow per month will vary due to our clinical activities and the timing of expenses incurred, we expect our current cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities resources will be sufficient to allow us to continue our ReMEDy2 Phase 2/3 trial in patients with AIS, complete patient follow-up in our REDUX Phase 2 trial in patients with CKD, and otherwise fund our planned operations for at least the next twelve months from the date of issuance of the consolidated financial statements included in this report. However, the amount and timing of future funding requirements will depend on many factors, including the timing and results of our ongoing development efforts, including the initiation of new sites and enrollment in our clinical studies, the potential expansion of current development programs, potential new development programs, the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on our clinical programs and operations, and related G&A support. We may require significant additional funds earlier than we currently expect and there is no assurance that we will not need or seek additional funding prior to such time, especially if market conditions for raising additional capital are favorable.
Since our inception, we have financed our operations from public and private sales of equity, the exercise of warrants and stock options, interest income on funds available for investment, and government incentive grants, and we expect to continue this practice for the foreseeable future. We do not have any existing credit facilities under which we could borrow funds. We may seek to raise additional funds through various sources, such as equity or debt financings, or through strategic collaborations and license agreements. We can give no assurances that we will be able to secure additional sources of funds to support our operations, or if such funds are available to us, that such additional financing will be sufficient to meet our needs or on terms acceptable to us. This is particularly true if our clinical data is not positive or economic and market conditions deteriorate.
To the extent we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interests of our shareholders will be diluted. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include conversion discounts or covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through government or other third-party funding, marketing and distribution arrangements or other collaborations, or strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. The availability of financing will be affected by our clinical data and other results of scientific and clinical research; the ability to attain regulatory approvals; market acceptance of our product candidates; the state of the capital markets generally with particular reference to pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical companies; the status of strategic alliance agreements; and other relevant commercial considerations.
If adequate funding is not available when needed, we may be required to scale back our operations by taking actions that may include, among other things, implementing cost reduction strategies, such as reducing use of outside professional service providers, reducing the number of our employees or employee compensation, modifying or delaying the development of our DM199 product candidate; licensing to third parties the rights to commercialize our DM199 product candidate for AIS, CKD or other indications that we would otherwise seek to pursue, or otherwise relinquishing significant rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or granting licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us; and/or divesting assets or ceasing operations through a merger, sale, or liquidation of our company.
Commitments and Contingencies
In the normal course of business, we incur obligations to make future payments as we execute our business plan. These obligations may relate to preclinical or clinical studies, manufacturing or manufacturing process development and other related activities. Currently, these obligations include costs to be incurred with contract research organizations, central laboratory and pharmacy services, clinical study sites, home nursing services and various other vendors supporting the performance of our clinical trials. The contracts we enter into with these vendors and the commitments within these contracts are subject to significant variability based upon the actual activities/services performed by each vendor. As a result, the ultimate amounts due may be materially different as these obligations are affected by, among other factors, the number and pace of patients enrolled, the number of clinical study sites enrolling subjects, the amount of time to complete trial enrollments and the time required to finalize, analyze and report of trial results. Clinical research agreements are generally cancelable upon up to 60 days’ notice, with the Company’s obligation limited to costs incurred up to that date, including any non-cancelable costs. Cancelation terms for product manufacturing and process development contracts vary and are generally dependent upon timelines for sourcing research materials and reserving laboratory time. As of December 31, 2021, the Company estimates that its outstanding commitments, including such cancellable contracts, are approximately $6.0 million over the next 12 months and $6.9 million in the following 12 months.
As of December 31, 2021, we had future operating lease commitments totaling approximately $45,000 over the remainder of the lease, of which the entirety is due over the next 12 months.
We have entered into a license agreement with Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC (Catalent) whereby we have licensed certain gene expression technology and we contract with Catalent for the manufacture of DM199. Under the terms of this license, certain milestone and royalty payments may become due under this agreement and are dependent upon, among other factors, clinical trials, regulatory approvals and ultimately the successful development of a new drug, the outcome and timing of which is uncertain. During fourth quarter of 2021, we remitted a milestone payment of $185,000 due upon the initiation of dosing in our ReMEDy2 pivotal trial of DM199 in AIS. As of December 31, 2021, one milestone payment obligation remains, $185,000 due upon our first regulatory approval of DM199 for commercial sale. Following the launch of our first product, we will also incur a royalty of less than 1% on net sales. The royalty term is indefinite but the license agreement may be canceled by us on 90 days’ prior written notice. The license may not be terminated by Catalent unless we fail to make required milestone and royalty payments.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
This Item 7A is inapplicable to DiaMedica as a smaller reporting company and has been omitted pursuant to Item 305(e) of SEC Regulation S-K.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB Firm ID |
89 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020 |
90 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 |
91 |
| Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 |
92 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 |
93 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
94-108 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. and Subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for the years then ended, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board of the United States of America (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/
We have served as the Company’s auditors since 2018.
