Intended to Restore Natural, Healthy Function
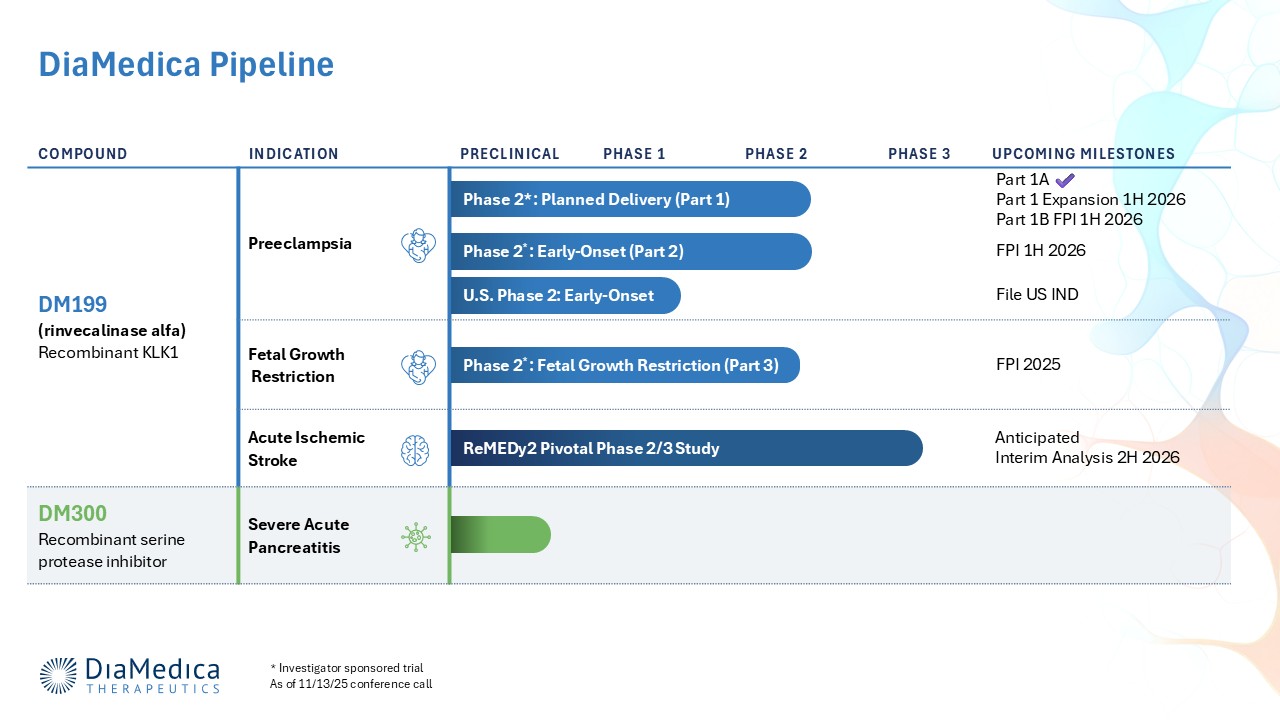
DiaMedica’s lead candidate, DM199 (rhKLK1), is a recombinant form of the human tissue KLK1 protein which enhances blood flow and vascular health by increasing the available levels of nitric oxide (NO), prostacyclin (PGI2), and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF). Through this novel mechanism of action, DM199 has the potential to modify disease progression in preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction and enhance collateral circulation in acute ischemic stroke.