DM199: Restoring the Body's Supply of an Essential Protein
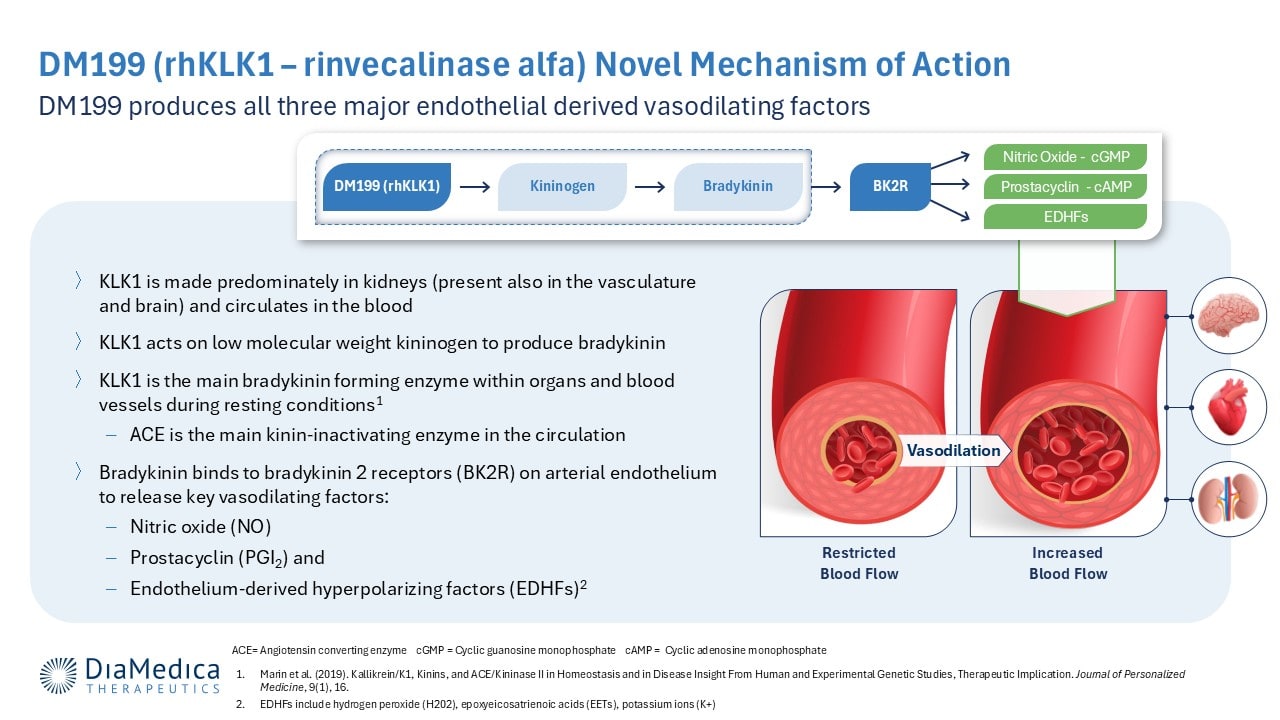
DiaMedica Therapeutics is developing DM199 (rhKLK1), a recombinant protein replacement therapy intended to restore normal, healthy levels of human tissue kallikrein-1 (KLK1). KLK1 is a naturally occurring protein believed to stimulate the production of key vasodilating signaling molecules that help to increase blood flow and improve endothelial health. Through this novel mechanism, DM199 may have the potential to treat several ischemic conditions, including preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction, and acute ischemic stroke.