March 14, 2022
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share amounts)
| December 31, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | $ | ||||||
| Marketable securities | ||||||||
| Amounts receivable | ||||||||
| Deposits | ||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | ||||||||
| Total current assets | ||||||||
| Non-current assets: | ||||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use asset | ||||||||
| Property and equipment, net | ||||||||
| Total non-current assets | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | $ | ||||||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | $ | ||||||
| Accrued liabilities | ||||||||
| Finance lease obligation | ||||||||
| Operating lease obligation | ||||||||
| Total current liabilities | ||||||||
| Non-current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Finance lease obligation, non-current | ||||||||
| Operating lease obligation, non-current | ||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | ||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | ||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity: | ||||||||
| Common shares, par value; authorized; and shares issued and outstanding, as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively | ||||||||
| Paid-in capital | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accumulated deficit | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | ||||||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | $ | ||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Research and development | $ | $ | ||||||
| General and administrative | ||||||||
| Total operating expenses | ||||||||
| Operating loss | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Other income: | ||||||||
| Other income, net | ||||||||
| Governmental assistance - research incentives | ||||||||
| Total other income, net | ||||||||
| Loss before income tax expense | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Income tax expense | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net loss | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Other comprehensive loss | ||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net loss and comprehensive loss | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
| Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity
(In thousands, except share amounts)
| Common Shares | Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Gain (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total Shareholders’ Equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2019 | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares, net of offering costs of $ | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of common stock options | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities | — | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2020 | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares, net of offering costs of $ | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of common stock options | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares in settlement of deferred stock units | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities | — | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2021 | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands, except share amounts)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Share-based compensation | ||||||||
| Amortization of discount on marketable securities | ( | ) | ||||||
| Non-cash lease expense | ||||||||
| Depreciation | ||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Amounts receivable | ||||||||
| Deposits | ( | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Accounts payable | ( | ) | ||||||
| Accrued liabilities | ( | ) | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||
| Purchase of marketable securities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Maturities of marketable securities | ||||||||
| Purchase of property and equipment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Disposition of property and equipment, net | ||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common shares, net of offering costs | ||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | ||||||||
| Principal payments on finance lease obligations | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | ||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | ( | ) | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | $ | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | ||||||||
| Cash paid for income taxes | $ | $ | ||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Business
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, DiaMedica USA, Inc. and DiaMedica Australia Pty Ltd. (collectively we, us, our, DiaMedica and the Company), exist for the primary purpose of advancing the clinical and commercial development of a proprietary recombinant KLK1 protein for the treatment of neurological and kidney diseases. Currently, our primary focus is on acute ischemic stroke (AIS) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Our parent company is governed under British Columbia’s Business Corporations Act, and our common shares are publicly traded on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “DMAC.”
2. Risks and Uncertainties
DiaMedica operates in a highly regulated and competitive environment. The development, manufacturing and marketing of pharmaceutical products require approval from, and are subject to ongoing oversight by, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the European Union and comparable agencies in other countries. We are in the clinical stage of development of our initial product candidate, DM199, for the treatment of AIS and CKD. The Company has not completed the development of any product candidate and does not generate any revenues from the commercial sale of any product candidate. DM199 requires significant additional clinical testing and investment prior to seeking marketing approval and is not expected to be commercially available for at least three to four years, if at all. Additionally, clinical testing has been adversely impacted by the surge in the Delta and other variants of the COVID-19 virus. We have experienced slower than expected site activations and enrollment in our clinical trials due to the reduction or suspension of activities at our clinical study sites, staffing shortages and patient concerns related to visiting clinical study sites. We anticipate that the continuing development of variants of COVID-19 will likely continue to adversely affect our ability to recruit or enroll patients and initiate new clinical trial sites, and we cannot provide any assurance as to when these issues will resolve. The Company’s future success is dependent upon the success of its development efforts, its ability to demonstrate clinical progress for its DM199 product candidate in the United States or other markets, its ability to obtain required governmental approvals of its product candidate, its ability to license or market and sell its DM199 product candidate and its ability to obtain additional financing to fund these efforts.
As of December 31, 2021, we have incurred losses of $
Our principal sources of cash have included net proceeds from the issuance of our equity securities. See Note 11 titled “Shareholders’ Equity” for additional information. Although the Company has previously been successful in obtaining financing through equity securities offerings, there is no assurance that we will be able to do so in the future. This is particularly true if our clinical data is not positive or economic and market conditions deteriorate.
Notwithstanding the completion of our September 2021 private placement in which we received net proceeds of $
3. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the assets, liabilities and expenses of DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc., and our wholly-owned subsidiaries, DiaMedica USA, Inc. and DiaMedica Australia Pty Ltd. All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
Functional currency
The United States dollar is our functional currency as it represents the economic effects of the underlying transactions, events and conditions and various other factors including the currency of historical and future expenditures and the currency in which funds from financing activities are mostly generated by the Company. A change in the functional currency occurs only when there is a material change in the underlying transactions, events and condition. A change in functional currency could result in material differences in the amounts recorded in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss for foreign exchange gains and losses. All amounts in the accompanying consolidated financial statements are in U.S. dollars unless otherwise indicated.
Use of estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and the accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all bank deposits, including money market funds, and other investments, purchased with an original maturity to the Company of three months or less, to be cash and cash equivalents. The carrying amount of our cash equivalents approximates fair value due to the short maturity of the investments.
Marketable securities
The Company’s marketable securities typically consist of obligations of the United States government and its agencies, bank certificates of deposit and investment grade corporate obligations, which are classified as available-for-sale and included in current assets. All marketable securities mature within twelve months from their date of purchase and generally are intended to fund current operations. Securities are valued based on market prices for similar assets using third party certified pricing sources. Available-for-sale securities are carried at fair value with unrealized gains and losses reported as a component of shareholders’ equity in accumulated other comprehensive gain (loss). The amortized cost of debt securities is adjusted for amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts to maturity. Such amortization or accretion is included in interest income. Realized gains and losses, if any, are calculated on the specific identification method and are included in other income in the consolidated statements of operations.
Available-for-sale securities are reviewed for possible impairment at least quarterly, or more frequently if circumstances arise that may indicate impairment. When the fair value of the securities declines below the amortized cost basis and impairment is indicated, it must be determined whether the impairment is other than temporary. Impairment is considered to be other than temporary if the Company: (i) intends to sell the security, (ii) will more likely than not be forced to sell the security before recovering its cost, or (iii) does not expect to recover the security’s amortized cost basis. If the decline in fair value is considered other than temporary, the cost basis of the security is adjusted to its fair market value and the realized loss is reported in earnings. Subsequent increases or decreases in fair value are reported as a component of shareholders’ equity in accumulated other comprehensive gain (loss). There were no other-than-temporary unrealized losses as of December 31, 2021.
Fair value measurements
Under the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements, fair value is defined as the exit price, or the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants as of the measurement date. The authoritative guidance also establishes a hierarchy for inputs used in measuring fair value that maximizes the use of observable inputs and minimizes the use of unobservable inputs by requiring that the most observable inputs be used when available. Observable inputs are inputs market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability developed based on market data obtained from sources independent of the Company. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect the Company’s assumptions about the factors market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability developed based upon the best information available in the circumstances. The categorization of financial assets and financial liabilities within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The hierarchy is broken down into three levels defined as follows:
Level 1 Inputs — quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities
Level 2 Inputs — observable inputs other than quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities
Level 3 Inputs — unobservable inputs
As of December 31, 2021, the Company believes that the carrying amounts of its other financial instruments, including amounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities, approximate their fair value due to the short-term maturities of these instruments. See Note 4, titled “Marketable Securities” for additional information.
Concentration of credit risk
Financial instruments that potentially expose the Company to concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities. The Company maintains its cash balances primarily with two financial institutions. These balances generally exceed federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant credit risk in cash and cash equivalents. The Company believes that the credit risk related to marketable securities is limited due to the adherence to an investment policy focused on the preservation of principal.
Long-lived assets
Property and equipment are stated at purchased cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of property and equipment is computed using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives of to years for office equipment and years for computer equipment. Upon retirement or sale, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the consolidated balance sheets and the resulting gain or loss is reflected in the consolidated statements of operations. Repairs and maintenance are expensed as incurred.
Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the asset or related group of assets may not be recoverable. If the expected future undiscounted cash flows are less than the carrying amount of the asset, an impairment loss is recognized at that time. Measurement of impairment may be based upon appraisal, market value of similar assets or discounted cash flows.
Research and development costs
Research and development costs include expenses incurred in the conduct of human clinical trials, for third-party service providers performing various treatment, testing, data accumulation and analysis related to clinical studies; sponsored non-clinical research; developing the manufacturing process necessary to produce sufficient amounts of the DM199 compound for use in our clinical studies; consulting resources with specialized expertise related to execution of our development plan for our DM199 or other product candidates; and personnel costs, including salaries, benefits and share-based compensation.
We charge research and development costs, including clinical trial costs, to expense when incurred. Our human clinical trials are performed at clinical trial sites and are administered jointly by us with assistance from various contract research organizations. Costs of setting up clinical trial sites are accrued upon execution of the study agreement. Expenses related to the performance of clinical trials are recorded or accrued based on actual invoices received and estimates of work completed to date by contract research organizations, outside contractors and clinical trial sites that assist with management and performance of the trials, and those that manufacture the investigational product. We obtain initial estimates of accrued costs based on the trial protocol, actual enrollment of subjects, trial duration, project and data management costs, patient treatment costs and other activities as required by the trial protocol. Additionally, actual costs may be charged to us and are recognized as the tasks are completed by the clinical trial site. Accrued clinical trial costs may be subject to revisions as clinical trials progress and any revisions are recorded in the period in which the facts that give rise to the revisions become known.
Patent costs
Costs associated with applying for, prosecuting and maintaining patents are expensed as incurred given the uncertainty of patent approval and, if approved, the resulting probable future economic benefit to the Company. Patent-related costs, consisting primarily of legal expenses and filing/maintenance fees, are included in general and administrative costs and were $
Share-based compensation
The cost of employee and non-employee services received in exchange for awards of equity instruments is measured and recognized based on the estimated grant date fair value of those awards. Compensation cost is recognized ratably using the straight-line attribution method over the vesting period, which is considered to be the requisite service period. We record forfeitures in the periods in which they occur.
The fair value of option awards is estimated at the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The determination of the fair value of share-based awards is affected by our share price, as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. Risk free interest rates are based upon United States Government bond rates appropriate for the expected term of each award. Expected volatility rates are based on the historical volatility over a term equal to the expected life of the option. The assumed dividend yield is zero, as we do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future. The expected term of options is estimated considering the vesting period at the grant date, the life of the option and the average length of time similar grants have remained outstanding in the past.
Income taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the consolidated financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carry-forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted rates, for each of the jurisdictions in which the Company operates, expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in operations in the period that includes the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. The Company has provided a full valuation allowance against the gross deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020. See Note 14, “Income Taxes” for additional information. The Company’s policy is to classify interest and penalties related to income taxes as income tax expense.
Government assistance
Government assistance relating to research and development performed by DiaMedica Australia Pty Ltd. is recorded as a component of other (income) expense. Government assistance is recognized when the related expenditures are incurred. No study activities were undertaken by DiaMedica Australia during 2021. We recognized $
Net loss per share
We compute net loss per share by dividing our net loss (the numerator) by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding (the denominator) during the period. Shares issued during the period and shares reacquired during the period, if any, are weighted for the portion of the period that they were outstanding. The computation of diluted earnings per share, or EPS, is similar to the computation of basic EPS except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the dilutive potential common shares had been issued. Our diluted EPS is the same as basic EPS due to the exclusion of common share equivalents as their effect would be anti-dilutive.
The following table summarizes our calculation of net loss per common share for the periods presented (in thousands, except share and per share data):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Net loss | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
| Weighted average shares outstanding—basic and diluted | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
The following outstanding potential common shares were not included in the diluted net loss per share calculations as their effects were not dilutive:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Employee and non-employee stock options | ||||||||
| Common shares issuable under common share purchase warrants | ||||||||
| Common shares issuable upon settlement of deferred stock units | ||||||||
4. Marketable Securities
The available-for-sale marketable securities are primarily comprised of investments in commercial paper, corporate bonds and government securities and consist of the following, measured at fair value on a recurring basis (in thousands):
| Fair Value Measurements as of December 31, 2021 Using Inputs Considered as | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||
| Commercial paper and corporate bonds | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Government securities | ||||||||||||||||
| Total marketable securities | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Fair Value Measurements as of December 31, 2020 Using Inputs Considered as | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||
| Commercial paper and corporate bonds | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
| Bank certificates of deposit | ||||||||||||||||
| Government securities | ||||||||||||||||
| Total marketable securities | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
Accrued interest receivable on available-for-sale securities was $
There were no transfers of assets between Level 1 and Level 2 of the fair value measurement hierarchy during the year ended December 31, 2021.
Under the terms of the Company’s investment policy, purchases of marketable securities are limited to investment grade governmental and corporate obligations with a primary objective of principal preservation. Maturities of individual securities are less than one year and the amortized cost of all securities approximated fair value as of December 31, 2021.
5. Amounts Receivable
Amounts receivable consisted of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| Accrued interest receivable | $ | $ | ||||||
| Research and development incentives | ||||||||
| Other | ||||||||
| Total amounts receivable | $ | $ | ||||||
6. Deposits
Deposits consisted of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| Advances to vendors, current | $ | $ | ||||||
We periodically advance funds to vendors engaged to support the performance of our clinical trials and related supporting activities. The funds advanced are held, interest free, for varying periods of time and may be recovered by DiaMedica through partial reductions of ongoing invoices, application against final study/project invoices or refunded upon completion of services to be provided. Deposits are classified as current or non-current based upon their expected recovery time.
7. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consisted of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| Furniture and equipment | $ | $ | ||||||
| Computer equipment | ||||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Property and equipment, net | $ | $ | ||||||
Depreciation expense was $
8. Accounts Payable and Accrued Liabilities
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| Trade and other payables | $ | $ | ||||||
| Accrued compensation | ||||||||
| Accrued research and other professional fees | ||||||||
| Accrued clinical trial costs | ||||||||
| Accrued other liabilities | ||||||||
| Total accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | $ | ||||||
9. Operating Lease
We lease certain office space under a non-cancelable operating lease. This lease does not have significant rent escalation holidays, concessions, leasehold improvement incentives or other build-out clauses. Further this lease does not contain contingent rent provisions. This lease terminates on August 31, 2022 and we do not have an option to renew. This lease does include both lease (e.g., fixed rent) and non-lease components (e.g., common-area and other maintenance costs). The non-lease components are deemed to be executory costs and are therefore excluded from the minimum lease payments used to determine the present value of the operating lease obligation and related right-of-use asset.
This lease does not provide an implicit rate and, due to the lack of a commercially salable product, we are generally considered unable to obtain commercial credit. Therefore, considering the quoted rates for the lowest investment-grade debt and the interest rates implicit in recent financing leases, we estimated our incremental borrowing rate to be
Our operating lease costs were $
Maturities of our operating lease obligation are as follows as of December 31, 2021 (in thousands):
| 2022 | $ | |||
| Total lease payments | ||||
| Less interest portion | ( | ) | ||
| Present value of lease obligation | $ |
10. Commitments and Contingencies
Clinical trials and product development
In the normal course of business, we incur obligations to make future payments as we execute our business plan. These obligations may relate to preclinical or clinical studies, manufacturing or manufacturing process development and other related activities. Currently, these obligations include costs to be incurred with contract research organizations, central laboratory and pharmacy services, clinical study sites, home nursing services and various other vendors supporting the performance of our clinical trials. The contracts we enter into with these vendors and the commitments within these contracts are subject to significant variability based upon the actual activities/services performed by each vendor. As a result, the ultimate amounts due may be materially different as these obligations are affected by, among other factors, the number and pace of patients enrolled, the number of clinical study sites enrolling subjects, the amount of time to complete trial enrollments and the time required to finalize, analyze and report of trial results. Clinical research agreements are generally cancelable upon up to 60 days’ notice, with the Company’s obligation limited to costs incurred up to that date, including any non-cancelable costs. Cancelation terms for product manufacturing and process development contracts vary and are generally dependent upon timelines for sourcing research materials and reserving laboratory time. As of December 31, 2021, the Company estimates that its outstanding commitments, including such cancellable contracts, are approximately $
On November 11, 2021, we announced the enrollment of the first patient for our pivotal ReMEDy2 trial. The ReMEDy2 trial is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 2/3 adaptive trial intended to enroll approximately 350 patients. Patients enrolled in the trial will be treated with either DM199 or placebo within 24 hours of the onset of AIS symptoms. Treatment continues twice weekly for approximately three weeks with final follow-up at approximately 90 days after treatment commences.
Our REDUX clinical trial , a multi-center, open-label, Phase 2 clinical trial investigating patients with Stage II or III CKD has completed enrollment. The trial focused on participants with CKD caused by three specific conditions: Cohort 1 focused on non-diabetic, hypertensive African Americans with Stage II or III CKD; Cohort 2 focused on participants with IgA Nephropathy (IgAN); and Cohort 3 focused on participants with Type 2 diabetes mellitus with CKD, hypertension and albuminuria. Enrollment was closed at the end of 2021 and patient follow-ups and final data analysis is expected to complete by mid-2022.
Technology license
We have entered into a license agreement with Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC (Catalent) whereby we have licensed certain gene expression technology and we contract with Catalent for the manufacture of DM199. Under the terms of this license, certain milestone and royalty payments may become due under this agreement and are dependent upon, among other factors, clinical trials, regulatory approvals and ultimately the successful development of a new drug, the outcome and timing of which is uncertain. In the fourth quarter of 2021, we remitted the $
Indemnification of directors and officers
The Company, as permitted under laws of British Columbia and in accordance with the Company’s Articles and indemnification agreements, will indemnify and advance expenses to its directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by law and may choose to indemnify other employees or agents from time to time. The Company has secured insurance on behalf of any officer, director, employee or other agent for any liability arising out of his or her actions in connection with their services to the Company. As of December 31, 2021, there was pending litigation or proceeding involving any director or officer of the Company as to which indemnification is required or permitted, and we are not aware of any threatened litigation or proceeding that may result in a claim for indemnification. Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended (Securities Act) may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Company, the Company has been advised that, in the opinion of the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable. The Company believes the fair value of these indemnification agreements is minimal. Accordingly, the Company had recorded any liabilities for these obligations as of December 31, 2021 or 2020.
11. Shareholders’ Equity
Authorized capital stock
DiaMedica has authorized share capital of an unlimited number of common voting shares and the shares do not have a stated par value.
Common shareholders are entitled to receive dividends as declared by the Company, if any, and are entitled to one vote per share at the Company’s annual general meeting and any extraordinary general meeting.
Equity issued during the year ended December 31, 2021
On September 26, 2021, we issued and sold in a private placement an aggregate
During the year ended December 31, 2021,
Equity issued during the year ended December 31, 2020
On August 10, 2020, the Company issued and sold an aggregate of
On February 13, 2020, the Company issued and sold an aggregate of
During the year ended December 31, 2020,
Shares reserved
Common shares reserved for future issuance are as follows:
| December 31, 2021 | ||||
| Employee and non-employee stock options | ||||
| Common shares issuable upon settlement of deferred stock units | ||||
| Common shares issuable under common share purchase warrants | ||||
| Shares available for grant under the 2019 Omnibus Incentive Plan | ||||
| Shares available for grant under the 2021 Employment Inducement Incentive Plan | ||||
| Total | ||||
12. Share-Based Compensation
2019 Omnibus Incentive Plan
The DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2019 Omnibus Incentive Plan (2019 Plan) was adopted by the Board of Directors (Board) in March 2019 and approved by our shareholders at our annual general and special meeting of shareholders held on May 22, 2019. The 2019 Plan permits the Board, or a committee or subcommittee thereof, to grant to the Company’s eligible employees, non-employee directors and consultants non-statutory and incentive stock options (ISO), stock appreciation rights (SAR), restricted stock awards (RSA), restricted stock units (RSU), deferred stock units (DSU), performance awards, non-employee director awards and other stock-based awards. We grant options to purchase common shares under the 2019 Plan at no less than the fair market value of the underlying common shares as of the date of grant. Options granted to employees and non-employee directors have a maximum term of years and generally vest in approximately equal quarterly installments over to years. Options granted to non-employees have a maximum term of years and generally vest in approximately equal quarterly installments over year. Subject to adjustment as provided in the 2019 Plan, the maximum number of the Company’s common shares authorized for issuance under the 2019 Plan is
2021 Employment Inducement Incentive Plan
On December 3, 2021, the Board adopted the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2021 Employment Inducement Incentive Plan (Inducement Plan), to facilitate the granting of equity awards as an inducement material to new employees joining the Company. The Inducement Plan was adopted without shareholder approval pursuant to Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(c)(4) and is administered by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. The Board reserved
Prior Stock Option Plan
The DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. Stock Option Plan, Amended and Restated November 6, 2018 (Prior Plan), was terminated by the Board in conjunction with the shareholder approval of the 2019 Plan. Awards outstanding under the Prior Plan remain outstanding in accordance with and pursuant to the terms thereof. Options granted under the Prior Plan have terms similar to those used under the 2019 Plan. As of December 31, 2021, options to purchase
Prior Deferred Share Unit Plan
The DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. Amended and Restated Deferred Share Unit Plan (Prior DSU Plan) was terminated by the Board in conjunction with the shareholder approval of the 2019 Plan. Awards outstanding under the DSU Plan remain outstanding in accordance with and pursuant to the terms thereof. As of December 31, 2021, there were
Prior to December 31, 2018, all options granted under the Prior Plan were priced in Canadian dollars. Options granted after December 31, 2018 under the 2019 Plan and the Prior Plan have been priced in United States dollars.
Share-based compensation expense for each of the periods presented is as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | |||||||
| Research and development | $ | $ | ||||||
| General and administrative | ||||||||
| Total share-based compensation | $ | $ | ||||||
We recognize share-based compensation based on the fair value of each award as estimated using the Black-Scholes option valuation model. Ultimately, the actual expense recognized over the vesting period will only be for those shares that actually vest.
A summary of option activity is as follows (in thousands except share and per share amounts):
| Shares Underlying Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2019 | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Granted | ||||||||||||
| Exercised | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Expired/cancelled | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Forfeited | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2020 | $ | $ | ||||||||||
| Granted | ||||||||||||
| Exercised | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Expired/cancelled | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Forfeited | ( | ) | ||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2021 | $ | $ | ||||||||||
A summary of the status of our unvested shares underlying options during the year ended and as of December 31, 2021 is as follows:
| Shares Underlying Options | Weighted Grant Date Fair Value Per Share | |||||||
| Unvested at December 31, 2020 | $ | |||||||
| Granted | ||||||||
| Vested | ( | ) | ||||||
| Forfeited | ( | ) | ||||||
| Unvested at December 31, 2021 | $ | |||||||
Information about stock options outstanding, vested and expected to vest as of December 31, 2021, is as follows:
| Outstanding, Vested and Expected to Vest | Options Vested and Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Per Share Exercise Price | Shares | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Options Exercisable | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) | |||||||||||||||||
| $2.00 | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| $3.00 | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| $4.00 | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| $5.00 | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| $10.01 | - | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The cumulative grant date fair value of employee options vested during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 was $
As of December 31, 2021, total compensation expense related to unvested employee stock options not yet recognized was $
The aggregate intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 was $
The assumptions used in calculating the fair value under the Black-Scholes option valuation model are set forth in the following table for options issued by the Company for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||||
| Common share fair value | $ | – | $ | $ | – | $ | ||||
| Risk-free interest rate | – | – | ||||||||
| Expected dividend yield | ||||||||||
| Expected option life (years) | – | – | ||||||||
| Expected stock price volatility | – | – | ||||||||
Deferred Stock Units and Restricted Stock Units
Under our non-employee director compensation program, non-employee directors may elect to receive RSUs or DSUs in lieu of all or a portion of the annual cash retainers payable to such director. Each RSU or DSU represents the right to receive one share of our common stock. These recipients receive a number of DSUs equal to the amount of the elected portion of the annual cash retainers divided by the 10-trading day average closing sale price of the common stock as determined on the third (3rd) business day prior to the anticipated grant date of the award. Vesting for these annual RSU and DSU grants is quarterly over year, conditioned on continuous service. The cost of DSUs is measured and recognized base on the fair market value of our common shares on the date of grant. RSUs will be settled immediately upon vesting and DSU awards will be settled following a separation from service by such director.
There were approximately
13. Related Party Transaction
During 2020, we engaged a consulting firm owned by our former Vice President of Regulatory Affairs to perform certain tasks supporting our quality and regulatory activities. The work was performed as required by us and all services were invoiced on an hourly basis with no minimum commitment. We terminated this agreement effective June 16, 2021. Total charges invoiced were and for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
14. Employee Benefit Plan
We maintain an employee 401(k) retirement savings plan (401(k) Plan). The 401(k) Plan provides eligible employees with an opportunity to make tax-deferred contributions into a long-term investment and savings program. All employees over the age of 21 may elect to participate in the 401(k) Plan beginning on their hire date. The 401(k) Plan allows eligible employees to contribute a portion of their annual compensation, subject only to maximum limits required by law. We contribute an amount up to
We have recorded contribution expenses of $
15. Income Taxes
The Company has incurred net operating losses since inception. The Company has not reflected the benefit of net operating loss carryforwards in the accompanying consolidated financial statements and has established a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets.
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes as well as operating losses and tax credit carryforwards.
The significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities): | ||||||||
| Non-capital losses carried forward | $ | $ | ||||||
| Research and development expenditures | ||||||||
| Share issue costs | ||||||||
| Patents and other | ||||||||
| Accruals | ||||||||
| Property and equipment | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Total deferred tax asset, net | ||||||||
| Valuation allowance | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset | $ | $ | ||||||
Realization of the future tax benefits is dependent on our ability to generate sufficient taxable income within the carryforward period. Because of our history of operating losses, management believes that the deferred tax assets arising from the above-mentioned future tax benefits are currently not likely to be realized and, accordingly, we have provided a full valuation allowance.
The reconciliation of the Canadian statutory income tax rate applied to the net loss for the year to the income tax expense is as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
| Statutory income tax rate | % | % | ||||||
| Income tax recovery based on statutory rate | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
| Share-based compensation | ||||||||
| Prior-year true-ups | ||||||||
| Share issuance costs | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||
| Australian research and development incentive | ( | ) | ||||||
| Other | ||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance | ||||||||
| Income tax expense | $ | $ | ||||||
Net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards as of December 31, 2021, are as follows:
| Amount (In thousands) | Expiration Years | ||||
| Non-capital income tax losses, net | $ | Beginning 2026 | |||
| Research and development expense carry forwards | Indefinitely | ||||
| Tax credits | Beginning 2021 | ||||
The Company is subject to taxation in Canada, the United States and Australia. Tax returns, since the inception of DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc., are subject to examinations by Canadian tax authorities and may change upon examination. Tax returns of DiaMedica USA, Inc., since its inception in and thereafter, are subject to examination by the U.S. federal and state tax authorities. Tax returns of DiaMedica Therapeutics Australia Pty Ltd., since its inception in and thereafter, are subject to examination by the Australian tax authorities.
Item 9. Changes In and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (Exchange Act)) that are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Our management evaluated, with the participation of its Chief Executive Officer and its Chief Financial Officer, the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered in this report. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the end of such period to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act.
Our management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the criteria set forth in “Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013)” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2021, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
This annual report on Form 10-K does not include an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm on internal control over financial reporting due to an exemption established by the JOBS Act for “emerging growth companies.”
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2021 that has materially affected or is reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Directors
The information in the “Voting Proposal One – Election of Directors” section of our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our next annual general meeting of shareholders, which involves the election of directors, is incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference.
Executive Officers
Information concerning our executive officers is included in this annual report on Form 10-K under Item 1 of Part I under “Information About Our Executive Officers.”
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a code of business conduct and ethics applicable to all of our directors, officers and employees, in accordance with Section 406 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the rules of the SEC promulgated thereunder, and the Nasdaq Listing Rules. In the event that any changes are made or any waivers from the provisions of the code of business conduct and ethics are made, these events would be disclosed on our website or in a report on Form 8-K within four business days of such event. The code of business conduct and ethics is posted on our website at www.diamedica.com. Copies of the code of business conduct and ethics will be provided free of charge upon written request directed to Investor Relations, DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc., Two Carlson Parkway, Suite 260, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55447.
Changes to Nomination Procedures
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2021, we made no material changes to the procedures by which shareholders may recommend nominees to our Board of Directors.
Audit Committee Matters
The information in the “Corporate Governance—Audit Committee” section of our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our next annual general meeting of shareholders, which involves the election of directors, is incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information in the “Director Compensation” and “Executive Compensation” sections of our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our next annual general meeting of shareholders, which involves the election of directors, is incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Stock Ownership
The information in the “Stock Ownership—Security Ownership of Significant Beneficial Owners” and “Stock Ownership—Security Ownership of Management” sections of our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our next annual general meeting of shareholders, which involves the election of directors, is incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table summarizes outstanding options and other awards under our equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2021. Our equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2021 were the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2019 Omnibus Incentive Plan (2019 Plan), the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. Stock Option Plan, Amended and Restated November 6, 2018 (Prior Plan), the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. Amended and Restated Deferred Share Unit Plan (DSU Plan) and the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2021 Employment Inducement Incentive Plan (Inducement Plan).
Equity Compensation Plan Information
| (a) |
(b) |
(c) |
||||||||||
| Plan Category |
Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights |
Weighted-Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights |
Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) |
|||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
1,964,259 |
(1)
|
$ | 5.24 | (2) | 507,651 | (3) | |||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
— | $ | — | 1,000,000 | (4) | |||||||
| Total |
1,964,259 | (1) | $ | 5.24 | (2) | 1,507,651 | (3) | |||||
______________________
| (1) |
Amount includes 1,418,690 common shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options and 50,326 common shares issuable upon the settlement of DSU awards outstanding under the 2019 Plan, 477,910 common shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options under the Prior Plan and 17,333 common shares issuable under the DSU Plan. |
| (2) |
Not included in the weighted-average exercise price calculation are 50,326 deferred stock unit awards under the 2019 Plan and 17,333 deferred stock unit awards under the DSU Plan. |
| (3) |
Amount includes 507,651 shares remaining available for future issuance under the 2019 Plan and 1,000,000 remaining available for future issuance under the 2021 Plan. |
| (4) |
On December 3, 2021, the Board adopted Inducement Plan to facilitate the granting of equity awards as an inducement material to new employees joining the Company. The Inducement Plan was adopted without shareholder approval pursuant to Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(c)(4) and is administered by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. The Board reserved 1,000,000 common shares of the Company for issuance under the Inducement Plan, which permits the grant of non-statutory options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, performance awards and other stock-based awards, to eligible recipients. The only persons eligible to receive awards under the Inducement Plan are individuals who are new employees and satisfy the standards for inducement grants under Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(c)(4) or 5635(c)(3), as applicable. Also on December 3, 2021, the Compensation Committee adopted a form of notice of option grant and option award agreement for use under the Inducement Plan, which contains terms substantially identical to the form of notice of option grant and option award agreement for use under the shareholder-approved 2019 Plan. The Inducement Plan has a term of 10 years. The share reserve under the Inducement Plan may be increased at the discretion of and approval by the Board. As of December 31, 2021, no options or other equity awards had been granted under the Inducement Plan. However, subsequent thereto, options to purchase an aggregate of 325,000 common shares were granted under the Inducement Plan. |
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information in the “Related Person Relationships and Transactions” and “Corporate Governance—Director Independence” sections of our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our next annual general meeting of shareholders, which involves the election of directors, is incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information in the “Voting Proposal Two—Appointment of Baker Tilly US, LLP as our Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm and Authorization to Fix Remuneration” section of our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our next annual general meeting of shareholders, which involves the election of directors, is incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
Financial Statements
Our consolidated financial statements are included in “Part II, Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Financial Statement Schedules
All financial statement schedules are omitted because they are inapplicable since we are a smaller reporting company.
Exhibits
The exhibits being filed or furnished with this report are listed below, along with an indication as to each management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
A copy of any of the exhibits listed or referred to herein will be furnished at a reasonable cost to any person who is a shareholder upon receipt from any such person of a written request for any such exhibit. Such request should be sent to: Mr. Scott Kellen, Chief Financial Officer and Corporate Secretary, DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc., Two Carlson Parkway, Suite 260, Minneapolis, Minnesota 55447, Attn: Shareholder Information.
| Item No. |
Item |
Method of Filing |
| 3.1 |
Notice of Articles of DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. dated May 31, 2019 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 4, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
| 3.2 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 4, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 4.1 |
Description of Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to DiaMedica’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020 (File No. 001-36291) |
| 4.2 |
Specimen Certificate representing Voting Common Shares of DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 4, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
| 4.3 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 11, 2018 |
| Item No. | Item | Method of Filing |
| 4.4 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.8 to DiaMedica’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 4.5 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to DiaMedica’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2020 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 4.6 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-3 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 5, 2021 (File No. 333-260066) |
|
| 10.1# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 23, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 10.2# |
Form of Option Award Agreement under the DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2019 Omnibus Incentive Plan |
Filed herewith |
| 10.3# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 21, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 10.4# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2020 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 10.5# |
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. 2021 Employment Inducement Incentive Plan |
Filed herewith |
| 10.6# |
Filed herewith |
|
| 10.7# |
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. Stock Option Plan Amended and Restated November 6, 2018 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| 10.8# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| Item No. | Item | Method of Filing |
| 10.9# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
|
| 10.10# |
DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. Amended and Restated Deferred Share Unit Plan |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| 10.11# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 21, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 10.12# |
Form of Indemnification Agreement between DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc. and Each Director and Officer |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 4, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
| 10.13# |
Employment Agreement effective as of September 12, 2018 between DiaMedica USA, Inc. and Rick Pauls |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| 10.14# |
Employment Agreement effective as of September 12, 2018 between DiaMedica USA, Inc. and Scott Kellen |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to DiaMedica’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2018 (File No. 001-36291) |
| 10.15# |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to DiaMedica’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2018 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 10.16 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
|
| 10.17 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| Item No. | Item | Method of Filing |
| 10.18 |
First Amendment to Lease dated May 3, 2017 between One Two Holding LLC and DiaMedica USA Inc. |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| 10.19 |
Second Amendment to Lease dated September 5, 2017 between One Two Holding LLC and DiaMedica USA Inc. |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
| 10.20(1) |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
|
| 10.21 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to DiaMedica’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 9, 2018 (File No. 333-228313) |
|
| 10.22 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 to DiaMedica’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 10.23 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to DiaMedica’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 27, 2021 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 21.1 |
Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 21.1 to DiaMedica’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 (File No. 001-36291) |
|
| 23.1 |
Filed herewith |
|
| 31.1 |
Filed herewith |
|
| 31.2 |
Filed herewith |
|
| 32.1 |
Furnished herewith |
|
| 32.2 |
Furnished herewith |
|
| 101 |
The following materials from DiaMedica Therapeutics Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021, formatted in Inline XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss), (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Equity, (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
Filed herewith |
| 104 |
Cover Page Interactive Data File |
Embedded within the Inline XBRL document |
__________________________
| # |
Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| (1) |
Portions of this exhibit have been redacted and are subject to an order granting confidential treatment under Rule 406 of the United States Securities Act of 1933, as amended (File No. 333-228313, CF #36833). The redacted material was filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| DIAMEDICA THERAPEUTICS INC. | ||
| Date: March 14, 2022 | By: | /s/ Rick Pauls |
| Rick Pauls | ||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Name |
Title |
Date |
||
| /s/ Rick Pauls |
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| Rick Pauls | (principal executive officer) | |||
| /s/ Scott Kellen |
Chief Financial Officer and Secretary |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| Scott Kellen | (principal financial and accounting officer) | |||
| /s/ Richard Pilnik |
Chairman of the Board |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| Richard Pilnik | ||||
| /s/ Amy L. Burroughs |
Director |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| Amy L. Burroughs | ||||
| /s/ Michael Giuffre, M.D. |
Director |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| Michael Giuffre, M.D. | ||||
| /s/ James Parsons |
Director |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| James Parsons | ||||
| /s/ Charles P. Semba, M.D. |
Director |
March 14, 2022 |
||
| Charles P. Semba, M.D. |
[page intentionally left blank]